
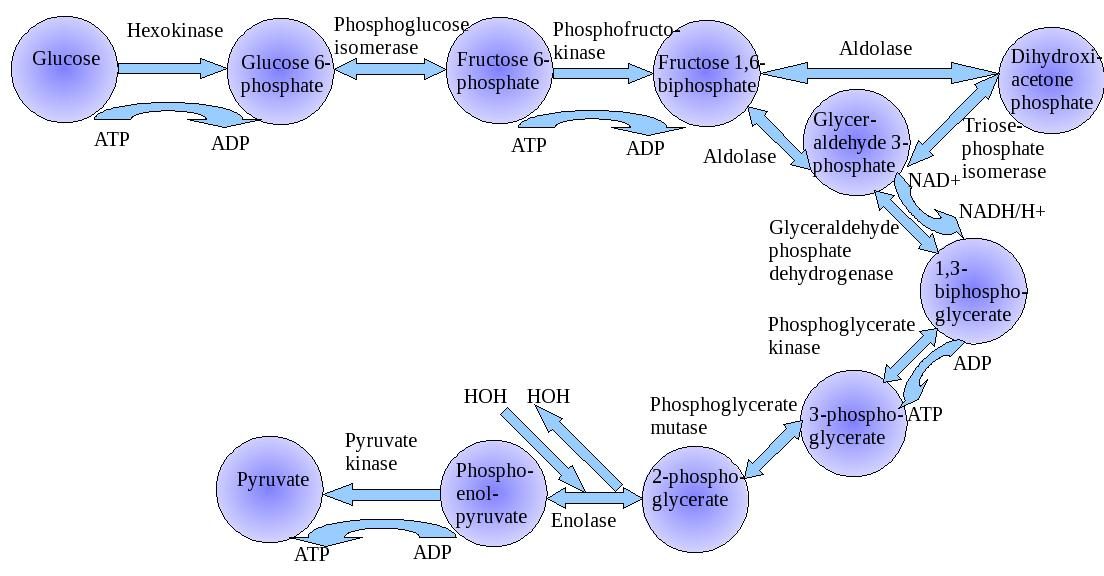
Give the schematic representation of glycolysis.
Answer
530.3k+ views
Hint: Glucose is a six-ring molecule present in the blood which typically comes from the sugar breakdown of carbohydrates. It enters cells by specific transporter proteins that transfer them into the cytosol of the cell from outside the cell.
Complete answer:
Glycolysis is the first of the major cellular respiration metabolic pathways to generate ATP energy. Glycolysis is a sequence of reactions in which two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates, are separated to derive energy from glucose. To break down sugar, there are 10 enzymes involved. The 10 stages of glycolysis are ordered by the order in which the mechanism operates on specific enzymes.
1.Glucose undergoes partial oxidation in this process to form two pyruvic acid molecules.
2.This glucose in plants is derived from sucrose, which is converted by the enzyme, invertase, into glucose and fructose, and these two monosaccharides quickly join the glycolytic pathway.
3.This glucose in plants is derived from sucrose, which is converted by the enzyme, invertase, into glucose and fructose, and these two monosaccharides quickly join the glycolytic pathway.
4.The action of the enzyme hexokinase allows glucose and fructose to be phosphorylated to give rise to glucose-6-phosphate.
5.In order to produce fructose-6-phosphate, this phosphorylated source of glucose then isomerises.
6.A series of ten reactions take place to generate pyruvate from glucose, under the influence of various enzymes.
Note: With or without oxygen, glycolysis can occur. In the presence of oxygen, the first step of cellular respiration is glycolysis. Glycolysis helps cells to make small quantities of ATP by a fermentation process in the absence of oxygen.
Complete answer:
Glycolysis is the first of the major cellular respiration metabolic pathways to generate ATP energy. Glycolysis is a sequence of reactions in which two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates, are separated to derive energy from glucose. To break down sugar, there are 10 enzymes involved. The 10 stages of glycolysis are ordered by the order in which the mechanism operates on specific enzymes.
1.Glucose undergoes partial oxidation in this process to form two pyruvic acid molecules.
2.This glucose in plants is derived from sucrose, which is converted by the enzyme, invertase, into glucose and fructose, and these two monosaccharides quickly join the glycolytic pathway.
3.This glucose in plants is derived from sucrose, which is converted by the enzyme, invertase, into glucose and fructose, and these two monosaccharides quickly join the glycolytic pathway.
4.The action of the enzyme hexokinase allows glucose and fructose to be phosphorylated to give rise to glucose-6-phosphate.
5.In order to produce fructose-6-phosphate, this phosphorylated source of glucose then isomerises.
6.A series of ten reactions take place to generate pyruvate from glucose, under the influence of various enzymes.

Note: With or without oxygen, glycolysis can occur. In the presence of oxygen, the first step of cellular respiration is glycolysis. Glycolysis helps cells to make small quantities of ATP by a fermentation process in the absence of oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




