
Give the schematic representation of calvin cycle.
Answer
527.8k+ views
Hint: The Calvin cycle is a process that converts carbon dioxide into sugar or the food autotrophs need to grow. The Calvin cycle has three main steps: carbon fixation, reduction phase and regeneration phase.
Complete answer:
As we already mentioned that by Calvin cycle, plants make their food. Carbon dioxide enters into the leaf through the stomata and then enters into the stroma of the chloroplast where the Calvin cycle synthesizes the sugar. We also called it the light-independent reactions because they are not directly driven by light.
Calvin cycle is divided into three main steps:
- Carbon fixation
- Reduction phase
- Regeneration phase.
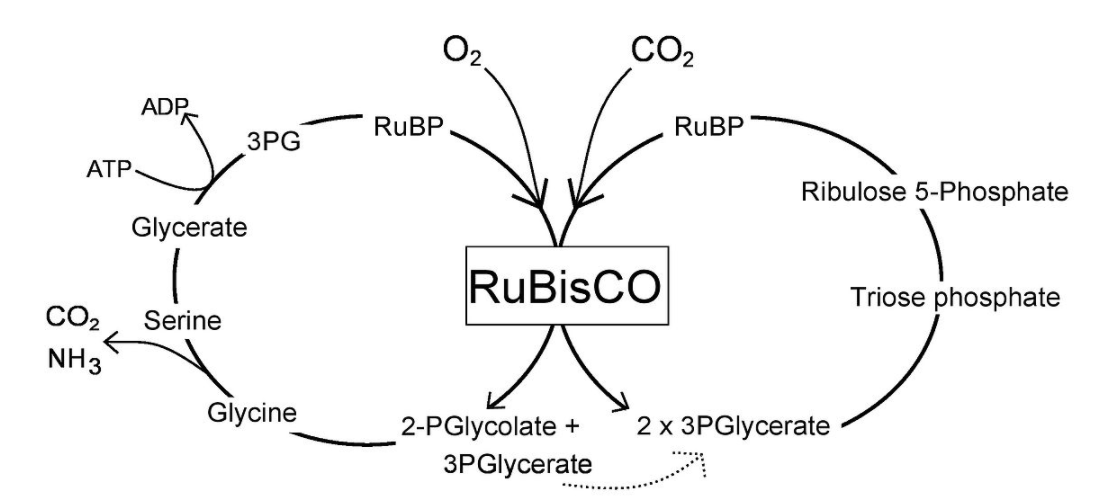
> Carbon fixation: In this step, a reaction between three molecules of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) (which has five atoms of carbon) and 3 molecules of CO$_2$ occur. An enzyme called ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCO) catalyses this reaction. They form 6 molecules of a 3 carbon compound 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA). This process is called carbon fixation because CO$_2$ is “fixed” from an inorganic form into organic molecules.
> Reduction: 3-PGA gains electrons and by using ATP and NADPH, it converts into six molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) and ATP and NADPH converted into ADP and NADP+. 1 molecule of G3P leaves the cycle and form other compounds.
> Regeneration: Remaining five molecules of G3P used in regeneration of RuBP. In this regeneration 3 molecules of ATP are used. As G3P has 3C atop. So, it will take 3 turns of the Calvin cycle to export one G3P. Each turn makes 2 G3P so total 6 G3P will form in three cycles. 1 of them leaves the cycle and the other 5 regenerate RuBP.
Note: In the first step we had 6 C. So, it will take six turns of the Calvin cycle to make one carbohydrate molecule, as only one G3P leaving the cycle in one turn. So, it takes 6 turns to synthesize glucose.
Complete answer:
As we already mentioned that by Calvin cycle, plants make their food. Carbon dioxide enters into the leaf through the stomata and then enters into the stroma of the chloroplast where the Calvin cycle synthesizes the sugar. We also called it the light-independent reactions because they are not directly driven by light.
Calvin cycle is divided into three main steps:
- Carbon fixation
- Reduction phase
- Regeneration phase.

> Carbon fixation: In this step, a reaction between three molecules of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) (which has five atoms of carbon) and 3 molecules of CO$_2$ occur. An enzyme called ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCO) catalyses this reaction. They form 6 molecules of a 3 carbon compound 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA). This process is called carbon fixation because CO$_2$ is “fixed” from an inorganic form into organic molecules.
> Reduction: 3-PGA gains electrons and by using ATP and NADPH, it converts into six molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) and ATP and NADPH converted into ADP and NADP+. 1 molecule of G3P leaves the cycle and form other compounds.
> Regeneration: Remaining five molecules of G3P used in regeneration of RuBP. In this regeneration 3 molecules of ATP are used. As G3P has 3C atop. So, it will take 3 turns of the Calvin cycle to export one G3P. Each turn makes 2 G3P so total 6 G3P will form in three cycles. 1 of them leaves the cycle and the other 5 regenerate RuBP.
Note: In the first step we had 6 C. So, it will take six turns of the Calvin cycle to make one carbohydrate molecule, as only one G3P leaving the cycle in one turn. So, it takes 6 turns to synthesize glucose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




