
How was the formula for the area of a kite created?
Answer
534k+ views
Hint: A kite is a special type of quadrilateral that has a consecutive pair of sides equal while having opposite sides that are not equal.
Major properties of Kite involve:
I.Angles occurring at the point of joining unequal sides are the same.
II.It's longer diagonal bisect perpendicularly the shorter diagonal.
III.The longer diagonal divides the kite symmetrically, giving us two congruent triangles with IV.the common base being the longer diagonal itself.
The shorter diagonal provides us with two isosceles triangles from the kite.
Complete step by step solution:
To find the area of the kite, using the property 3 given in the hints, we will find the area of two triangles; ABD and CBD, which are actually congruent, giving us the areas also equal , then add them to get the final result for the formula of The Area of Kite.
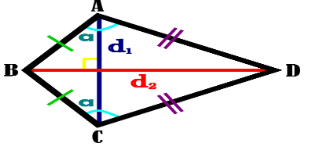
So, Area of Kite = Area of \[\Delta \,ABD\] + Area of \[\Delta \,CBD\] -------(1)
The \[\Delta \,ABD\] and \[\Delta \,CBD\] are congruent, then
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta ABD = \Delta \,CBD\]
Then equation (1) becomes
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of kite \[ = 2 \times \] Area of \[\Delta ABD\] ---------(2)
As we know, Area of \[\,\Delta ABD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\] .
In \[\Delta \,ABD\] base \[ = {d_2}\] and height \[ = \dfrac{{{d_1}}}{2}\] , then
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[\Delta ABD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_2} \times \dfrac{{{d_1}}}{2}\]
Finally, equation (2) becomes,
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of kite \[ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_2} \times \dfrac{{{d_1}}}{2}\]
On simplification we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d_2} \times {d_1}}}{2}\]
Hence, Area of the Kite is \[\dfrac{{{d_1} \times {d_2}}}{2}\] .
So, the correct answer is “ \[\dfrac{{{d_1} \times {d_2}}}{2}\] ”.
Note: To find the area of any given geometrical shape, we try to find simpler shapes in it such that we can find the area of these simpler shapes using the given numeric values, we can then evaluate the area of given geometry by applying basic operations like addition or subtraction or multiplication or division.
Similarly, to find the formula of any geometric shape, we assume some variables and then try to find the formula using the steps given in the above statement.
Major properties of Kite involve:
I.Angles occurring at the point of joining unequal sides are the same.
II.It's longer diagonal bisect perpendicularly the shorter diagonal.
III.The longer diagonal divides the kite symmetrically, giving us two congruent triangles with IV.the common base being the longer diagonal itself.
The shorter diagonal provides us with two isosceles triangles from the kite.
Complete step by step solution:
To find the area of the kite, using the property 3 given in the hints, we will find the area of two triangles; ABD and CBD, which are actually congruent, giving us the areas also equal , then add them to get the final result for the formula of The Area of Kite.

So, Area of Kite = Area of \[\Delta \,ABD\] + Area of \[\Delta \,CBD\] -------(1)
The \[\Delta \,ABD\] and \[\Delta \,CBD\] are congruent, then
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta ABD = \Delta \,CBD\]
Then equation (1) becomes
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of kite \[ = 2 \times \] Area of \[\Delta ABD\] ---------(2)
As we know, Area of \[\,\Delta ABD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\] .
In \[\Delta \,ABD\] base \[ = {d_2}\] and height \[ = \dfrac{{{d_1}}}{2}\] , then
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[\Delta ABD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_2} \times \dfrac{{{d_1}}}{2}\]
Finally, equation (2) becomes,
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of kite \[ = 2 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_2} \times \dfrac{{{d_1}}}{2}\]
On simplification we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d_2} \times {d_1}}}{2}\]
Hence, Area of the Kite is \[\dfrac{{{d_1} \times {d_2}}}{2}\] .
So, the correct answer is “ \[\dfrac{{{d_1} \times {d_2}}}{2}\] ”.
Note: To find the area of any given geometrical shape, we try to find simpler shapes in it such that we can find the area of these simpler shapes using the given numeric values, we can then evaluate the area of given geometry by applying basic operations like addition or subtraction or multiplication or division.
Similarly, to find the formula of any geometric shape, we assume some variables and then try to find the formula using the steps given in the above statement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





