
What is the function of plastids?
A. Leucoplasts store the reserve food in the form of starch grains or oil droplets or proteins.
B. Chromoplasts help in pollination and dispersal of seeds and fruits.
C. Chloroplasts are sites of photosynthesis so are called the kitchen of the cell.
D. All of the above.
Answer
605.4k+ views
Hint: Plastids are DNA containing double membraned structures. One type of plastid shows similarity with mitochondria.
Complete answer:
Plastids are the largest cell organelle in plant cells containing DNA, their plasma membrane is double layer like mitochondria. Plastids store a variety of substance and are classified into three types, this classification was given by Haeckel:
- Leucoplasts: These are the largest of all plastids, they are colorless. Depending upon the components stored in leucoplasts, it is of three types:
Amyloplast: Carbohydrate is stored in the form of starch.
Aleuroplasts: Proteins are stored here. It is also known as the proteinoplast.
Elaioplasts: Oils and fat storage occurs in them.
- Chromoplast: Coloured pigments are stored in chromoplasts. They contain carotenoids which are fat-soluble. They give color to flowers and therefore help in the attraction of pollinators and dispersers of seeds and fruits.
- Chloroplast: It is a semi-autonomous organelle in the plant cell, it contains chloroplast. It is the main photosynthetic organelle in plants and therefore is also known as the kitchen of the cell.
Additional Information:
- The chloroplast is also a semi-autonomous cell organelle like mitochondria.
- The chloroplast is semi-autonomous because it has the following two features:
- It has its DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
- It also has its protein-synthesizing machinery.
- Chloroplast has different shapes in different organisms. Cup-shaped, girdle shapes, spiral, stellate, reticulate, and discoidal shapes of chloroplast have been observed.
So, the correct answer is, “ all of the above.”
Note: It is to be remembered that out of all the three types of plastids, leucoplast, chromoplast, and chloroplast, the only chloroplast is semi-autonomous and not the others. It is believed that these semi-autonomous organelles have originated from unicellular prokaryotes during evolution.
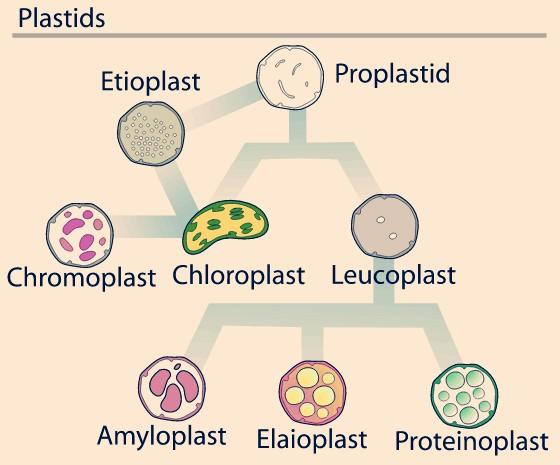
Complete answer:
Plastids are the largest cell organelle in plant cells containing DNA, their plasma membrane is double layer like mitochondria. Plastids store a variety of substance and are classified into three types, this classification was given by Haeckel:
- Leucoplasts: These are the largest of all plastids, they are colorless. Depending upon the components stored in leucoplasts, it is of three types:
Amyloplast: Carbohydrate is stored in the form of starch.
Aleuroplasts: Proteins are stored here. It is also known as the proteinoplast.
Elaioplasts: Oils and fat storage occurs in them.
- Chromoplast: Coloured pigments are stored in chromoplasts. They contain carotenoids which are fat-soluble. They give color to flowers and therefore help in the attraction of pollinators and dispersers of seeds and fruits.
- Chloroplast: It is a semi-autonomous organelle in the plant cell, it contains chloroplast. It is the main photosynthetic organelle in plants and therefore is also known as the kitchen of the cell.
Additional Information:
- The chloroplast is also a semi-autonomous cell organelle like mitochondria.
- The chloroplast is semi-autonomous because it has the following two features:
- It has its DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
- It also has its protein-synthesizing machinery.
- Chloroplast has different shapes in different organisms. Cup-shaped, girdle shapes, spiral, stellate, reticulate, and discoidal shapes of chloroplast have been observed.
So, the correct answer is, “ all of the above.”
Note: It is to be remembered that out of all the three types of plastids, leucoplast, chromoplast, and chloroplast, the only chloroplast is semi-autonomous and not the others. It is believed that these semi-autonomous organelles have originated from unicellular prokaryotes during evolution.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




