
From a window (\[h\] metres high above the ground) of a house in a street, the angle of elevation and depression to the top and the foot of another house on the opposite side of the street are \[\theta \] and \[\phi \] respectively.
Find the height of the opposite house if \[\theta = 60^\circ \], \[\phi = 45^\circ \], and \[h = 120\] metres.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint:
Here, we need to find the height of the opposite house. We will find the distance between the two houses using the formula for tangent of an angle. Using the angle of elevation and the distance between the two houses, we will find the difference between the heights of the first and second house. By adding the height of the first house in this difference, we will find the required height of the opposite house.
Formula Used: The tangent of an angle \[\theta \] in a right angled triangle is given by \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\].
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will draw the diagram using the information given in the question.
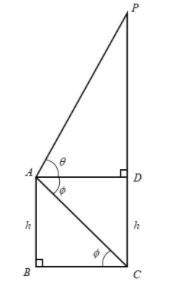
Here, \[AB\] is the height of the first house. \[PC\] is the height of the opposite house. \[\angle PAD = \theta \] is the angle of elevation to the top of the opposite house. \[\angle DAC = \phi \] is the angle of depression to the foot of the opposite house. \[BC\] is the distance between the two houses.
Now, \[BC\] and \[AD\] are the shortest straight distances between the two houses.
Therefore, we can observe that \[BC\] and \[AD\] are equal and parallel.
We know that the alternate interior angles between two parallel lines, on the opposite sides of a transversal are equal.
Therefore, since \[BC\] and \[AD\] are parallel and \[AC\] is the transversal, we get
\[\angle BCA = \angle DAC = \phi \]
Now, we will use the formula for tangent of an angle of a right angled triangle to find the distance between the two houses.
We know that the tangent of an angle \[\theta \] in a right angled triangle is given by \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\].
Therefore, in triangle
\[ABC\], we have
\[\begin{array}{l}\tan \angle BCA = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan \phi = \dfrac{h}{{BC}}\end{array}\]
Substituting \[\phi = 45^\circ \] and \[h = 120\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \tan 45^\circ = \dfrac{{120}}{{BC}}\]
The tangent of the angle measuring \[45^\circ \] is equal to 1.
Substituting \[\tan 45^\circ = 1\] in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{120}}{{BC}}\]
Thus, we get
\[\therefore BC=120\text{ m}\]
Therefore, the distance between the two houses is 120 metres.
Also, we can see that \[AB = BC = 120{\text{ m}}\] and \[\angle ABC = 90^\circ \].
Therefore,
\[ABCD\] is a square.
Thus, we get \[AB = BC = CD = AD = 120{\text{ m}}\].
Now, in triangle \[PAD\], we have
\[\begin{array}{l}\tan \angle PAD = \dfrac{{PD}}{{AD}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{PD}}{{AD}}\end{array}\]
Substituting \[\theta = 60^\circ \] and \[AD = 120\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \tan 60^\circ = \dfrac{{PD}}{{120}}\]
The tangent of the angle measuring \[60^\circ \] is equal to \[\sqrt 3 \].
Substituting \[\tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 \] in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{PD}}{{120}}\]
Thus, we get
\[\therefore PD=120\sqrt{3}\text{ m}\]
Finally, we can calculate the height of the opposite house.
We know that the height \[PC\] of the opposite house can be written as \[PC = PD + CD\].
Substituting \[PD = 120\sqrt 3 \] and \[CD = 120\], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}PC = 120\sqrt 3 + 120\\ \Rightarrow PC = 120\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)\end{array}\]
The value of \[\sqrt 3 \] is approximately \[1.732\].
Substituting \[\sqrt 3 = 1.732\], we get the approximate height of the opposite house as
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow PC \approx 120\left( {1.732 + 1} \right)\\ \Rightarrow PC \approx 120\left( {2.732} \right)\\ \Rightarrow PC \approx 327.84{\text{ m}}\end{array}\]
Therefore, the height of the opposite house is \[327.84\] metres.
Note:
Most of the time, the value of \[\sqrt 3 \] is given in the question, but in this question it is not given. You should remember the approximate value of \[\sqrt 3 = 1.732\] to simplify the final equation. A common mistake is to use \[1.414\], which is the value of \[\sqrt 2 \], and not \[\sqrt 3 \]. Using \[\sqrt 3 = 1.414\], you will get the incorrect answer.
Here, we need to find the height of the opposite house. We will find the distance between the two houses using the formula for tangent of an angle. Using the angle of elevation and the distance between the two houses, we will find the difference between the heights of the first and second house. By adding the height of the first house in this difference, we will find the required height of the opposite house.
Formula Used: The tangent of an angle \[\theta \] in a right angled triangle is given by \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\].
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will draw the diagram using the information given in the question.

Here, \[AB\] is the height of the first house. \[PC\] is the height of the opposite house. \[\angle PAD = \theta \] is the angle of elevation to the top of the opposite house. \[\angle DAC = \phi \] is the angle of depression to the foot of the opposite house. \[BC\] is the distance between the two houses.
Now, \[BC\] and \[AD\] are the shortest straight distances between the two houses.
Therefore, we can observe that \[BC\] and \[AD\] are equal and parallel.
We know that the alternate interior angles between two parallel lines, on the opposite sides of a transversal are equal.
Therefore, since \[BC\] and \[AD\] are parallel and \[AC\] is the transversal, we get
\[\angle BCA = \angle DAC = \phi \]
Now, we will use the formula for tangent of an angle of a right angled triangle to find the distance between the two houses.
We know that the tangent of an angle \[\theta \] in a right angled triangle is given by \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\].
Therefore, in triangle
\[ABC\], we have
\[\begin{array}{l}\tan \angle BCA = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan \phi = \dfrac{h}{{BC}}\end{array}\]
Substituting \[\phi = 45^\circ \] and \[h = 120\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \tan 45^\circ = \dfrac{{120}}{{BC}}\]
The tangent of the angle measuring \[45^\circ \] is equal to 1.
Substituting \[\tan 45^\circ = 1\] in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{120}}{{BC}}\]
Thus, we get
\[\therefore BC=120\text{ m}\]
Therefore, the distance between the two houses is 120 metres.
Also, we can see that \[AB = BC = 120{\text{ m}}\] and \[\angle ABC = 90^\circ \].
Therefore,
\[ABCD\] is a square.
Thus, we get \[AB = BC = CD = AD = 120{\text{ m}}\].
Now, in triangle \[PAD\], we have
\[\begin{array}{l}\tan \angle PAD = \dfrac{{PD}}{{AD}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{PD}}{{AD}}\end{array}\]
Substituting \[\theta = 60^\circ \] and \[AD = 120\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \tan 60^\circ = \dfrac{{PD}}{{120}}\]
The tangent of the angle measuring \[60^\circ \] is equal to \[\sqrt 3 \].
Substituting \[\tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 \] in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{PD}}{{120}}\]
Thus, we get
\[\therefore PD=120\sqrt{3}\text{ m}\]
Finally, we can calculate the height of the opposite house.
We know that the height \[PC\] of the opposite house can be written as \[PC = PD + CD\].
Substituting \[PD = 120\sqrt 3 \] and \[CD = 120\], we get
\[\begin{array}{l}PC = 120\sqrt 3 + 120\\ \Rightarrow PC = 120\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)\end{array}\]
The value of \[\sqrt 3 \] is approximately \[1.732\].
Substituting \[\sqrt 3 = 1.732\], we get the approximate height of the opposite house as
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow PC \approx 120\left( {1.732 + 1} \right)\\ \Rightarrow PC \approx 120\left( {2.732} \right)\\ \Rightarrow PC \approx 327.84{\text{ m}}\end{array}\]
Therefore, the height of the opposite house is \[327.84\] metres.
Note:
Most of the time, the value of \[\sqrt 3 \] is given in the question, but in this question it is not given. You should remember the approximate value of \[\sqrt 3 = 1.732\] to simplify the final equation. A common mistake is to use \[1.414\], which is the value of \[\sqrt 2 \], and not \[\sqrt 3 \]. Using \[\sqrt 3 = 1.414\], you will get the incorrect answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




