
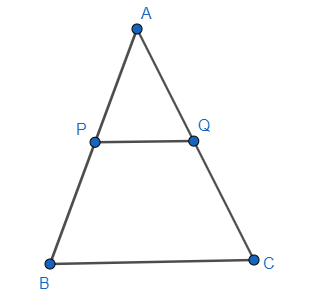
Given $area\left( \Delta ABC \right)=360c{{m}^{2}},area\left( BPQC \right)=110c{{m}^{2}}$, $PQ||BC;AP=10cm$. Find $\dfrac{AQ}{QC}$.

Answer
512.7k+ views
Hint: We first find the same angles between the $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta APQ$. Based on the parallel condition of the lines $PQ||BC$, we find the same angles and the ratio of the similar sides. We use the relation between sides and area of the triangle to find the value for $\dfrac{AQ}{QC}$.
Complete step by step answer:
We are going to use the concept of similar triangles and then use the ratio of the sides of those triangles.
In the given figure we have two triangles where we take $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta APQ$.
It’s given that $PQ||BC$ and AB and AC are the transverse lines.
So, we have two sets of equal corresponding angles where $\angle ABC=\angle APQ;\angle ACB=\angle AQP$.
Also $\angle BAC=\angle PAQ$ is the common angle.
We also know that the sum of three angles of a triangle is always equal to ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
We know that if three angles of two triangles are the same then the triangles are similar triangles and the ratio of opposite sides of similar angles are equal.
Therefore, for $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta APQ$ we get $\dfrac{AB}{AP}=\dfrac{AC}{AQ}=\dfrac{BC}{PQ}$.
We have that the ratio of area of two similar triangles is square to the ratio of the respective sides.
So, \[{{\left( \dfrac{AC}{AQ} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{area\left( \Delta ABC \right)}{area\left( \Delta APQ \right)}\].
Now $area\left( \Delta APQ \right)=area\left( \Delta ABC \right)-area\left( BPQC \right)=360-110=250c{{m}^{2}}$.
So, \[{{\left( \dfrac{AC}{AQ} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{area\left( \Delta ABC \right)}{area\left( \Delta APQ \right)}=\dfrac{360}{250}=\dfrac{36}{25}\].
Simplifying we get \[\dfrac{AC}{AQ}=\sqrt{\dfrac{36}{25}}=\dfrac{6}{5}\]. We now subtract 1 both sides to get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AC}{AQ}-1=\dfrac{6}{5}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AC-AQ}{AQ}=\dfrac{6-5}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{QC}{AQ}=\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AQ}{QC}=5 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the value of $\dfrac{AQ}{QC}$ is 5.
Note: Similar triangles are two or more triangles with the same shape, equal pair of corresponding angles and the same ratio of the corresponding sides. In Euclidean geometry, two objects are similar if they have the same shape, or one has the same shape as the mirror image of the other.
Complete step by step answer:
We are going to use the concept of similar triangles and then use the ratio of the sides of those triangles.
In the given figure we have two triangles where we take $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta APQ$.
It’s given that $PQ||BC$ and AB and AC are the transverse lines.
So, we have two sets of equal corresponding angles where $\angle ABC=\angle APQ;\angle ACB=\angle AQP$.
Also $\angle BAC=\angle PAQ$ is the common angle.
We also know that the sum of three angles of a triangle is always equal to ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
We know that if three angles of two triangles are the same then the triangles are similar triangles and the ratio of opposite sides of similar angles are equal.
Therefore, for $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta APQ$ we get $\dfrac{AB}{AP}=\dfrac{AC}{AQ}=\dfrac{BC}{PQ}$.
We have that the ratio of area of two similar triangles is square to the ratio of the respective sides.
So, \[{{\left( \dfrac{AC}{AQ} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{area\left( \Delta ABC \right)}{area\left( \Delta APQ \right)}\].
Now $area\left( \Delta APQ \right)=area\left( \Delta ABC \right)-area\left( BPQC \right)=360-110=250c{{m}^{2}}$.
So, \[{{\left( \dfrac{AC}{AQ} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{area\left( \Delta ABC \right)}{area\left( \Delta APQ \right)}=\dfrac{360}{250}=\dfrac{36}{25}\].
Simplifying we get \[\dfrac{AC}{AQ}=\sqrt{\dfrac{36}{25}}=\dfrac{6}{5}\]. We now subtract 1 both sides to get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AC}{AQ}-1=\dfrac{6}{5}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AC-AQ}{AQ}=\dfrac{6-5}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{QC}{AQ}=\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AQ}{QC}=5 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the value of $\dfrac{AQ}{QC}$ is 5.
Note: Similar triangles are two or more triangles with the same shape, equal pair of corresponding angles and the same ratio of the corresponding sides. In Euclidean geometry, two objects are similar if they have the same shape, or one has the same shape as the mirror image of the other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

Who was Subhash Chandra Bose Why was he called Net class 10 english CBSE




