
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: They are also known as the heart muscles as these muscles are present in the heart of our body.
Cardiac muscles are known as the heart muscles or myocardium.
Cardiac muscles are one of the three types of vertebrate muscles.
Complete answer:
Features of cardiac muscles
>The cardiac muscles are involuntary in function, their functioning cannot be controlled by humans. >They are involved in continuous rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
>Cells of cardiac muscles called cardiomyocytes are uninucleate (single nucleus), cylindrical, elongated, striated, and branched.
>The cardiac muscles if damaged have no regenerative capacity.
Additional information:
>The cardiac muscles are myogenic which means the contractions are generated within the muscles.
>Cardiac muscles have striations due to the presence of actin and myosin filaments which are arranged into sarcomeres.
>These muscles are joined to one another by intercalated discs that contain gap junctions.
>These Intercalated discs have proteins that allow direct transmission of current from cell to cell across the chambers of the heart so that the cells contract altogether.
>It helps in coordinated muscle contraction and maintenance of circulation.
>Cardiac muscles resist fatigue so well because it has got more mitochondria than other muscles. >Mitochondria continuously provides energy resulting in the heart never stopping until a person dies.
>The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical impulse.
>The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells located in the right atrium, called the SA (sinoatrial) node which is the heart's natural pacemaker.
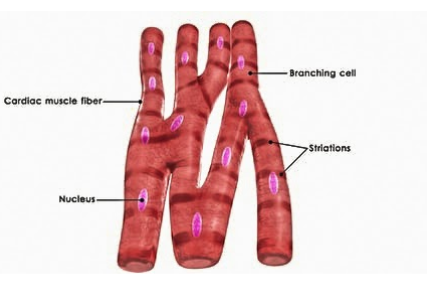
Note: Vertebrate body consists of three types of muscles: skeletal muscles (striated, voluntary, unbranched, and multinucleate), smooth muscles (non-striated, involuntary, uninucleate and branched) and cardiac muscles.
Cardiac muscles are known as the heart muscles or myocardium.
Cardiac muscles are one of the three types of vertebrate muscles.
Complete answer:
Features of cardiac muscles
>The cardiac muscles are involuntary in function, their functioning cannot be controlled by humans. >They are involved in continuous rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
>Cells of cardiac muscles called cardiomyocytes are uninucleate (single nucleus), cylindrical, elongated, striated, and branched.
>The cardiac muscles if damaged have no regenerative capacity.
Additional information:
>The cardiac muscles are myogenic which means the contractions are generated within the muscles.
>Cardiac muscles have striations due to the presence of actin and myosin filaments which are arranged into sarcomeres.
>These muscles are joined to one another by intercalated discs that contain gap junctions.
>These Intercalated discs have proteins that allow direct transmission of current from cell to cell across the chambers of the heart so that the cells contract altogether.
>It helps in coordinated muscle contraction and maintenance of circulation.
>Cardiac muscles resist fatigue so well because it has got more mitochondria than other muscles. >Mitochondria continuously provides energy resulting in the heart never stopping until a person dies.
>The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical impulse.
>The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells located in the right atrium, called the SA (sinoatrial) node which is the heart's natural pacemaker.

Note: Vertebrate body consists of three types of muscles: skeletal muscles (striated, voluntary, unbranched, and multinucleate), smooth muscles (non-striated, involuntary, uninucleate and branched) and cardiac muscles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




