
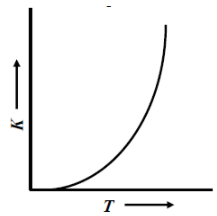
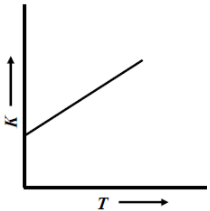
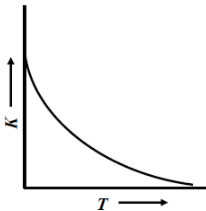
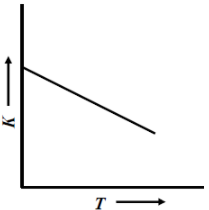
Given below are the plots which show the variation of the rate constant (k) with temperature (T). Select the plot which follows the Arrhenius equation.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)




Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The Arrhenius equation is a formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. The units of the pre-exponential factor A are identical to those of the rate constant and will vary depending on the order of the reaction. If the reaction is first order it has the units: ${{s}^{-1}}$ , and for that reason it is often called the frequency factor or attempt frequency of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The Arrhenius equation is $k=A{{e}^{(-Ea/RT)}}$, where A is the frequency or pre-exponential factor and ${{e}^{(-Ea/RT)}}$ is the fraction of collisions that have enough energy to react (i.e., have energy greater than or equal to the activation energy Ea) at temperature T.
Rate constant K increases exponentially with the rise in temperature. Since the rate constant K also depends upon orientation factor A. Hence, its maximum value is not infinity, rather it is limited to an optimal value.
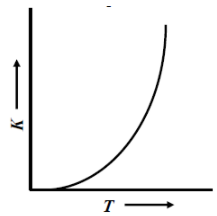
Therefore, the correct representation of variation of the rate constant (k) with temperature (T) is shown
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Activation energy is the energy that must be provided to compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (Ea) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). This equation has a vast and important application in determining the rate of chemical reactions and for calculation of energy of activation.
Complete step by step answer:
The Arrhenius equation is $k=A{{e}^{(-Ea/RT)}}$, where A is the frequency or pre-exponential factor and ${{e}^{(-Ea/RT)}}$ is the fraction of collisions that have enough energy to react (i.e., have energy greater than or equal to the activation energy Ea) at temperature T.
Rate constant K increases exponentially with the rise in temperature. Since the rate constant K also depends upon orientation factor A. Hence, its maximum value is not infinity, rather it is limited to an optimal value.

Therefore, the correct representation of variation of the rate constant (k) with temperature (T) is shown
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Activation energy is the energy that must be provided to compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (Ea) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). This equation has a vast and important application in determining the rate of chemical reactions and for calculation of energy of activation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




