
What is the formula for copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate?
Answer
481.8k+ views
Hint: Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is a chemical compound which is an ionic solid at ambient temperatures. It consists of copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ cations $ C{u^{2 + }} $ and carbonate anions $ CO_3^{2 - } $ . Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is a grey coloured ionic solid. It is a non-flammable compound.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is rarely confronted because it is very strenuous to prepare and reacts with water moisture of the air very rapidly. The terms “Copper carbonate”, “Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate” and “cupric carbonate” are referring to the basic copper carbonate.
The structure of Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is shown in the figure below:
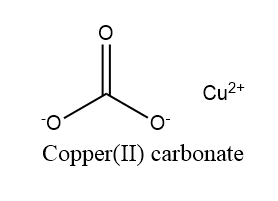
The Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate reacts very rapidly with water and air thus it is practically a monotonous process to prepare.
Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate can be yield by the reaction of copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ sulphate $ CuS{O_4} $ and sodium carbonate $ N{a_2}C{O_3} $ in ambient condition, produce instead a basic carbonate and $ C{O_2} $ , because of the great affinity of the $ C{u^{2 + }} $ ion for the hydroxide anion $ O{H^ - } $ .
W.F.T Pistorius in $ 1960 $ ; asserted synthesis by heating basic copper carbonate at $ {180^ \circ }C $ in the atmosphere of carbon dioxide and water for $ 36 $ hours. The proportions of the products were malachite $ C{u_2}C{O_3}{\left( {OH} \right)_2} $ , but small amount of rhombohedral substance was also formed, claimed $ CuC{O_3} $ . But this synthesis was apparently not reproduced.
The chemical formula of Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is $ CuC{O_3} $ which contain Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ cation $ C{u^{2 + }} $ and carbonate anion $ CO_3^{2 - } $ .
Note:
The stability of dry carbon $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate depends upon the partial pressure of carbon dioxide $ C{O_2} $ . It is stable for months in dry air however slowly decomposes into copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ oxide and carbon dioxide.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is rarely confronted because it is very strenuous to prepare and reacts with water moisture of the air very rapidly. The terms “Copper carbonate”, “Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate” and “cupric carbonate” are referring to the basic copper carbonate.
The structure of Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is shown in the figure below:

The Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate reacts very rapidly with water and air thus it is practically a monotonous process to prepare.
Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate can be yield by the reaction of copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ sulphate $ CuS{O_4} $ and sodium carbonate $ N{a_2}C{O_3} $ in ambient condition, produce instead a basic carbonate and $ C{O_2} $ , because of the great affinity of the $ C{u^{2 + }} $ ion for the hydroxide anion $ O{H^ - } $ .
W.F.T Pistorius in $ 1960 $ ; asserted synthesis by heating basic copper carbonate at $ {180^ \circ }C $ in the atmosphere of carbon dioxide and water for $ 36 $ hours. The proportions of the products were malachite $ C{u_2}C{O_3}{\left( {OH} \right)_2} $ , but small amount of rhombohedral substance was also formed, claimed $ CuC{O_3} $ . But this synthesis was apparently not reproduced.
The chemical formula of Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate is $ CuC{O_3} $ which contain Copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ cation $ C{u^{2 + }} $ and carbonate anion $ CO_3^{2 - } $ .
Note:
The stability of dry carbon $ \left( {II} \right) $ carbonate depends upon the partial pressure of carbon dioxide $ C{O_2} $ . It is stable for months in dry air however slowly decomposes into copper $ \left( {II} \right) $ oxide and carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




