
Give the diagrammatic representation of ${{C}_{4}}$cycle.
Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: Photosynthesis in higher plants involves additional processes, but it remains fundamentally the same. It is a physicochemical process in which organic compounds are synthesized using sunlight. Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast, which is found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast, which is found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves. In photosynthesis, four pigments are involved:
- Chlorophyll a
- Chlorophyll b
- Xanthophylls
- Carotenoids
${{C}_{4}}$ carbon fixation, also known as the Hatch–Slack pathway, is one of three known photosynthetic carbon fixation processes in plants. The names are derived from the discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that when supplied with\[14C{{O}_{2}}\], some plants first incorporate the \[14C\]label into four-carbon molecules.
All about ${{C}_{4}}$Cycle:
- It's a cyclic path.
- Mesophyll cells and Bundle Sheath cells contain the enzymes involved in the ${{C}_{4}}$ pathway.
- Plants use this pathway to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into a four-carbon chemical compound.
- The primary carbon dioxide acceptor is phosphoenolpyruvate, which is found in mesophyll cells. Phosphatidyl Pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the reaction.
- Following that, aspartic acid and malic acid are synthesized within the mesophyll cells and transported to the bundle sheath cells. The ${{C}_{4}}$ acids degrade here, releasing three-carbon molecules and carbon dioxide.
- The three-carbon molecules move back to the mesophyll cells where they get converted into phosphoenolpyruvate and complete the cycle.
- The Calvin cycle is completed when carbon dioxide enters the bundle sheath cells.
The diagrammatic representation of ${{C}_{4}}$cycle is as follows:
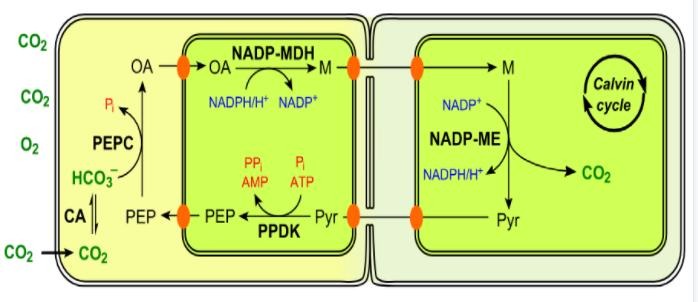
Note: The ancestral and more common ${{C}_{3}}$ carbon fixation is supplemented by ${{C}_{4}}$ fixation. RuBisCO is the main carboxylating enzyme in ${{C}_{3}}$photosynthesis, and it catalyzes two distinct reactions with $C{{o}_{2}}$ (carboxylation) and with oxygen (oxygenation), resulting in the wasteful process of photorespiration.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast, which is found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves. In photosynthesis, four pigments are involved:
- Chlorophyll a
- Chlorophyll b
- Xanthophylls
- Carotenoids
${{C}_{4}}$ carbon fixation, also known as the Hatch–Slack pathway, is one of three known photosynthetic carbon fixation processes in plants. The names are derived from the discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that when supplied with\[14C{{O}_{2}}\], some plants first incorporate the \[14C\]label into four-carbon molecules.
All about ${{C}_{4}}$Cycle:
- It's a cyclic path.
- Mesophyll cells and Bundle Sheath cells contain the enzymes involved in the ${{C}_{4}}$ pathway.
- Plants use this pathway to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into a four-carbon chemical compound.
- The primary carbon dioxide acceptor is phosphoenolpyruvate, which is found in mesophyll cells. Phosphatidyl Pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the reaction.
- Following that, aspartic acid and malic acid are synthesized within the mesophyll cells and transported to the bundle sheath cells. The ${{C}_{4}}$ acids degrade here, releasing three-carbon molecules and carbon dioxide.
- The three-carbon molecules move back to the mesophyll cells where they get converted into phosphoenolpyruvate and complete the cycle.
- The Calvin cycle is completed when carbon dioxide enters the bundle sheath cells.
The diagrammatic representation of ${{C}_{4}}$cycle is as follows:

Note: The ancestral and more common ${{C}_{3}}$ carbon fixation is supplemented by ${{C}_{4}}$ fixation. RuBisCO is the main carboxylating enzyme in ${{C}_{3}}$photosynthesis, and it catalyzes two distinct reactions with $C{{o}_{2}}$ (carboxylation) and with oxygen (oxygenation), resulting in the wasteful process of photorespiration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




