
What is functional isomerism? Give one example.
Answer
527.3k+ views
Hint: To draw a functional isomer, first make a compound that has the same molecular formula. Functional isomerism is the type of isomerism in which the compounds that have the same molecular formula, but have different functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us begin this question by understanding the term ‘functional isomerism’.
“Functional isomers are structural isomers that have the same molecular formula (that is, the same number of atoms of the same elements), but the atoms are connected in different ways so that the groupings are dissimilar. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, functionalities.”
Let us consider alcohol and an ether. Both have a general formula – \[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n+2}}O\].
When n=3, the molecular formula becomes \[{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}O\].
Let us draw all possible structures –
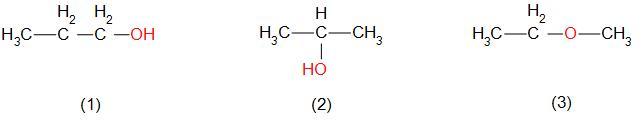
All the structures have the same molecular formula. Compound (1) & (2) is alcohol and compound (3) is an ether. Here,
Compound (1) and (3) are functional isomers
Compound (2) and (3) are functional isomers
Compound (1) and (2) are not functional isomers, because both the compounds have the same functional group (it is a position isomer).
Additional Information:
While deciding the kind of structural isomerism, follow this order to avoid confusion –
Ring Chain isomerism (consider it at priority)
Tautomerism
Functional isomerism
Metamerism
Chain isomerism
Position isomerism
Note: Stereoisomerism is another kind of isomerism, which is further divided into conformational and configurational isomerism. This kind of isomerism deals with the spatial arrangement or orientation of molecules atoms in a compound in space.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us begin this question by understanding the term ‘functional isomerism’.
“Functional isomers are structural isomers that have the same molecular formula (that is, the same number of atoms of the same elements), but the atoms are connected in different ways so that the groupings are dissimilar. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, functionalities.”
Let us consider alcohol and an ether. Both have a general formula – \[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n+2}}O\].
When n=3, the molecular formula becomes \[{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}O\].
Let us draw all possible structures –

All the structures have the same molecular formula. Compound (1) & (2) is alcohol and compound (3) is an ether. Here,
Compound (1) and (3) are functional isomers
Compound (2) and (3) are functional isomers
Compound (1) and (2) are not functional isomers, because both the compounds have the same functional group (it is a position isomer).
Additional Information:
While deciding the kind of structural isomerism, follow this order to avoid confusion –
Ring Chain isomerism (consider it at priority)
Tautomerism
Functional isomerism
Metamerism
Chain isomerism
Position isomerism
Note: Stereoisomerism is another kind of isomerism, which is further divided into conformational and configurational isomerism. This kind of isomerism deals with the spatial arrangement or orientation of molecules atoms in a compound in space.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




