
From a point on the ground \[20\]m away from the foot of a vertical tower the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is \[{60^0}\]. Find the height of the tower.
(a) \[10\sqrt 3 \]m
(b) \[30\sqrt 3 \]m
(c) \[20\sqrt 3 \]m
(d) none of these.
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: The given question is based on trigonometry. In this question we are going to find the height of the tower using trigonometry formulas because the height of the tower, the ground and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower all together form \[{60^0}\]. From the given details, let's draw a diagram, which will help us to solve our problem easily.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this problem, we are given that,
The tower is \[20\]m away from the point on the ground.
The angle of elevation of the top of the tower is \[{60^0}\].
Let draw the diagram on the given,
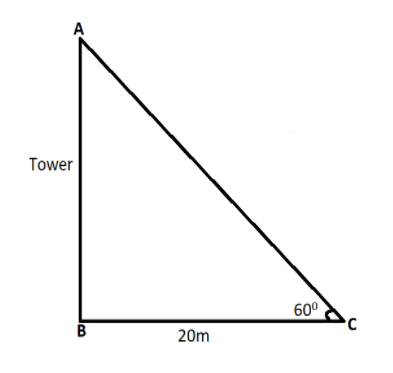
Here,
\[AC\] is the hypotenuse.
The opposite side of the hypotenuse, \[AB\] be the tower and its height be \[h\].
From point \[C\], the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is \[{60^0}\].
We can say that,
The adjacent side, \[BC = 20\]m.
Hypotenuse \[ < ACB = {60^0}\].
And we have considered that, \[AB = h\].
From the diagram, we can see that it is a right-angled triangle. In \[\Delta ABC\], we know an angle and the base of the triangle, that is, we know the adjacent side and angle of elevation. In trigonometry if the values of adjacent sides and angle of elevation, then \[\tan \theta \] is used.
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent}}}}\]
\[\tan {60^0} = \dfrac{h}{{20}}\]
The value of \[\tan {60^0} = \sqrt 3 \].
\[\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{h}{{20}}\]
By cross multiplication,
\[h = 20 \times \sqrt 3 \]
\[h = 20\sqrt 3 \]
The value of \[\sqrt 3 \] is \[1.732\]
\[\therefore h = 20 \times 1.732\]
\[h = 34.64\].
Therefore, the height of the tower is \[\;20\sqrt 3 = 34.64\]m.
Hence the option (C) \[20\sqrt 3 \]m is correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The trigonometry values are used to find the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. In a right-angled triangle there are three sides: the slope in the triangle is called hypotenuse, the side adjacent to the hypotenuse (or base) and the side opposite (or perpendicular) to the hypotenuse.
The formulas to be remember in trigonometry is:
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\] , \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\], \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}\].
\[{\text{cosec}}\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}\], \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}\], \[\cot \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this problem, we are given that,
The tower is \[20\]m away from the point on the ground.
The angle of elevation of the top of the tower is \[{60^0}\].
Let draw the diagram on the given,

Here,
\[AC\] is the hypotenuse.
The opposite side of the hypotenuse, \[AB\] be the tower and its height be \[h\].
From point \[C\], the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is \[{60^0}\].
We can say that,
The adjacent side, \[BC = 20\]m.
Hypotenuse \[ < ACB = {60^0}\].
And we have considered that, \[AB = h\].
From the diagram, we can see that it is a right-angled triangle. In \[\Delta ABC\], we know an angle and the base of the triangle, that is, we know the adjacent side and angle of elevation. In trigonometry if the values of adjacent sides and angle of elevation, then \[\tan \theta \] is used.
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opposite side}}}}{{{\text{adjacent}}}}\]
\[\tan {60^0} = \dfrac{h}{{20}}\]
The value of \[\tan {60^0} = \sqrt 3 \].
\[\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{h}{{20}}\]
By cross multiplication,
\[h = 20 \times \sqrt 3 \]
\[h = 20\sqrt 3 \]
The value of \[\sqrt 3 \] is \[1.732\]
\[\therefore h = 20 \times 1.732\]
\[h = 34.64\].
Therefore, the height of the tower is \[\;20\sqrt 3 = 34.64\]m.
Hence the option (C) \[20\sqrt 3 \]m is correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The trigonometry values are used to find the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. In a right-angled triangle there are three sides: the slope in the triangle is called hypotenuse, the side adjacent to the hypotenuse (or base) and the side opposite (or perpendicular) to the hypotenuse.
The formulas to be remember in trigonometry is:
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\] , \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\], \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}\].
\[{\text{cosec}}\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}\], \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}\], \[\cot \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




