
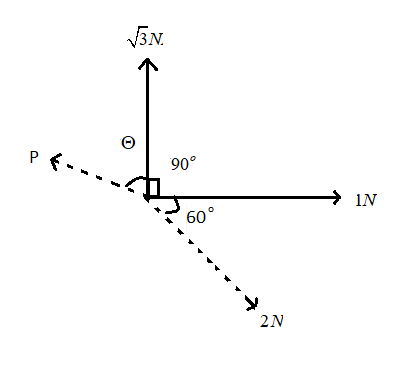
Four coplanar concurrent forces are acting on a body as shown in the figure to keep it in equilibrium. Then the value of $P$ and $\Theta $ are
A. $P = 4N,\Theta = {90^o}$
B. $P = 2N,\Theta = {90^o}$
C. $P = 1N,\Theta = {90^o}$
D. $P = 5N,\Theta = {90^o}$

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the coplanar concurrent forces is the system of two or more forces acting on the same plane intersecting the same point on the plane. This problem is solved by the coplanar concurrent forces system. When all the forces are acting in the same plane, they are known as coplanar forces whereas when the forces act at the same point on the same plane at same time, it is known as concurrent forces.
Complete answer:
We can split each force in two or more components , this is known as resolution of a force. After the resolution of the force the effect of the force remains as it is as earlier. So we can split up the force in two perpendicular components i.e. horizontal components and vertical components.
The resultant of concurrent forces can be found by resolving each force into its rectangular components. After that we add the all components algebraically according to their direction such as all the components along the y-axis are added together and along the x-axis are added together and sum of all the forces is zero :\[{F_X} = 0,{F_Y} = 0\].
For the given question , balancing the forces in the y-direction,
$
\sqrt 3 + p\cos \theta - 2 \times \sin {60^0} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 + p\cos \theta - 2 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow p\cos \theta = 0 \\
$
So the, $\theta = {90^0}$
For balancing the force along the X-direction, $1 + 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} - p \times 1 = 0$$ \Rightarrow p = 2$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
If all the forces acting on the body, keeps the body in the resting state or in the uniform motion in which its velocity is constant, then the system is said to be in equilibrium and net force on the system is zero in that condition.
Complete answer:
We can split each force in two or more components , this is known as resolution of a force. After the resolution of the force the effect of the force remains as it is as earlier. So we can split up the force in two perpendicular components i.e. horizontal components and vertical components.
The resultant of concurrent forces can be found by resolving each force into its rectangular components. After that we add the all components algebraically according to their direction such as all the components along the y-axis are added together and along the x-axis are added together and sum of all the forces is zero :\[{F_X} = 0,{F_Y} = 0\].
For the given question , balancing the forces in the y-direction,
$
\sqrt 3 + p\cos \theta - 2 \times \sin {60^0} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 + p\cos \theta - 2 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow p\cos \theta = 0 \\
$
So the, $\theta = {90^0}$
For balancing the force along the X-direction, $1 + 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} - p \times 1 = 0$$ \Rightarrow p = 2$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
If all the forces acting on the body, keeps the body in the resting state or in the uniform motion in which its velocity is constant, then the system is said to be in equilibrium and net force on the system is zero in that condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




