
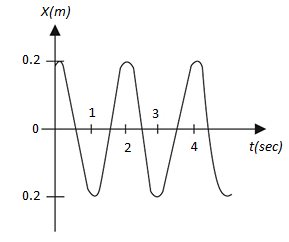
From the displacement time graph of an oscillating particle, find the maximum velocity of the particle.
A. \[2\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
B. \[\pi \,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
C. \[0.2\pi \,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: From the given displacement-time graph determine the period of oscillation. Amplitude of the oscillation is the distance between the mean position and extreme position. Use the formula for maximum velocity of the particle performing S.H.M.
Formula used:
The maximum velocity of the particle performing S.H.M is given by,
\[{v_{\max }} = \omega A\]
Here, \[\omega \] is the angular frequency and A is the amplitude of the oscillations.
The angular frequency of the particle is,
\[\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}\]
Here, \[T\] is the period of the oscillation.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the maximum velocity of the particle performing S.H.M is given by,
\[{v_{\max }} = \omega A\] …… (1)
Here, \[\omega \] is the angular frequency and A is the amplitude of the oscillations.
Therefore, from the above equation we need to determine the amplitude and angular frequency of the oscillations.
We know that the amplitude of the oscillations is the maximum vibration of the particle from its mean position. From the above equation, we can observe that the amplitude of the oscillation is 0.2 m.
We have the relation between angular frequency and period of the particle performing S.H.M as,
\[\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}\]
Here, \[T\] is the period of the oscillation.
The period of oscillation is the time taken by the particle to complete one oscillation. One oscillation is the one complete wavelength of the particle. From the above equation, the time required to complete one oscillation is 2 seconds.
Therefore, the angular frequency of the oscillations is,
\[\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \omega = \pi \,rad/s\]
We substitute \[\pi \,rad/s\] for \[\omega \] and 0.2 m for T in equation (1).
\[{v_{\max }} = \left( \pi \right)\left( {0.2\,} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_{\max }} = 0.2\pi \,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
Therefore, the maximum velocity of the particle is \[0.2\pi \,m{s^{ - 1}}\].
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:
While determining the wavelength of the particle in a displacement-time graph, students should measure the distance between the adjacent crests or the adjacent troughs if the particle does not start from the mean position. Students should always remember that the amplitude is the distance from the mean position to the extreme position and not the distance between the two extremes.
Formula used:
The maximum velocity of the particle performing S.H.M is given by,
\[{v_{\max }} = \omega A\]
Here, \[\omega \] is the angular frequency and A is the amplitude of the oscillations.
The angular frequency of the particle is,
\[\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}\]
Here, \[T\] is the period of the oscillation.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the maximum velocity of the particle performing S.H.M is given by,
\[{v_{\max }} = \omega A\] …… (1)
Here, \[\omega \] is the angular frequency and A is the amplitude of the oscillations.
Therefore, from the above equation we need to determine the amplitude and angular frequency of the oscillations.
We know that the amplitude of the oscillations is the maximum vibration of the particle from its mean position. From the above equation, we can observe that the amplitude of the oscillation is 0.2 m.
We have the relation between angular frequency and period of the particle performing S.H.M as,
\[\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}\]
Here, \[T\] is the period of the oscillation.
The period of oscillation is the time taken by the particle to complete one oscillation. One oscillation is the one complete wavelength of the particle. From the above equation, the time required to complete one oscillation is 2 seconds.
Therefore, the angular frequency of the oscillations is,
\[\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \omega = \pi \,rad/s\]
We substitute \[\pi \,rad/s\] for \[\omega \] and 0.2 m for T in equation (1).
\[{v_{\max }} = \left( \pi \right)\left( {0.2\,} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_{\max }} = 0.2\pi \,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
Therefore, the maximum velocity of the particle is \[0.2\pi \,m{s^{ - 1}}\].
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:
While determining the wavelength of the particle in a displacement-time graph, students should measure the distance between the adjacent crests or the adjacent troughs if the particle does not start from the mean position. Students should always remember that the amplitude is the distance from the mean position to the extreme position and not the distance between the two extremes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




