
Force between two objects of equal masses is F. If $25\% $ mass of one object is transferred to the other object, then the new force will be
$A.$ $\dfrac{F}{4}$
$B.$ $\dfrac{{3F}}{4}$
$C.$ $\dfrac{{15F}}{{16}}$
$D.$ $F$
Answer
522.3k+ views
Hint: Universal law of gravitation states that “the force of attraction between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centres of two masses”.
Formula used:
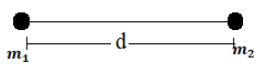
$F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$ $...\left( 1 \right)$
Where, $F = $ Gravitational force, $G = $Gravitational constant, ${m_1}$ and ${m_2}$ are masses and $d = $ Distance between centres of masses.
Complete step by step answer:
According to universal law of gravitation
$F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$$..................\left( 2 \right)$
Given: ${m_1} = {m_2} = m$ ($\because $ Two objects have equal masses)
Therefore equation $\left( 2 \right)$ becomes,
$F = \dfrac{{Gmm}}{{{d^2}}}$$....................(3)$
And also,
\[{F^1} = \dfrac{{Gm_1^1m_2^1}}{{{d^2}}}\]$................\left( 4 \right)$
According to the question,
$m_1^1 = 75{\raise0.5ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}\kern-0.1em/\kern-0.15em\lower0.25ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}}m \\
\Rightarrow m_1^1 = \dfrac{{75}}{{100}}m$$.............\left( 5 \right)$
And also,
$m_2^1 = 125{\raise0.5ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}\kern-0.1em/\kern-0.15em\lower0.25ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}}m \\
\Rightarrow m_2^1 = \dfrac{{125}}{{100}}m$ $..........\left( 6 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 5 \right)$ and equation$\left( 6 \right)$ in equation$\left( 4 \right)$,
\[{F^1} = \dfrac{{G\left( {\dfrac{{75}}{{100}}m} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{125}}{{100}}m} \right)}}{{{d^2}}}\]$.................(7)$
On simplifying above equation, we get
\[{F^1} = \left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{16}}} \right)\dfrac{{G\left( m \right)\left( m \right)}}{{{d^2}}}\]$.....................(8)$
Substituting equation$\left( 3 \right)$ in equation $\left( 8 \right)$, we get
\[\therefore {F^1} = \left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{16}}} \right)F\]
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Newton’s law of universal gravitation can also be stated as that every object in the universe will attract every other object. The value of Gravitational constant is \[6.67408{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}{10^{ - 11}}\;{m^3}\;k{g^{ - 1}}\;{s^{ - 2}}\]. Newton’s law of gravitation is similar to that of coulomb’s law in electrostatics which is used to obtain the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two charges
Formula used:
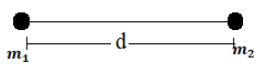
$F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$ $...\left( 1 \right)$
Where, $F = $ Gravitational force, $G = $Gravitational constant, ${m_1}$ and ${m_2}$ are masses and $d = $ Distance between centres of masses.
Complete step by step answer:
According to universal law of gravitation
$F = \dfrac{{G{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$$..................\left( 2 \right)$
Given: ${m_1} = {m_2} = m$ ($\because $ Two objects have equal masses)
Therefore equation $\left( 2 \right)$ becomes,
$F = \dfrac{{Gmm}}{{{d^2}}}$$....................(3)$
And also,
\[{F^1} = \dfrac{{Gm_1^1m_2^1}}{{{d^2}}}\]$................\left( 4 \right)$
According to the question,
$m_1^1 = 75{\raise0.5ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}\kern-0.1em/\kern-0.15em\lower0.25ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}}m \\
\Rightarrow m_1^1 = \dfrac{{75}}{{100}}m$$.............\left( 5 \right)$
And also,
$m_2^1 = 125{\raise0.5ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}\kern-0.1em/\kern-0.15em\lower0.25ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 0$}}m \\
\Rightarrow m_2^1 = \dfrac{{125}}{{100}}m$ $..........\left( 6 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 5 \right)$ and equation$\left( 6 \right)$ in equation$\left( 4 \right)$,
\[{F^1} = \dfrac{{G\left( {\dfrac{{75}}{{100}}m} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{125}}{{100}}m} \right)}}{{{d^2}}}\]$.................(7)$
On simplifying above equation, we get
\[{F^1} = \left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{16}}} \right)\dfrac{{G\left( m \right)\left( m \right)}}{{{d^2}}}\]$.....................(8)$
Substituting equation$\left( 3 \right)$ in equation $\left( 8 \right)$, we get
\[\therefore {F^1} = \left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{16}}} \right)F\]
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Newton’s law of universal gravitation can also be stated as that every object in the universe will attract every other object. The value of Gravitational constant is \[6.67408{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}{10^{ - 11}}\;{m^3}\;k{g^{ - 1}}\;{s^{ - 2}}\]. Newton’s law of gravitation is similar to that of coulomb’s law in electrostatics which is used to obtain the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two charges
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




