
Four resistance $4\Omega ,4\Omega ,4\Omega $ and \[12\Omega \] form a Wheatstone’s network. Calculate the resistance needed to balance the network which when connected across the $12\Omega $ resistance.
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: The reciprocal of the equivalent resistance when the resistors are connected in parallel can be found by taking the sum of the reciprocal of each of the resistances connected. Using this, find the resistance connected in parallel to the\[12\Omega \]. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete answer:
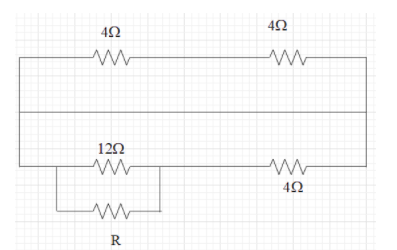
the resistance connected across the $12\Omega $ will be parallel. Therefore the equivalent resistance at this point will be given as,
\[{{R}_{eq}}=4\Omega \]
This is because the balancing of the wheatstone bridge should be done. For that we have to satisfy the equation mentioned as,
\[\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{R}{S}\]
Where all the variables are the resistances.
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{4}{4}=\dfrac{4}{4}\]
When the resistance are connected in parallel we can write that,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}\]
Where \[{{R}_{eq}}\]be the equivalent resistance, \[{{R}_{1}}\]and \[{{R}_{2}}\] be the resistances which are connected.
Now as these unknown resistance and the \[12\Omega \]are connected in parallel and their equivalent resistance has been found to be \[4\Omega \], we can write that,
\[\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{12}+\dfrac{1}{R}\]
Rearranging this equation will give,
\[\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{12}=\dfrac{1}{R}\]
Let us simplify this equation,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{3-1}{12}=\dfrac{2}{12}=\dfrac{1}{6} \\
& \therefore R=6\Omega \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore in order to maintain the wheatstone bridge conditions, the resistance which is to be connected in parallel to the \[12\Omega \] resistance has been found to be \[6\Omega \]. Therefore the answer for the question has been calculated.
Note:
A Wheatstone bridge is defined as a basic circuit which is helpful in calculating an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two branches of a bridge circuit, with one branch consisting of the unknown component. The major use of the circuit is its ability to give perfectly accurate measurements. The Wheatstone bridge has a point which is known as a null point where the current will not flow through the arm of the galvanometer. Therefore no effect of the resistance of the galvanometer will be there.
Complete answer:

the resistance connected across the $12\Omega $ will be parallel. Therefore the equivalent resistance at this point will be given as,
\[{{R}_{eq}}=4\Omega \]
This is because the balancing of the wheatstone bridge should be done. For that we have to satisfy the equation mentioned as,
\[\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{R}{S}\]
Where all the variables are the resistances.
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{4}{4}=\dfrac{4}{4}\]
When the resistance are connected in parallel we can write that,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}\]
Where \[{{R}_{eq}}\]be the equivalent resistance, \[{{R}_{1}}\]and \[{{R}_{2}}\] be the resistances which are connected.
Now as these unknown resistance and the \[12\Omega \]are connected in parallel and their equivalent resistance has been found to be \[4\Omega \], we can write that,
\[\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{12}+\dfrac{1}{R}\]
Rearranging this equation will give,
\[\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{12}=\dfrac{1}{R}\]
Let us simplify this equation,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{3-1}{12}=\dfrac{2}{12}=\dfrac{1}{6} \\
& \therefore R=6\Omega \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore in order to maintain the wheatstone bridge conditions, the resistance which is to be connected in parallel to the \[12\Omega \] resistance has been found to be \[6\Omega \]. Therefore the answer for the question has been calculated.
Note:
A Wheatstone bridge is defined as a basic circuit which is helpful in calculating an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two branches of a bridge circuit, with one branch consisting of the unknown component. The major use of the circuit is its ability to give perfectly accurate measurements. The Wheatstone bridge has a point which is known as a null point where the current will not flow through the arm of the galvanometer. Therefore no effect of the resistance of the galvanometer will be there.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




