
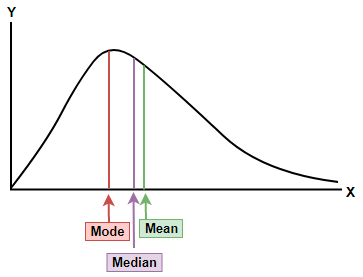
From the graph, which of the following provides a measure of central location for the data?
(a) Mean
(b) Mode
(c) Median
(d) Range

Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Here first we will know about the terms mean, median, mode and range given in the options one by one. Further we will see the type of data set (symmetrical or skew) is present in the graph. In case the data set is symmetric then mean is generally taken as the measure of central tendency. In case the data set is skewed or slightly asymmetrical then median is taken as the best measure.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we have been provided with a graph of a data set as shown below and we are asked to determine the correct term that provides the measure of the central location for the data. First let us see each term provided in the option one by one.
(1) Mean: - Mean of a data set is defined as the ratio of sum of all the observations to the number of observations. Mathematically it is given by the formula $\overline{x}=\dfrac{\left( \sum\limits_{1}^{n}{{{x}_{i}}} \right)}{n}$ where $\overline{x}$ represents the mean, n is the number of observations.
(2) Mode: - Mode is defined as the data value that appears the most in a data set.
(3) Median: - Median is the middle value of a data set. It is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample or a probability distribution.
(4) Range: - The range is the difference between the largest and the smallest value in a data set. It is not a measure of central location but is a measure of spread.
Now, on observing the graph we can say that the data set is skewed or slightly asymmetrical in nature because the left and right side of the peak value is not the same, so for an asymmetrical data set we consider the median as the best measure for the central location.
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note: Note that in case of symmetrical distributions the mean, median and mode of the data coincides and mean is often taken as the measure of central location because it includes all of the data in the calculations. In case of moderately asymmetrical distributions we have the empirical relation given as Mode = 3(Median) – 2(Mean).
Complete step by step answer:
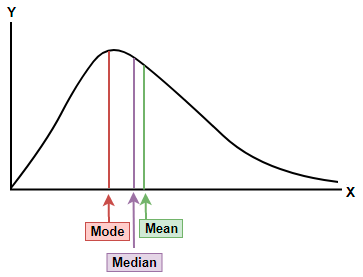
Here we have been provided with a graph of a data set as shown below and we are asked to determine the correct term that provides the measure of the central location for the data. First let us see each term provided in the option one by one.

(1) Mean: - Mean of a data set is defined as the ratio of sum of all the observations to the number of observations. Mathematically it is given by the formula $\overline{x}=\dfrac{\left( \sum\limits_{1}^{n}{{{x}_{i}}} \right)}{n}$ where $\overline{x}$ represents the mean, n is the number of observations.
(2) Mode: - Mode is defined as the data value that appears the most in a data set.
(3) Median: - Median is the middle value of a data set. It is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample or a probability distribution.
(4) Range: - The range is the difference between the largest and the smallest value in a data set. It is not a measure of central location but is a measure of spread.
Now, on observing the graph we can say that the data set is skewed or slightly asymmetrical in nature because the left and right side of the peak value is not the same, so for an asymmetrical data set we consider the median as the best measure for the central location.
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note: Note that in case of symmetrical distributions the mean, median and mode of the data coincides and mean is often taken as the measure of central location because it includes all of the data in the calculations. In case of moderately asymmetrical distributions we have the empirical relation given as Mode = 3(Median) – 2(Mean).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




