
Given a tetrahedron D−ABC with \[AB = 12\], \[CD = 6\]. If the shortest distance between the skew lines AB and CD is 8 and the angle between them is \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\], then find the volume of tetrahedron.
Answer
539.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will draw a tetrahedron and then try to find the required volume with the help of our observation and conceptual knowledge. First of all, we will construct two lines on two different planes such that they are parallel to the given lines respectively. Then we will find the volume of an oblique triangular prism. After finding its value, the question becomes easy as we just have to divide it by 3 to find the value of the volume of tetrahedron.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume two planes to be \[{P_{AB}}\] and \[{P_{CD}}\] such that the two lines AB and CD exists on these planes respectively.
Now, \[{P_{AB}}\] is parallel to \[{P_{CD}}\].
Therefore the distance between the two will be,
\[{P_{AB}} + {P_{CD}} = 8\]
Now, take a point D’ on the plane \[{P_{AB}}\] such that the line CD is parallel to BD’.
Also, their lengths are equal, hence,
\[CD = BD'\]
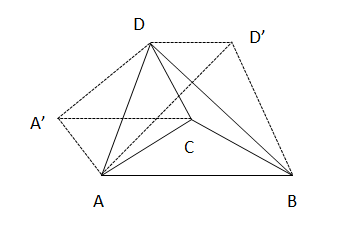
Similarly, take a point A’ on the plane \[{P_{CD}}\] such that the line AB is parallel to A’C
Also, their lengths are equal, hence,
\[AB = A'C\]
Now, we will join all the points together by constructing lines,
We will find that
\[ABD' - A'CD\] is an oblique triangular prism.
As we know, the volume of a triangular prism is base area \[ \times \] height.
Hence, volume of this prism = Area of \[\Delta {\rm{ABD}}' \times {\rm{height}}\]
Substituting the values on the above formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = \] \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \]AB \[ \times \] BD’ \[ \times \]\[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) \times 8\]
It is given that \[AB = 12\], \[CD = 6\] and the angle between them is \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\].
Also, the shortest distance between the skew lines AB and CD is 8 i.e. the height.
And, as CD is equal to BD’, \[BD' = 6\]
Therefore, volume of prism is:
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 6 \times \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) \times 8\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = 6 \times 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times 8\]
Solving further, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = 18 \times 8 = 144\]square units
Now we will use the volume of the prism to find the volume of the tetrahedron.
Hence, the volume of tetrahedron \[ = \] Volume of prism \[ \times \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Substituting 144 for the volume of prism, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of tetrahedron \[ = 144 \times \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of tetrahedron \[ = 48\] square units
Hence, the required volume of tetrahedron is \[48\] square units.
Note: To solve this question we should know that the volume of tetrahedron is one third the volume of prism which contains the tetrahedron. Also, the volume of the prism is base area multiplied by the height. Without knowing these formulas, we can never find the answer to these questions. Here, it is important to draw a diagram , so that we can visualise the problem and solve it easily.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume two planes to be \[{P_{AB}}\] and \[{P_{CD}}\] such that the two lines AB and CD exists on these planes respectively.
Now, \[{P_{AB}}\] is parallel to \[{P_{CD}}\].
Therefore the distance between the two will be,
\[{P_{AB}} + {P_{CD}} = 8\]
Now, take a point D’ on the plane \[{P_{AB}}\] such that the line CD is parallel to BD’.
Also, their lengths are equal, hence,
\[CD = BD'\]

Similarly, take a point A’ on the plane \[{P_{CD}}\] such that the line AB is parallel to A’C
Also, their lengths are equal, hence,
\[AB = A'C\]
Now, we will join all the points together by constructing lines,
We will find that
\[ABD' - A'CD\] is an oblique triangular prism.
As we know, the volume of a triangular prism is base area \[ \times \] height.
Hence, volume of this prism = Area of \[\Delta {\rm{ABD}}' \times {\rm{height}}\]
Substituting the values on the above formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = \] \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \]AB \[ \times \] BD’ \[ \times \]\[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) \times 8\]
It is given that \[AB = 12\], \[CD = 6\] and the angle between them is \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\].
Also, the shortest distance between the skew lines AB and CD is 8 i.e. the height.
And, as CD is equal to BD’, \[BD' = 6\]
Therefore, volume of prism is:
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 6 \times \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) \times 8\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = 6 \times 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times 8\]
Solving further, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of this prism \[ = 18 \times 8 = 144\]square units
Now we will use the volume of the prism to find the volume of the tetrahedron.
Hence, the volume of tetrahedron \[ = \] Volume of prism \[ \times \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Substituting 144 for the volume of prism, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of tetrahedron \[ = 144 \times \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of tetrahedron \[ = 48\] square units
Hence, the required volume of tetrahedron is \[48\] square units.
Note: To solve this question we should know that the volume of tetrahedron is one third the volume of prism which contains the tetrahedron. Also, the volume of the prism is base area multiplied by the height. Without knowing these formulas, we can never find the answer to these questions. Here, it is important to draw a diagram , so that we can visualise the problem and solve it easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

The plural of Chief is Chieves A True B False class 7 english CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





