
What is genetics? Explain Mendel's law of dominance with a line diagram.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The traits that are contrasting by Mendel are the colour of flower (purple or white), the position of flower (axial or terminal), the length of the stem (long or short), the shape of the seed (round or wrinkled), the seed colour (green or green), the pod shape (inflated or constricted), and the pod colour (yellow or green).
Complete answer:To solve this question, first, we need to know about genetics.
Genetics is a genetics branch related to the study of chromosomes, genetic differences, and heredity in organisms. While heredity has been studied for centuries, Gregor Mendel was the first to research genetics scientifically. Mendel researched "Characteristic Inheritance" variations in the way the characteristics are passed down from parents to offspring.
Now, let us find the solution-
Genetics is a study of inheritance. Heredity is a biological mechanism in which the parent transmits those genes to their offspring or children. Every child will develop genes from both their biological parents, which, in turn, convey unique traits.
The Law of Dominance is used to describe the expression of only one trait of the parent in a monohybrid cross in F1 Generation and the expression of both in the F2 generation.
It also describes the proportion of 3:1 obtained in F2. The dominant characteristic will always be displayed if it is present based on the rule of dominance.
In the presence of the dominant trait, the expression of the recessive trait is obscured.
The Law of Segregation states that the two alleles divide separately during the development of the gamete.
1. In the case of the height character, T is used for the Tall characteristic and t for the 'dwarf,' and T and T are each other's alleles.
2. Thus, in pea plants, the set of alleles for height will be TT, Tt, or tt.
3. Mendel also suggested that the allelic set of genes for height be similar, TT and tt, respectively, in the true-breeding, large, or dwarf pea form.
4. As Mendel observed that the phenotype of the F1 heterozygous Tt was the same as the TT parent in appearance, he suggested that in a set of no similar factors, one would dominate the other (as in the F1) and would therefore be named as the dominant factor, while the other factor would be recessive.
5. In this case, 'T' (for height) is dominant over 't' (for dwarfness), which is recessive. In the following, there is a diagram to understand the typical monohybrid cross between true-breeding tall pea plants and true-breeding dwarf pea plants.
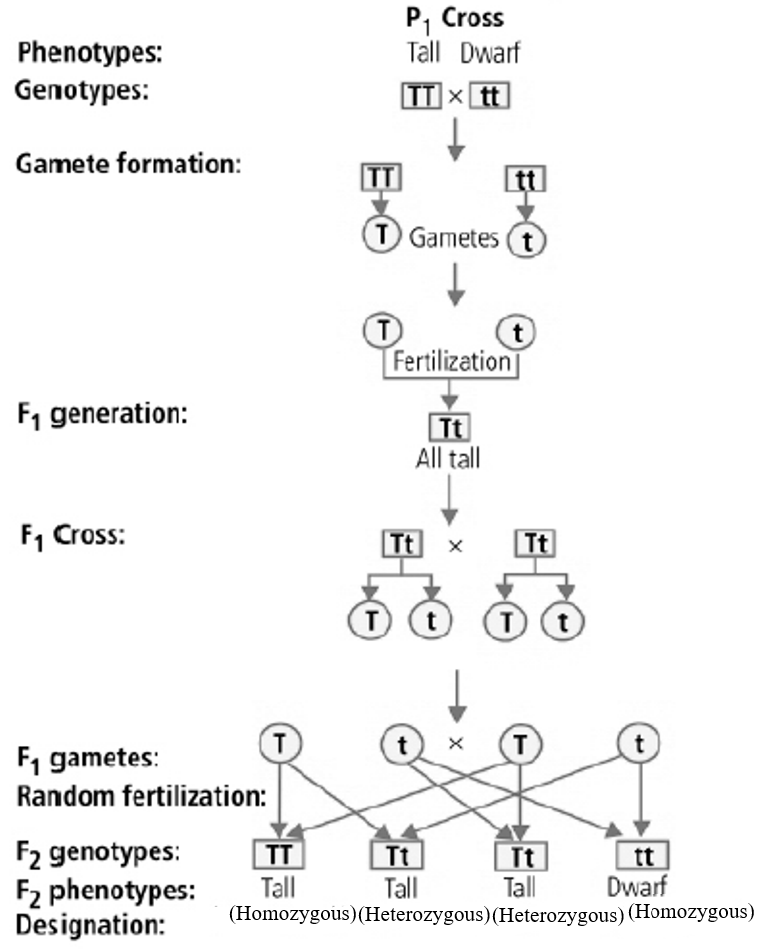
Note:Mendel proposed three laws of Genetics.
They are- law of segregation,
the law of independent assortment, and the law of dominance.
Complete answer:To solve this question, first, we need to know about genetics.
Genetics is a genetics branch related to the study of chromosomes, genetic differences, and heredity in organisms. While heredity has been studied for centuries, Gregor Mendel was the first to research genetics scientifically. Mendel researched "Characteristic Inheritance" variations in the way the characteristics are passed down from parents to offspring.
Now, let us find the solution-
Genetics is a study of inheritance. Heredity is a biological mechanism in which the parent transmits those genes to their offspring or children. Every child will develop genes from both their biological parents, which, in turn, convey unique traits.
The Law of Dominance is used to describe the expression of only one trait of the parent in a monohybrid cross in F1 Generation and the expression of both in the F2 generation.
It also describes the proportion of 3:1 obtained in F2. The dominant characteristic will always be displayed if it is present based on the rule of dominance.
In the presence of the dominant trait, the expression of the recessive trait is obscured.
The Law of Segregation states that the two alleles divide separately during the development of the gamete.
1. In the case of the height character, T is used for the Tall characteristic and t for the 'dwarf,' and T and T are each other's alleles.
2. Thus, in pea plants, the set of alleles for height will be TT, Tt, or tt.
3. Mendel also suggested that the allelic set of genes for height be similar, TT and tt, respectively, in the true-breeding, large, or dwarf pea form.
4. As Mendel observed that the phenotype of the F1 heterozygous Tt was the same as the TT parent in appearance, he suggested that in a set of no similar factors, one would dominate the other (as in the F1) and would therefore be named as the dominant factor, while the other factor would be recessive.
5. In this case, 'T' (for height) is dominant over 't' (for dwarfness), which is recessive. In the following, there is a diagram to understand the typical monohybrid cross between true-breeding tall pea plants and true-breeding dwarf pea plants.

Note:Mendel proposed three laws of Genetics.
They are- law of segregation,
the law of independent assortment, and the law of dominance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




