
What is the formal charge on carbon atom in the following two structures are:
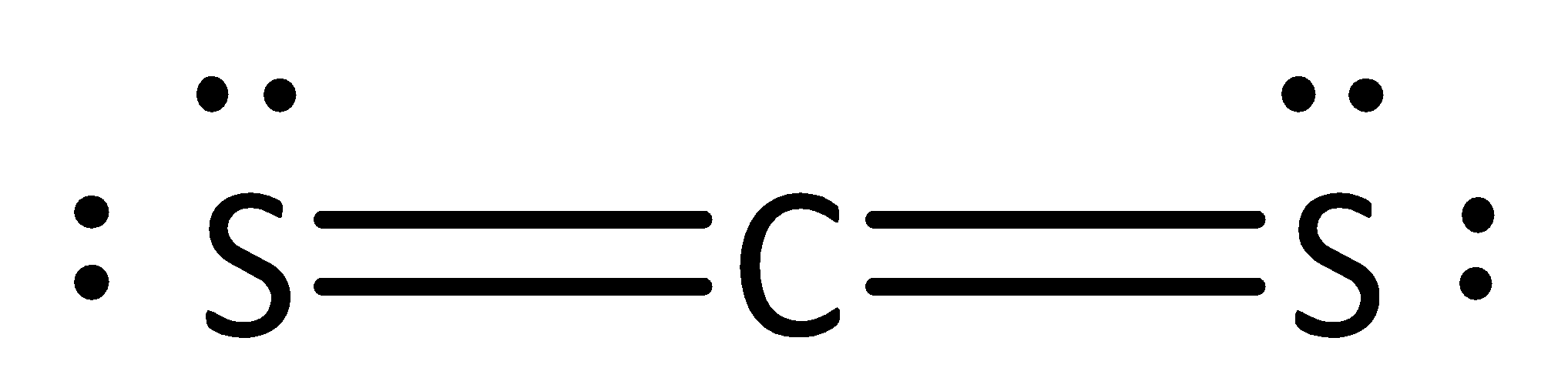
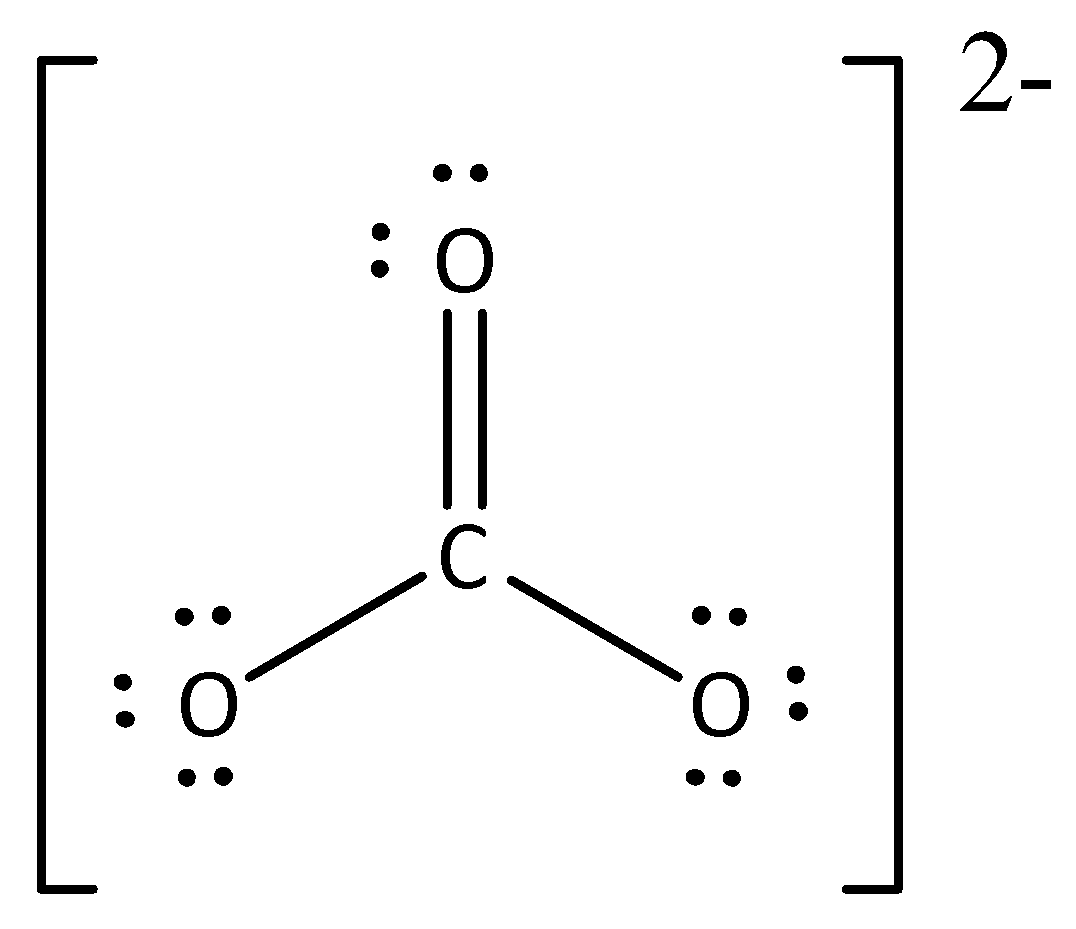
A. 0,-2
B. 0,0
C. +2,-2
D. +1,-1
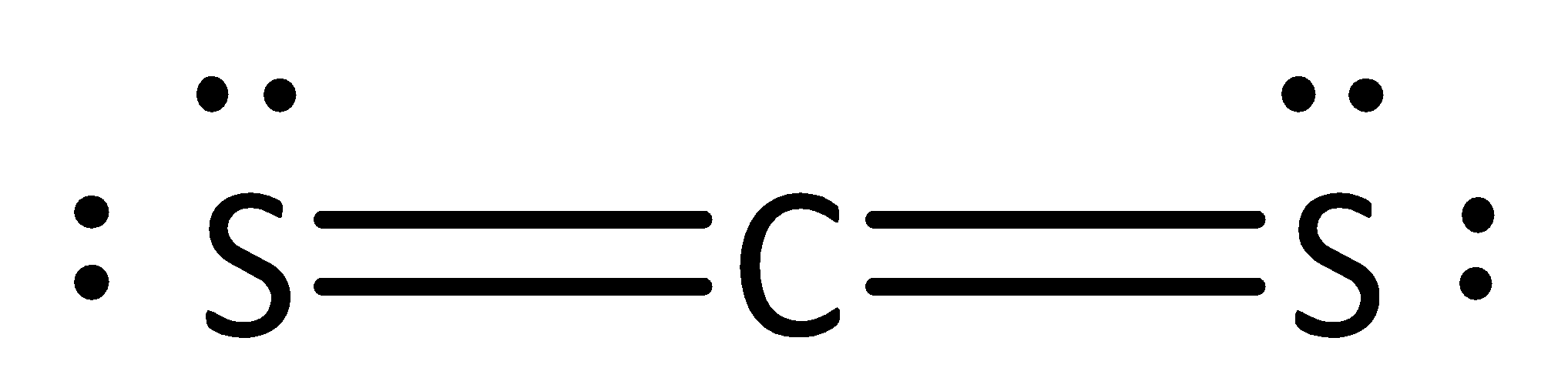

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: We also remember that the charges that are assigned to each atom in a molecule or ion by a set of arbitrary rules and don't actually represent the actual charges on the atoms are called formal charges.
We can calculate the formal charge using the formula,
${\text{F}}{\text{.C = Valence}}\,{\text{electrons - No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{non - bonding}}\,{\text{electrons - }}\dfrac{{{\text{No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{bonding}}\,{\text{electrons}}}}{{\text{2}}}$
The Lewis structure with zero formal charge or least separated formal charges is the preferred structure of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
The given Lewis formula is,
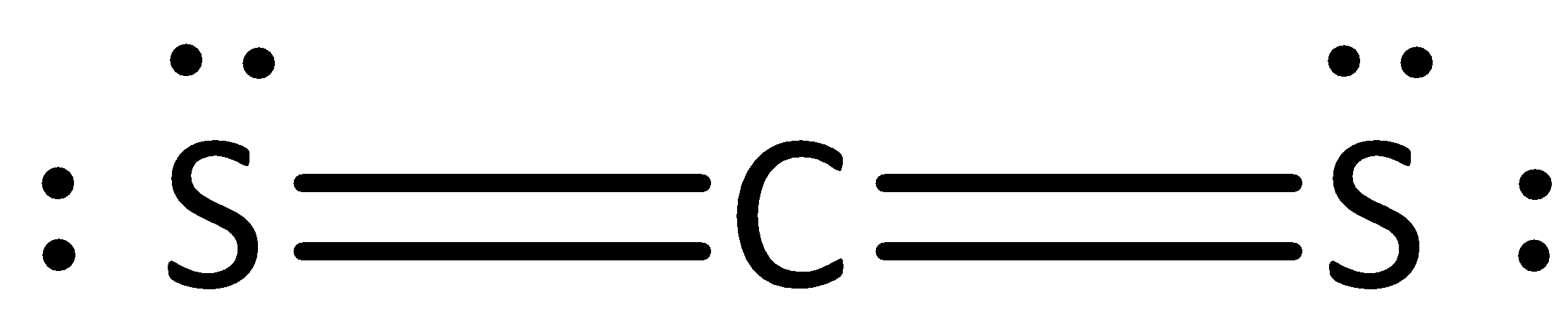
We know that the number of valence electrons in carbon is four.
In carbon disulfide, the number of nonbonding electrons (or) lone pairs in carbon is zero. In carbon disulfide, the number of bonding electrons is eight.
We can calculate the formal charge using the formula,
The formal charge for carbon atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on carbon= $4 - 0 - \dfrac{8}{2} = 4 - 0 - 4 = 0$
The formal charge for carbon atoms in carbon disulfide is zero.
The Lewis formula is,
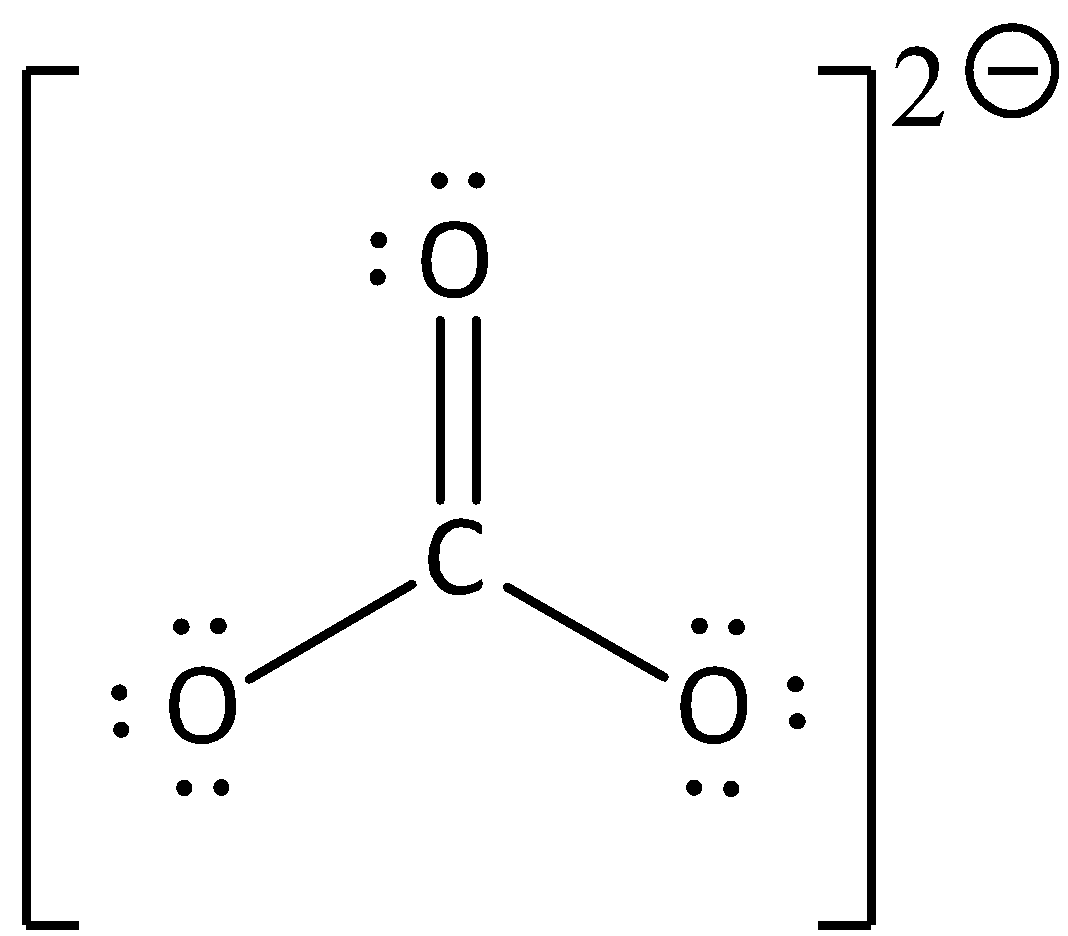
We know that the number of valence electrons in carbon is four.
In carbonate anion, the number of nonbonding electrons (or) lone pairs in carbon is zero.
In carbonate anion, the number of bonding electrons is eight.
We can calculate the formal charge using the formula,
The formal charge for carbon atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on carbon=$4 - 0 - \dfrac{8}{2} = 4 - 0 - 4 = 0$
The formal charge for carbon atom in carbonate anion is zero.
So, the correct answer is Option B .
Note:
Now we see the procedure to write Lewis structure: A Lewis structure shows a covalent bond as pair of electrons shared between two atoms.
Procedure to write Lewis formulas:
The symbols of the atoms that are bonded together in the molecule next to one another are arranged.
The total number of valence electrons in the molecule is calculated by adding the number of valence electrons for all the atoms in the molecules. If the species is an ion, then the charge of ions is taken into account by adding electrons, if it is a negative ion or subtracting electrons if it is a positive ion.
A two-electron covalent bond is represented by placing a line between the atoms, which are assumed to be bonded to each other.
The remaining valence electrons as lone pairs about each atom are arranged so that the octet rule is satisfied for each other.
For example: Draw the Lewis structure and formal charges of each atom in ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$
The total number of valence electrons in ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ is,
Number of valence electrons in sulphur=$\left( 1 \right)\left( 6 \right){\text{ = 6}}$ electrons
Number of valence electrons in fluorine=$\left( 4 \right)\left( 7 \right){\text{ = 28}}$ electrons
The total number of valence electrons is thirty-four.
One sulphur atom forms four bonds with fluorine that is eight electrons are used to form bonds and the remaining twenty-six electrons are used to satisfy the octet rule of atoms. More electrons are added to sulphur atoms, since it can expand the octet rule.
The Lewis formula is,
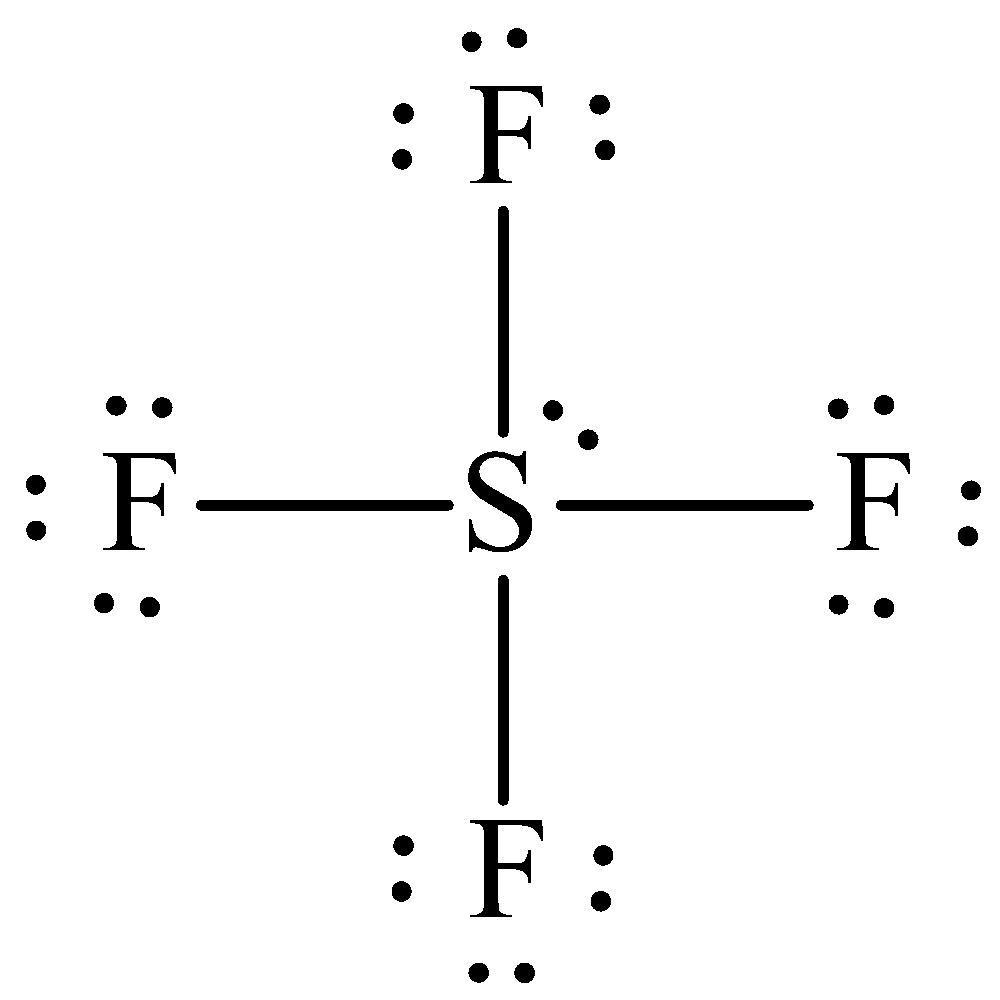
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on sulphur=${\text{6 - 2 - }}\dfrac{8}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 0}}$
Formula charge on fluorine=${\text{7 - 6 - }}\dfrac{{\text{2}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 0}}$.
We can calculate the formal charge using the formula,
${\text{F}}{\text{.C = Valence}}\,{\text{electrons - No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{non - bonding}}\,{\text{electrons - }}\dfrac{{{\text{No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{bonding}}\,{\text{electrons}}}}{{\text{2}}}$
The Lewis structure with zero formal charge or least separated formal charges is the preferred structure of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
The given Lewis formula is,
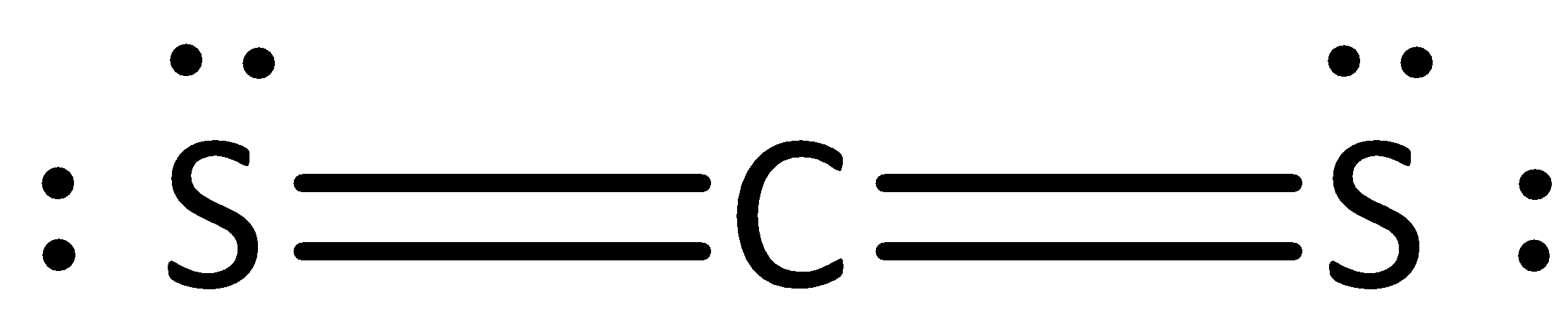
We know that the number of valence electrons in carbon is four.
In carbon disulfide, the number of nonbonding electrons (or) lone pairs in carbon is zero. In carbon disulfide, the number of bonding electrons is eight.
We can calculate the formal charge using the formula,
${\text{F}}{\text{.C = Valence}}\,{\text{electrons - No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{non - bonding}}\,{\text{electrons - }}\dfrac{{{\text{No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{bonding}}\,{\text{electrons}}}}{{\text{2}}}$
The formal charge for carbon atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on carbon= $4 - 0 - \dfrac{8}{2} = 4 - 0 - 4 = 0$
The formal charge for carbon atoms in carbon disulfide is zero.
The Lewis formula is,

We know that the number of valence electrons in carbon is four.
In carbonate anion, the number of nonbonding electrons (or) lone pairs in carbon is zero.
In carbonate anion, the number of bonding electrons is eight.
We can calculate the formal charge using the formula,
${\text{F}}{\text{.C = Valence}}\,{\text{electrons - No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{non - bonding}}\,{\text{electrons - }}\dfrac{{{\text{No}}\,{\text{of}}\,{\text{bonding}}\,{\text{electrons}}}}{{\text{2}}}$
The formal charge for carbon atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on carbon=$4 - 0 - \dfrac{8}{2} = 4 - 0 - 4 = 0$
The formal charge for carbon atom in carbonate anion is zero.
So, the correct answer is Option B .
Note:
Now we see the procedure to write Lewis structure: A Lewis structure shows a covalent bond as pair of electrons shared between two atoms.
Procedure to write Lewis formulas:
The symbols of the atoms that are bonded together in the molecule next to one another are arranged.
The total number of valence electrons in the molecule is calculated by adding the number of valence electrons for all the atoms in the molecules. If the species is an ion, then the charge of ions is taken into account by adding electrons, if it is a negative ion or subtracting electrons if it is a positive ion.
A two-electron covalent bond is represented by placing a line between the atoms, which are assumed to be bonded to each other.
The remaining valence electrons as lone pairs about each atom are arranged so that the octet rule is satisfied for each other.
For example: Draw the Lewis structure and formal charges of each atom in ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$
The total number of valence electrons in ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ is,
Number of valence electrons in sulphur=$\left( 1 \right)\left( 6 \right){\text{ = 6}}$ electrons
Number of valence electrons in fluorine=$\left( 4 \right)\left( 7 \right){\text{ = 28}}$ electrons
The total number of valence electrons is thirty-four.
One sulphur atom forms four bonds with fluorine that is eight electrons are used to form bonds and the remaining twenty-six electrons are used to satisfy the octet rule of atoms. More electrons are added to sulphur atoms, since it can expand the octet rule.
The Lewis formula is,

The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on sulphur=${\text{6 - 2 - }}\dfrac{8}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 0}}$
Formula charge on fluorine=${\text{7 - 6 - }}\dfrac{{\text{2}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 0}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




