
Give an account for the structure and function of hindbrain.
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The hindbrain is the rear part of the brain. It includes most of the brainstem and the cerebellum.
Complete answer:The hindbrain is derived from the rhombencephalon. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and coordinates many vital functions, such as breathing and heartbeat. Hindbrain consists of- pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. Cranial nerves are found in the hindbrain.
Pons
The pons form ‘bridge’, and connects the brainstem to the cerebral cortex. It has a bulb-like shape that sits right underneath the midbrain. It coordinates signals and communications flow between the brain and the spinal cord.
Four cranial nerves are found in the pons:
> The abducens nerve
> The facial nerve
> The vestibulocochlear nerve
> The trigeminal nerve
Cerebellum
Situated behind the pons. In appearance, it appears like a layered, wrinkly coral. It consists of two hemispheres. The dense grey matter layer is found in an inner region surrounded by white matter. It also contains Purkinje cells.
The cerebellum coordinates our motor & voluntary movements. It helps us maintain balance and posture.
Medulla oblongata
It is the lower part of the brainstem as well as of the hindbrain. It continues in the spinal cord. Measures about 3cm long. Its control centers autonomic vital functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, breathing - and many involuntary reflexes such as swallowing and sneezing.
The medulla also contains four cranial nerves stem from this region:
> The glossopharyngeal nerve
> The vagus nerve the gag reflex
> The accessory nerve
> The hypoglossal nerve
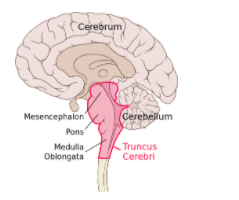
Note: Hindbrain or rhombencephalon, region of the brain. Mainly composed of the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the cerebellum. The hindbrain coordinates functions that are vital for survival such as respiratory rhythm, motor activity, circadian rhythm.
Complete answer:The hindbrain is derived from the rhombencephalon. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and coordinates many vital functions, such as breathing and heartbeat. Hindbrain consists of- pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. Cranial nerves are found in the hindbrain.
Pons
The pons form ‘bridge’, and connects the brainstem to the cerebral cortex. It has a bulb-like shape that sits right underneath the midbrain. It coordinates signals and communications flow between the brain and the spinal cord.
Four cranial nerves are found in the pons:
> The abducens nerve
> The facial nerve
> The vestibulocochlear nerve
> The trigeminal nerve
Cerebellum
Situated behind the pons. In appearance, it appears like a layered, wrinkly coral. It consists of two hemispheres. The dense grey matter layer is found in an inner region surrounded by white matter. It also contains Purkinje cells.
The cerebellum coordinates our motor & voluntary movements. It helps us maintain balance and posture.
Medulla oblongata
It is the lower part of the brainstem as well as of the hindbrain. It continues in the spinal cord. Measures about 3cm long. Its control centers autonomic vital functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, breathing - and many involuntary reflexes such as swallowing and sneezing.
The medulla also contains four cranial nerves stem from this region:
> The glossopharyngeal nerve
> The vagus nerve the gag reflex
> The accessory nerve
> The hypoglossal nerve

Note: Hindbrain or rhombencephalon, region of the brain. Mainly composed of the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the cerebellum. The hindbrain coordinates functions that are vital for survival such as respiratory rhythm, motor activity, circadian rhythm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




