
Free central placentation is present in
(a) Dianthus
(b) Argemone
(c) Primrose
(d) Both (a) and(b)
Answer
540.9k+ views
Hint: This type of placentation is present in ovaries with a single locule where ovules are borne on a central axis. Placentation is the arrangement of ovules within the ovary.
Complete answer:
The type of placenta is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Here there is a generation of a false septum that in turn causes the ovules to be arranged on a central axis and makes the ovary unilocular. It is observed in plants like Dianthus or Primrose.
In plants placentation is of the following types:
Basal: this type of placenta is found commonly in plants that have monocarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Here a single ovule is attached to the base of the ovary. Examples are sunflower, marigold.
Parietal: this type of placenta is commonly found in plants that have bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. A false septum is produced which makes a unilocular ovary bilocular. As observed in mustard and Argemone.
Axile: this type of placenta is found in bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The carpels in this ovary fuse and form a septum, this inturn forms a central axis as seen in china rose, tomato etc.
Marginal: this is a type of placenta is found in the monocarpellary unilocular ovary where placenta forms on the walls on the ovary on the ventral side and the ovules are arranged on a vertical axis like in peas.
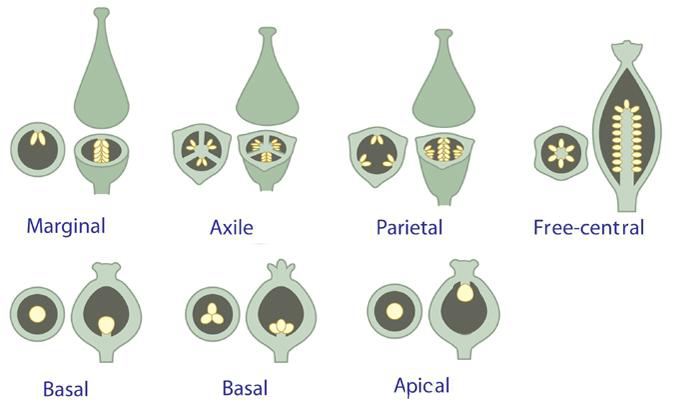
So, the correct answer is Dianthus
Note:
Placentation further decides seed arrangement in the fruit and the number of seeds in a single fruit. Its characterization is done on the basis of whether the central column in the ovary is present or not.
Complete answer:
The type of placenta is found in the bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Here there is a generation of a false septum that in turn causes the ovules to be arranged on a central axis and makes the ovary unilocular. It is observed in plants like Dianthus or Primrose.
In plants placentation is of the following types:
Basal: this type of placenta is found commonly in plants that have monocarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Here a single ovule is attached to the base of the ovary. Examples are sunflower, marigold.
Parietal: this type of placenta is commonly found in plants that have bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. A false septum is produced which makes a unilocular ovary bilocular. As observed in mustard and Argemone.
Axile: this type of placenta is found in bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The carpels in this ovary fuse and form a septum, this inturn forms a central axis as seen in china rose, tomato etc.
Marginal: this is a type of placenta is found in the monocarpellary unilocular ovary where placenta forms on the walls on the ovary on the ventral side and the ovules are arranged on a vertical axis like in peas.

So, the correct answer is Dianthus
Note:
Placentation further decides seed arrangement in the fruit and the number of seeds in a single fruit. Its characterization is done on the basis of whether the central column in the ovary is present or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




