
Force $F$ is gradually increased from zero. Determine whether the block will first slide or lift up?
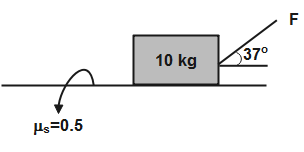

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: When an object just lifts up from the surface normal reaction on it becomes zero. Use the condition of horizontal and vertical equilibrium to determine the minimum force required for sliding and for lifting up the block. The case for which force F is lesser will occur first.
Complete step by step answer:
We first resolve the forces in horizontal and vertical directions.
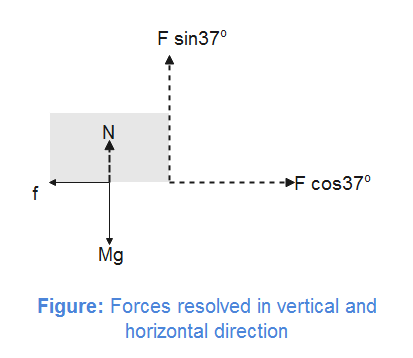
In vertical direction, gravitational force ($Mg$) is acting downward and sine components of force $F$ and normal reaction ($N$) are in upward direction. For vertical equilibrium,
$Mg=F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}+N$
Normal reaction on the block is
$N=Mg-F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
When the block lifts up from the surface, the normal reaction on it becomes zero and the equation becomes
$Mg=F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
From this equation, we can determine the minimum magnitude of force $F$ required to just lift the block. Solving the equation, we have
$F=\dfrac{Mg}{\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}}$
On substituting the values, we get the minimum value of force required to just lift the block
${{F}_{lift}}=\dfrac{10\times 10}{3/5}=\dfrac{500}{3}$
Similarly, frictional force ($f$) acts towards the left and cosine component of force $F$ acts in the right direction. For horizontal equilibrium,
$f=F\cos {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
This implies that
${{\mu }_{0}}N=F\cos {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
On substituting the values, we have
$0.5(100-F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }})=F\cos {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow 50=F(0.5\times \dfrac{3}{5}+\dfrac{4}{5})$
On solving, we get the minimum force required for the object to slide
${{F}_{slide}}=\dfrac{50}{\left( 11/10 \right)}=\dfrac{500}{11}$
We observe that the minimum force required for the block to slide is less than the minimum force required for the object to lift up. Therefore, the object will first slide before lifting up.
Note: When an object is just lifted up from the surface, the normal reaction acting on it becomes zero. The frictional force always acts opposite to the direction of motion.
To solve similar problems, we can use equations of motion and equilibrium equations.
Complete step by step answer:
We first resolve the forces in horizontal and vertical directions.

In vertical direction, gravitational force ($Mg$) is acting downward and sine components of force $F$ and normal reaction ($N$) are in upward direction. For vertical equilibrium,
$Mg=F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}+N$
Normal reaction on the block is
$N=Mg-F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
When the block lifts up from the surface, the normal reaction on it becomes zero and the equation becomes
$Mg=F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
From this equation, we can determine the minimum magnitude of force $F$ required to just lift the block. Solving the equation, we have
$F=\dfrac{Mg}{\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }}}$
On substituting the values, we get the minimum value of force required to just lift the block
${{F}_{lift}}=\dfrac{10\times 10}{3/5}=\dfrac{500}{3}$
Similarly, frictional force ($f$) acts towards the left and cosine component of force $F$ acts in the right direction. For horizontal equilibrium,
$f=F\cos {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
This implies that
${{\mu }_{0}}N=F\cos {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
On substituting the values, we have
$0.5(100-F\sin {{37}^{{}^\circ }})=F\cos {{37}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow 50=F(0.5\times \dfrac{3}{5}+\dfrac{4}{5})$
On solving, we get the minimum force required for the object to slide
${{F}_{slide}}=\dfrac{50}{\left( 11/10 \right)}=\dfrac{500}{11}$
We observe that the minimum force required for the block to slide is less than the minimum force required for the object to lift up. Therefore, the object will first slide before lifting up.
Note: When an object is just lifted up from the surface, the normal reaction acting on it becomes zero. The frictional force always acts opposite to the direction of motion.
To solve similar problems, we can use equations of motion and equilibrium equations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




