
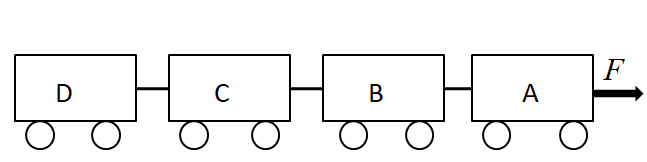
Four airline baggage carts are coupled as shown in the figure to make a “train”; each has a mass of $ 250kg $ . How do you find the answers to the following questions?
$ (a) $ Find the force $ F $ that must be applied to accelerates this “train” at $ 0.8\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}} $
$ (b) $ Find the tension in each of the three couplings between the baggage carts.

Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: In the first question, the force is asked. The formula of force in terms of mass and acceleration. By using the given mass and acceleration the force can be determined.
In the second question, the tension in each coupling is required. The numbers of baggage have to be noticed. Those are responsible for the tension in the couplings of the baggage carts. The tension also depends upon mass and acceleration.
The formula of force $ F = m \times a $
$ m $ is the mass and $ a $ is the acceleration.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are four airline baggage carts that are coupled as they look like a train.
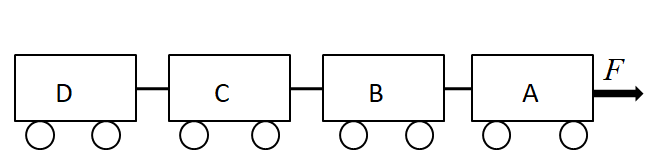
If the total force is $ F $ for these four baggage carts, The formula of the force will be $ F = 4m \times a $
Given that, $ m = 250kg $ and $ a = 0.8\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}} $
$ \therefore F = 4 \times 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow F = 4 \times 250 \times \dfrac{8}{{10}} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 800N $
$ (a) $ Answer: $ 800N $
Let, the tension between A and B is, $ {T_{AB}} $ ,
the tension between B and C is, $ {T_{BC}} $ ,
The tension between C and D is, $ {T_{CD}} $ .
The tension between A and B is for the three baggage carts, hence $ {T_{AB}} = 3ma $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{AB}} = 3 \times 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{AB}} = 600N $
The tension between B and C is for the two baggage carts, hence $ {T_{BC}} = 2ma $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{BC}} = 2 \times 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{BC}} = 400N $
The tension between C and D is for the one baggage cart, hence $ {T_{CD}} = ma $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{CD}} = 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{CD}} = 200N $
$ (b) $ Answer:
$ \Rightarrow {T_{AB}} = 600N $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{BC}} = 400N $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{CD}} = 200N $ .
Note:
The tension is the force that is transferred through a cable, wire, or strings after it is stretched by forces acting from the opposite poles. The direction of it is along the length of the cable and pulls equally on the materials on the opposite poles of the wire or the string. The force is the product of the total mass of the existing materials and the acceleration of the system. Hence the force can cause the change in motion for an object.
In the second question, the tension in each coupling is required. The numbers of baggage have to be noticed. Those are responsible for the tension in the couplings of the baggage carts. The tension also depends upon mass and acceleration.
The formula of force $ F = m \times a $
$ m $ is the mass and $ a $ is the acceleration.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are four airline baggage carts that are coupled as they look like a train.

If the total force is $ F $ for these four baggage carts, The formula of the force will be $ F = 4m \times a $
Given that, $ m = 250kg $ and $ a = 0.8\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}} $
$ \therefore F = 4 \times 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow F = 4 \times 250 \times \dfrac{8}{{10}} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 800N $
$ (a) $ Answer: $ 800N $
Let, the tension between A and B is, $ {T_{AB}} $ ,
the tension between B and C is, $ {T_{BC}} $ ,
The tension between C and D is, $ {T_{CD}} $ .
The tension between A and B is for the three baggage carts, hence $ {T_{AB}} = 3ma $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{AB}} = 3 \times 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{AB}} = 600N $
The tension between B and C is for the two baggage carts, hence $ {T_{BC}} = 2ma $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{BC}} = 2 \times 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{BC}} = 400N $
The tension between C and D is for the one baggage cart, hence $ {T_{CD}} = ma $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{CD}} = 250 \times 0.8 $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{CD}} = 200N $
$ (b) $ Answer:
$ \Rightarrow {T_{AB}} = 600N $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{BC}} = 400N $
$ \Rightarrow {T_{CD}} = 200N $ .
Note:
The tension is the force that is transferred through a cable, wire, or strings after it is stretched by forces acting from the opposite poles. The direction of it is along the length of the cable and pulls equally on the materials on the opposite poles of the wire or the string. The force is the product of the total mass of the existing materials and the acceleration of the system. Hence the force can cause the change in motion for an object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




