
Formula of acetic acid is:
A. $HCOOH$
B. $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$
C. $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
D. ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{7}}COOH$
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:. Acetic acid is classified as a carboxylic acid. The basic formula for any carboxylic acid group is $RCOOH$. The compound will be having a carboxyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
First let us look at the carboxylic acid groups that are present in acetic acid as well as other carboxylic acids.
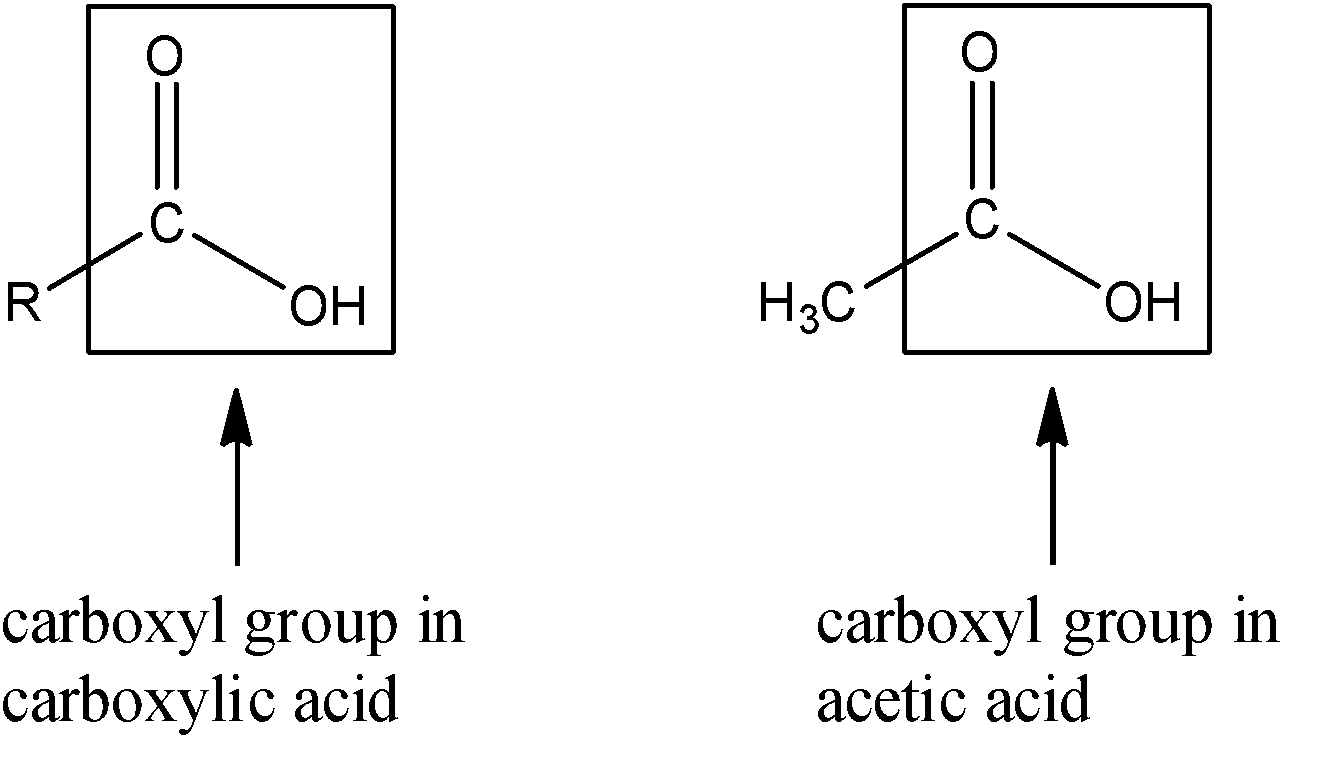
Acetic acid is considered as a part of the carboxylic acid homologous series since it has the group $-COOH$ present in the chemical structure. The carboxyl group is present in the longest chain of the acetic acid. Usually, all the organic molecules that contain the carboxyl group have ‘-oic acid’ added as a suffix after the name of the longest parent carbon chain is written.
The chemical name of acetic acid is ethanoic acid. The structure of acid contains the methyl and the carboxyl moiety. The methyl moiety contains 1 carbon atom along with 3 hydrogen atoms. The carboxyl moiety contains 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms and 1 hydrogen atom (1 oxygen and 1 hydrogen form the hydroxyl group). Since, thee compound has 2 carbon atoms, and the homologous series of alkanes contains ethane with 2 carbon atoms; the name of this compound is ethanoic acid.
Therefore, we can conclude that the formula of acetic Acid is $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
The preparation of acetic acid can be done by the oxidation of alcohols.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}}C{{H}_{3}}CHO\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}}C{{H}_{3}}COOH\]
Additional Information:
In the above equation, acetic acid is formed when Ethanol is converted into acetaldehyde in the presence of potassium dichromate and hydrogen ions. Acetaldehyde is then converted into Acetic acid in the presence of potassium dichromate and hydrogen ions. Basically, the alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde and then a carboxylic acid.
Only primary alcohols (carbon attached to alcohol group has 1 alkyl substituent) get oxidized to aldehydes and then acids. Secondary alcohols (carbon attached to alcohol group has 2 alkyl substituents) and tertiary alcohols (carbon attached to alcohol group has 3 alkyl substituents) are oxidized to ketones and then esters.
Note: When dissolved in water, acetic acid undergoes dissociation to form hydrogen $({{H}^{+}})$ ion. Because of the release of a proton, acetic acid has an acidic nature. It turns blue litmus paper red, indicating that it is acidic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
First let us look at the carboxylic acid groups that are present in acetic acid as well as other carboxylic acids.

Acetic acid is considered as a part of the carboxylic acid homologous series since it has the group $-COOH$ present in the chemical structure. The carboxyl group is present in the longest chain of the acetic acid. Usually, all the organic molecules that contain the carboxyl group have ‘-oic acid’ added as a suffix after the name of the longest parent carbon chain is written.
The chemical name of acetic acid is ethanoic acid. The structure of acid contains the methyl and the carboxyl moiety. The methyl moiety contains 1 carbon atom along with 3 hydrogen atoms. The carboxyl moiety contains 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms and 1 hydrogen atom (1 oxygen and 1 hydrogen form the hydroxyl group). Since, thee compound has 2 carbon atoms, and the homologous series of alkanes contains ethane with 2 carbon atoms; the name of this compound is ethanoic acid.
Therefore, we can conclude that the formula of acetic Acid is $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
The preparation of acetic acid can be done by the oxidation of alcohols.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}}C{{H}_{3}}CHO\xrightarrow[{{H}^{+}}]{{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}}C{{H}_{3}}COOH\]
Additional Information:
In the above equation, acetic acid is formed when Ethanol is converted into acetaldehyde in the presence of potassium dichromate and hydrogen ions. Acetaldehyde is then converted into Acetic acid in the presence of potassium dichromate and hydrogen ions. Basically, the alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde and then a carboxylic acid.
Only primary alcohols (carbon attached to alcohol group has 1 alkyl substituent) get oxidized to aldehydes and then acids. Secondary alcohols (carbon attached to alcohol group has 2 alkyl substituents) and tertiary alcohols (carbon attached to alcohol group has 3 alkyl substituents) are oxidized to ketones and then esters.
Note: When dissolved in water, acetic acid undergoes dissociation to form hydrogen $({{H}^{+}})$ ion. Because of the release of a proton, acetic acid has an acidic nature. It turns blue litmus paper red, indicating that it is acidic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




