
From where aspirin is obtained?
Answer
506.7k+ views
Hint: We have to know that aspirin, otherwise called acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a drug used to diminish agony, fever, or inflammation. Certain inflammatory conditions which aspirin is utilized to treat includes Kawasaki illness, rheumatic fever and pericarditis.
Complete answer:
We have to know that IUPAC name of aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid. The other names of aspirin include 2-acetoxybenzoic acid, acetylsalicylate, o-acetylsalicylic acid. We can draw the structure of aspirin as,
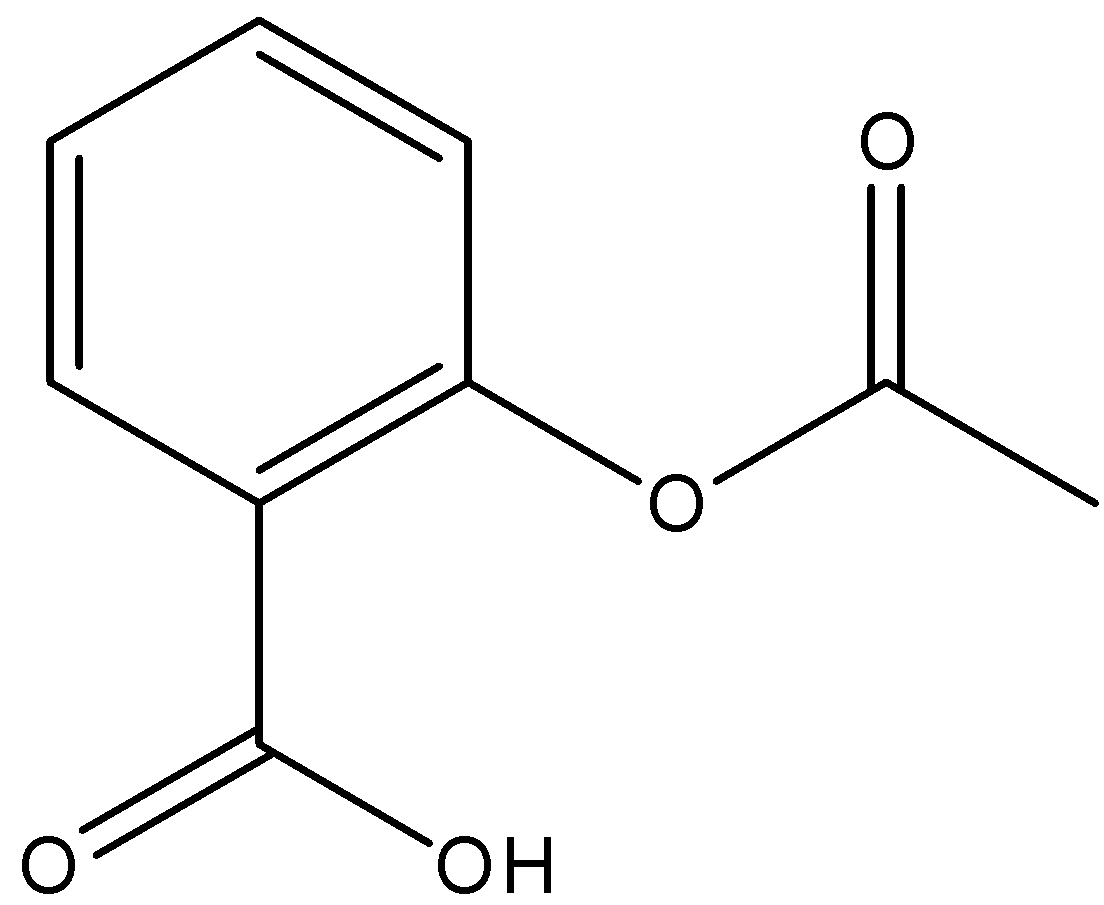
The preparation of aspirin is named an esterification reaction. Salicylic acid is treated with acetic anhydride, derivative of acetic acid, causing a chemical reaction that transforms salicylic acid’s hydroxyl group into an ester group. This cycle yields aspirin and acetic acid, which is viewed as a byproduct of this reaction. Modest quantities of sulfuric acid (and sporadically phosphoric acid) are quite often utilized as a catalyst. We can draw the chemical reaction as,
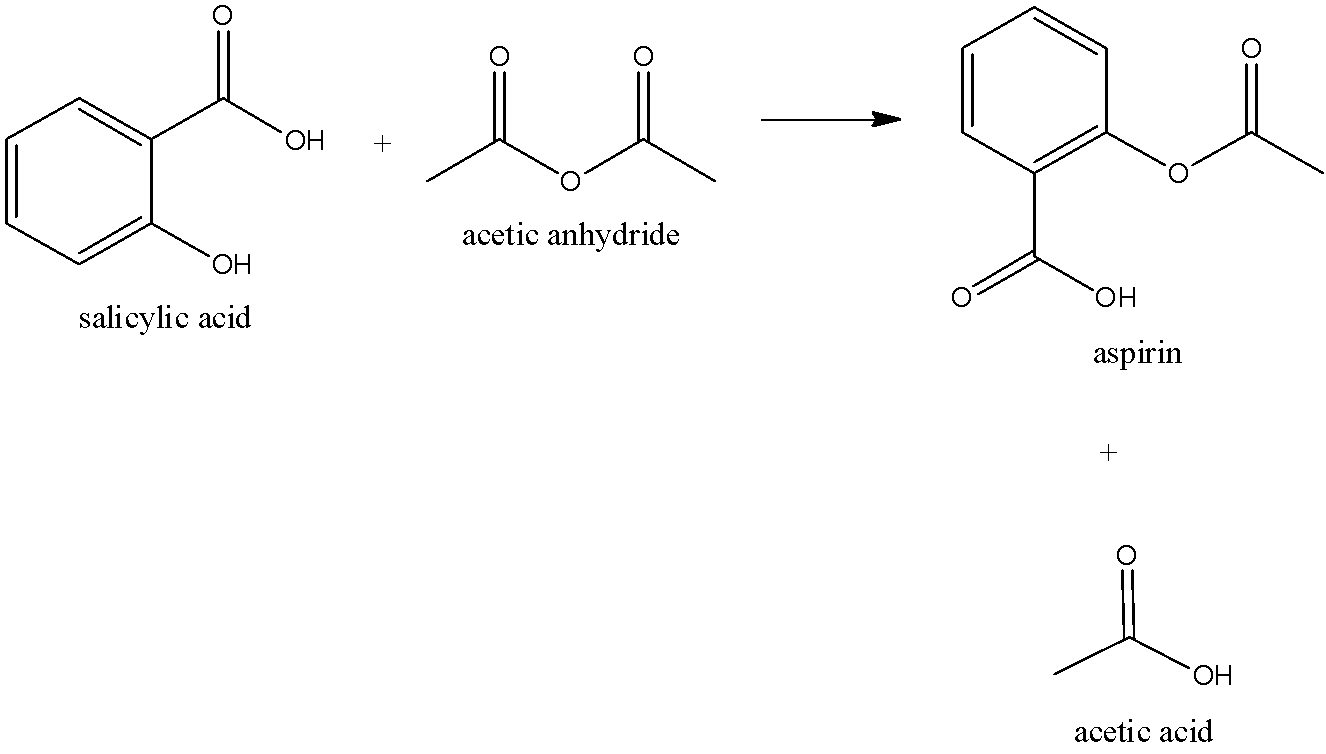
Formulations containing high concentrations of aspirin regularly smell like vinegar in light of the fact that aspirin can disintegrate through hydrolysis in damp conditions, yielding salicylic and acetic acids.
Additional information:
We have to know that aspirin is an acetyl derivative of salicylic acid.
It is white, crystalline, weakly acidic substance.
The melting point of aspirin is $136^\circ C$.
The boiling point of aspirin is $140^\circ C$.
At $25^\circ C$, the acid dissociation constant of aspirin is $3.5$
Note:
We need to know that the aspirin has pain relieving (diminishes torment), anti-inflammatory (lessens redness and growing), against platelet (decreases blood clumps) and antipyretic (temperature decrease) impacts. Alkaline urine increases the discharge of aspirin. Aspirin medicine is an oral non-steroidal calming drug.
Complete answer:
We have to know that IUPAC name of aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid. The other names of aspirin include 2-acetoxybenzoic acid, acetylsalicylate, o-acetylsalicylic acid. We can draw the structure of aspirin as,

The preparation of aspirin is named an esterification reaction. Salicylic acid is treated with acetic anhydride, derivative of acetic acid, causing a chemical reaction that transforms salicylic acid’s hydroxyl group into an ester group. This cycle yields aspirin and acetic acid, which is viewed as a byproduct of this reaction. Modest quantities of sulfuric acid (and sporadically phosphoric acid) are quite often utilized as a catalyst. We can draw the chemical reaction as,

Formulations containing high concentrations of aspirin regularly smell like vinegar in light of the fact that aspirin can disintegrate through hydrolysis in damp conditions, yielding salicylic and acetic acids.
Additional information:
We have to know that aspirin is an acetyl derivative of salicylic acid.
It is white, crystalline, weakly acidic substance.
The melting point of aspirin is $136^\circ C$.
The boiling point of aspirin is $140^\circ C$.
At $25^\circ C$, the acid dissociation constant of aspirin is $3.5$
Note:
We need to know that the aspirin has pain relieving (diminishes torment), anti-inflammatory (lessens redness and growing), against platelet (decreases blood clumps) and antipyretic (temperature decrease) impacts. Alkaline urine increases the discharge of aspirin. Aspirin medicine is an oral non-steroidal calming drug.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




