
Give one example of an organism other than a hydra that performs budding to differentiate between them the way they carry out budding.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: It is a type of asexual reproduction where the new organism (offspring) grows as an outgrowth from the body of the parent. Now, the new individual starts growing as a small body on one side of the parent organism and continues growing in size while still attached to the parent.
Complete answer:
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction. It is most usually connected with bacteria and yeast, however, some animal species reproduce through budding, as well. A parent organism makes a bud from its own cells, which at the point it forms on the basis of the offspring organism and develops into an organism resembling the parent. Other than hydra, yeast, and bacteria likewise show reproduction by budding.
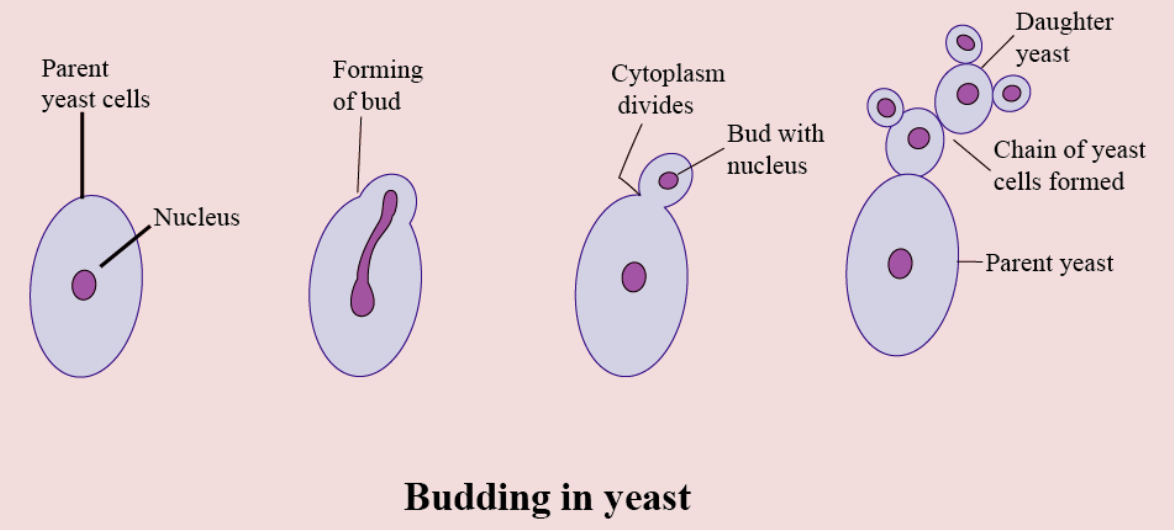
Budding starts with the softening of a small portion of the cell wall in the yeast cells. The protuberance (bud) is about 1µm wide at its base at this stage, and it is covered by the cell wall of the parent cell. The nuclear division of the parent cell also takes place at the same time so that the genetic material of the parent is passed to the new bud.
With the high variety of fungi, both sexual and agamic methods of reproduction have been seen in various species. Under adverse environmental conditions, sexual reproduction is common in mycelia, they also produce through fragmentation (a type of asexual reproduction) under favorable conditions.
Note: In yeast cells, During budding, replication of the parent DNA occurs through the S-phase characterized by DNA synthesis and the M-phase where DNA is copied. The formation of a secondary septum is accompanied by the separation of the two cells with the chitinous primary septum remaining with the mother cell.
Complete answer:
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction. It is most usually connected with bacteria and yeast, however, some animal species reproduce through budding, as well. A parent organism makes a bud from its own cells, which at the point it forms on the basis of the offspring organism and develops into an organism resembling the parent. Other than hydra, yeast, and bacteria likewise show reproduction by budding.

Budding starts with the softening of a small portion of the cell wall in the yeast cells. The protuberance (bud) is about 1µm wide at its base at this stage, and it is covered by the cell wall of the parent cell. The nuclear division of the parent cell also takes place at the same time so that the genetic material of the parent is passed to the new bud.
With the high variety of fungi, both sexual and agamic methods of reproduction have been seen in various species. Under adverse environmental conditions, sexual reproduction is common in mycelia, they also produce through fragmentation (a type of asexual reproduction) under favorable conditions.
Note: In yeast cells, During budding, replication of the parent DNA occurs through the S-phase characterized by DNA synthesis and the M-phase where DNA is copied. The formation of a secondary septum is accompanied by the separation of the two cells with the chitinous primary septum remaining with the mother cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




