
What is the function of the hormone cholecystokinin?
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: Cholecystokinin is a gut hormone. It is released after a meal. It aids in digestion and reduction of appetite. It is officially called pancreozymin. It is a peptide hormone, which is present in the gastrointestinal system. It is useful in stimulating the digestion of fats and proteins. In the first segment of the small intestine, duodenum, the hormone is secreted by the enteroendocrine cells residing there.
Complete answer
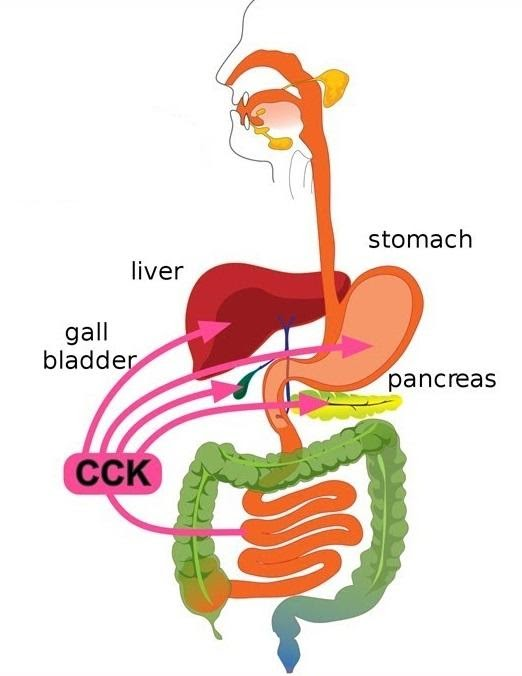
Figure: Functions of cholecystokinin
The most significant functions of the hormone cholecystokinin lie in the field of appetite and digestion.
It enhances digestion via slowing down the emptying of the food from the stomach and stimulation of production of bile in the liver and release of bile from the gallbladder.
It secretes and releases the digestive enzymes from the pancreas. It acts as a suppressant of hunger.
It facilitates digestion within the small intestine.
It is synthesized from the mucosal epithelial cells in the first segment of the small intestine (upper small intestine) or duodenum. It induces stimulation delivery into the small intestine of digestive enzymes obtained from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder.
It aids in the contraction of the gallbladder, induction of satiety and regulation of gastric emptying.
Note:
The secretion of the hormone cholecystokinin is induced by the introduction of amino acids, hydrochloric acid and fatty acids into the duodenum and stomach. I cells of duodenum are employed in the synthesis of cholecystokinin. The hormone is abbreviated as CCK. Presence of partially digested fats and proteins in the small intestine and during the flow of chyme into the small intestine, the hormone is released into the blood.
Complete answer

Figure: Functions of cholecystokinin
The most significant functions of the hormone cholecystokinin lie in the field of appetite and digestion.
It enhances digestion via slowing down the emptying of the food from the stomach and stimulation of production of bile in the liver and release of bile from the gallbladder.
It secretes and releases the digestive enzymes from the pancreas. It acts as a suppressant of hunger.
It facilitates digestion within the small intestine.
It is synthesized from the mucosal epithelial cells in the first segment of the small intestine (upper small intestine) or duodenum. It induces stimulation delivery into the small intestine of digestive enzymes obtained from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder.
It aids in the contraction of the gallbladder, induction of satiety and regulation of gastric emptying.
Note:
The secretion of the hormone cholecystokinin is induced by the introduction of amino acids, hydrochloric acid and fatty acids into the duodenum and stomach. I cells of duodenum are employed in the synthesis of cholecystokinin. The hormone is abbreviated as CCK. Presence of partially digested fats and proteins in the small intestine and during the flow of chyme into the small intestine, the hormone is released into the blood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




