
Give structural formula of glycerol.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Glycerol is an organic compound also known as glycyl alcohol or glycerine in some texts, which is colourless, odourless and has sweet taste. At room temperature, it is viscous and non-toxic in low concentrations.
Complete answer:
Glycerol was first discovered in 1779 by Carl Scheele who is more famous for the discovery of oxygen. When he was investigating the relationships between the soap and drying plaster known as Emplastrum simplex, during his experiments on the reaction of olive oil with the lead monoxide, he observed a new compound with a sweet taste and he named that compound as “sweet principle of fat”.
Glycerol is involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolisms. It is also used in Pharmaceutical industry, in cosmetic industry, detergents, plastics industry and in food industry. Glycerol also helps in production of dynamite.
Structurally, glycerol is the trihydroxy sugar alcohol when three carbon atoms and three hydroxyl groups. Structure of glycerol is shown below.
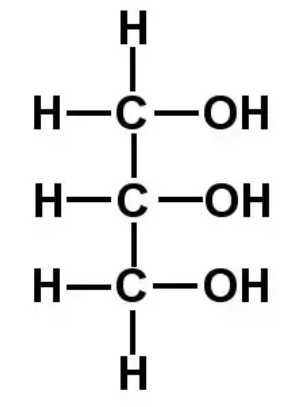
Glycerol is also used as moisture controlling reagent in the cosmetic industry and it enhances the texture of lotions and creams in the cosmetic industry. Glycerol helps in maintaining the water content or moisture of the creams and cosmetic products which prevent them from drying out or freezing.
In the food industry, it helps in increasing the shelf life of food and taste, it enhances the outlook of food, acts as preservative and lowers the toxicity of the food.
Note: Crude glycerol can be produced from the biofuels which is obtained from soya bean oil and from the other vegetable oils. Impurities from the methanol, salts and soap make it difficult to extract pure glycerol. Pure Glycerol is an important part of manufacturing processes of waxes, antifreeze and textile products.
Complete answer:
Glycerol was first discovered in 1779 by Carl Scheele who is more famous for the discovery of oxygen. When he was investigating the relationships between the soap and drying plaster known as Emplastrum simplex, during his experiments on the reaction of olive oil with the lead monoxide, he observed a new compound with a sweet taste and he named that compound as “sweet principle of fat”.
Glycerol is involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolisms. It is also used in Pharmaceutical industry, in cosmetic industry, detergents, plastics industry and in food industry. Glycerol also helps in production of dynamite.
Structurally, glycerol is the trihydroxy sugar alcohol when three carbon atoms and three hydroxyl groups. Structure of glycerol is shown below.

Glycerol is also used as moisture controlling reagent in the cosmetic industry and it enhances the texture of lotions and creams in the cosmetic industry. Glycerol helps in maintaining the water content or moisture of the creams and cosmetic products which prevent them from drying out or freezing.
In the food industry, it helps in increasing the shelf life of food and taste, it enhances the outlook of food, acts as preservative and lowers the toxicity of the food.
Note: Crude glycerol can be produced from the biofuels which is obtained from soya bean oil and from the other vegetable oils. Impurities from the methanol, salts and soap make it difficult to extract pure glycerol. Pure Glycerol is an important part of manufacturing processes of waxes, antifreeze and textile products.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




