
Give the difference between open and closed systems of circulation.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: The difference between the open and closed circulation system depends on the parts of the system, materials the system circulates, the organisms having the system, and the processes involved. In a closed circulation system, the blood flows within the compact tubes called blood vessels. On the contrary in open circulation, the flow of blood is directly in the organs.
Complete answer: The difference between open and closed circulation system are as follows:
Note: Closed circulatory systems in humans can be further classified as systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation, and portal circulation. In systemic circulation the oxygenated blood is transferred from the heart to all parts of the body via arteries and deoxygenated blood is collected back to the heart via veins. Pulmonary circulation describes the movement of blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation via a pulmonary vein and oxygenated blood is carried back to the heart from the lungs via the pulmonary artery. The movement of blood from the gut area to the heart via the liver is called portal circulation.
Complete answer: The difference between open and closed circulation system are as follows:
| Open circulation system | Closed circulation system |
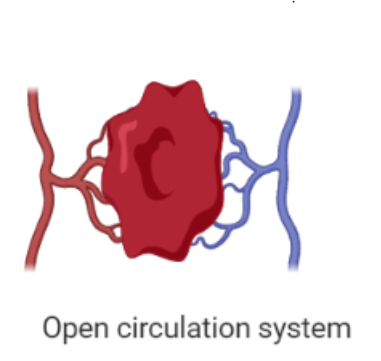
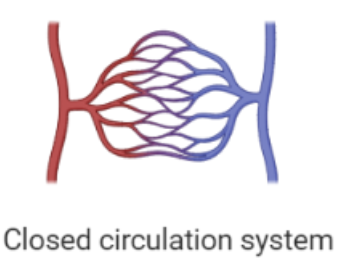
| 1. In open circulation blood is pumped into a cavity known as hemocoel and the fluid blood is not enclosed by blood vessels. | 1. In a closed circulation system blood is enclosed in blood vessels and hence is not in contact with the interstitial fluid of the body. |
| 2. Open system of circulation consists of only blood and heart. | 2. Closed circulatory system consists of the following components: heart, blood, and blood vessels. |
| 3. The transfusion process of blood is slower in the open circulatory system than in the closed circulatory system. | 3. The transfusion process of blood is faster in a closed circulatory system than in an open circulatory system. |
| 4. In an open circulation system it takes place directly between tissues and blood. | 4. Exchange of nutrients takes place via tissue fluid in a closed circulatory system. |
| 5. The fluid flowing in an open circulation system is called haemolymph. | 5. The fluid flowing in a closed circulation system is called blood. |
| 6. Respiratory pigments are absent in the open circulation system. | 6. Presence of respiratory pigments is seen in the closed circulation system. |
| 7. Open circulation systems can be seen in lower animals like cockroaches, snails, and clams. | 7. Closed type of circulation is observed in higher animals like cats, squid, and humans. |
| 
|
Note: Closed circulatory systems in humans can be further classified as systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation, and portal circulation. In systemic circulation the oxygenated blood is transferred from the heart to all parts of the body via arteries and deoxygenated blood is collected back to the heart via veins. Pulmonary circulation describes the movement of blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation via a pulmonary vein and oxygenated blood is carried back to the heart from the lungs via the pulmonary artery. The movement of blood from the gut area to the heart via the liver is called portal circulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




