
For which of the following values of m is the area of the region bounded by the curve \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] and the line \[y=mx\] equal to \[\dfrac{9}{2}\] .
(A) -4
(B) -2
(C) 2
(D) 4
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Using the equation \[y=mx\] and \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] calculate the coordinates of the points of the intersection when the straight line and the given curve intersect each other. Now, consider that m is negative, \[m<0\] . The area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line is equal to the summation of the area of the curve with the positive x-axis and the area of the straight line with the positive x-axis. The area of the region is equal to \[\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx}-\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{mx}dx\] . Now, make it equal to \[\dfrac{9}{2}\] and calculate the value of m. Similarly, consider that m is positive, \[m>0\] . The area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line is equal to the subtraction of the area of the curve with the negative x-axis and the area of the straight line with the negative x-axis. The area of the region is equal to \[-\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{mx}dx-\left( -\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx} \right)\] . Now, make it equal to \[\dfrac{9}{2}\] and get the value of m.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have
The equation of the straight line is \[y=mx\] ……………………………..(1)
The equation of the curve is \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] ………………………………….(2)
First of all, we need to find the coordinates of the points of the intersection when the straight line and the given curve intersect each other.
Now, on substituting the value of y from equation (1) in equation (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow mx=x-{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+mx-x=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\left\{ x+\left( m-1 \right) \right\}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, \[x=0\] and \[x=\left( 1-m \right)\] ………………………………….(3)
In the question, we don’t have any information for the value of \[m\] . That is, \[m\] can be either positive or negative.
Let us consider that m is negative, \[m<0\] ………………………………(4)
Taking the above into consideration, the straight line \[y=mx\] will have a negative slope.
Now, on plotting the graph of the curve \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] and \[y=mx\] , we get
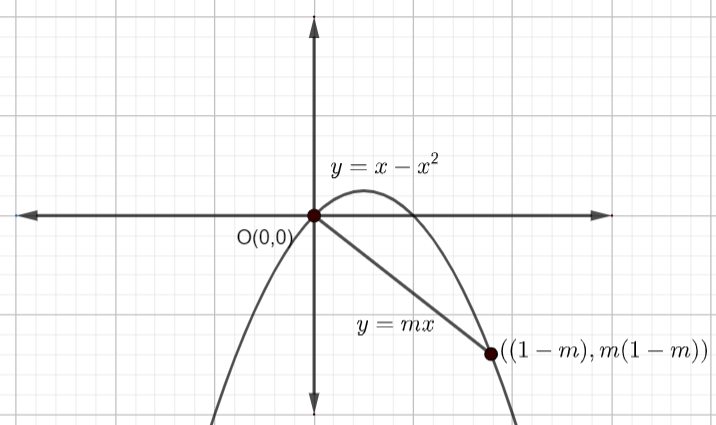
In the above figure, we can observe that the area between the curve and the straight line is equal to the summation of the area of the curve with the positive x-axis and area of the straight line with the positive x-axis …………………………………………..(5)
Since the straight line is below the x-axis so, the area of the straight line will be negative.
But, the area cannot be negative so, we have to include a negative sign before it.
The area of the straight line with the x-axis = \[-\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{mx}dx\] ………………………………..(6)
The area of the curve with the x-axis = \[\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)}dx\] ……………………………………..(7)
Now, from equation (5), equation (6), and equation (7), we get
The area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx}-\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{mx}dx\] ………………………(8)
On solving equation (8), we get
\[\begin{align}
& =\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}}-mx \right)dx} \\
& =\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( 1-m \right)x-{{x}^{2}}dx} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right){{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right]}_{0}}^{\left( 1-m \right)}-{{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right]}_{0}}^{\left( 1-m \right)} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right)\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \\
& =\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \\
& =\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}\] …………………………………(9)
But, in the question, we are given that the area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line is \[\dfrac{9}{2}\] ………………………………………….(10)
On comparing equation (9) and equation (10), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}=\dfrac{9}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}=27 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-m=3 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-3=m \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow -2=m\] ……………………………….(11)
Now, let us consider that m is positive, \[m>0\] ………………………………(12)
Taking the above into consideration, the straight line \[y=mx\] will have a positive slope.
Now, on plotting the graph of the curve \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] and \[y=mx\] , we get
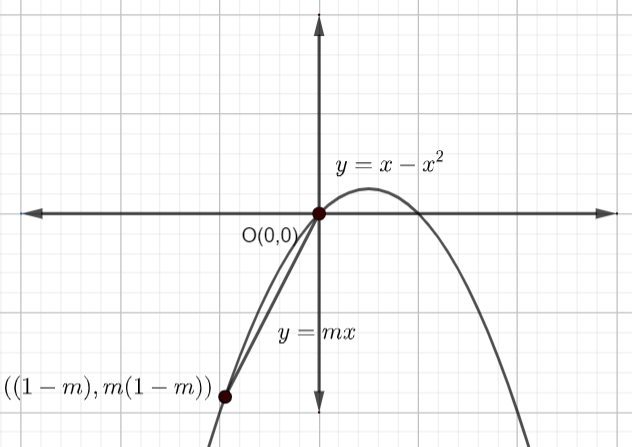
In the above figure, we can observe that the area between the curve and the straight line is equal to the subtraction of the area of the curve with the negative x-axis and area of the straight line with the negative x-axis …………………………………………..(12)
Since the straight line is below the x-axis so, the area of the straight line will be negative.
Similarly, the area of the given with the x-axis is also negative.
But, area cannot be negative so, we have to include a negative sign before them.
The area of the straight line with the x-axis = \[-\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{mx}dx\] ………………………………..(13)
The area of the curve with the x-axis = \[-\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)}dx\] ……………………………………..(14)
Now, from equation (12), equation (13), and equation (14), we get
The area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[-\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{mx}dx-\left( -\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx} \right)\] ………………………(15)
On solving equation (15), we get
\[\begin{align}
& =\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}}-mx \right)dx} \\
& =\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( 1-m \right)x-{{x}^{2}}dx} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right){{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right]}_{\left( 1-m \right)}}^{0}-{{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right]}_{\left( 1-m \right)}}^{0} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right)\left[ 0-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{2}}}{2} \right]-\left[ 0-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \right] \\
& =-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{2}+\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \\
& =-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}\] …………………………………(16)
On comparing equation (10) and equation (16), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}=\dfrac{9}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}=-27 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-m=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow 1+3=m \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow 4=m\] ……………………………….(17)
From equation (11) and equation (17), we have the values of \[m\] , \[m=-2\] and \[m=4\] .
Hence, the correct option is (B) and (D).
Note:
In this question, we have to remember one point. That is, the area of the curve below the x-axis with the x-axis is negative. But, the area cannot be negative. So, we add an additional negative sign before it to make the area a positive value.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have
The equation of the straight line is \[y=mx\] ……………………………..(1)
The equation of the curve is \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] ………………………………….(2)
First of all, we need to find the coordinates of the points of the intersection when the straight line and the given curve intersect each other.
Now, on substituting the value of y from equation (1) in equation (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow mx=x-{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+mx-x=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\left\{ x+\left( m-1 \right) \right\}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, \[x=0\] and \[x=\left( 1-m \right)\] ………………………………….(3)
In the question, we don’t have any information for the value of \[m\] . That is, \[m\] can be either positive or negative.
Let us consider that m is negative, \[m<0\] ………………………………(4)
Taking the above into consideration, the straight line \[y=mx\] will have a negative slope.
Now, on plotting the graph of the curve \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] and \[y=mx\] , we get

In the above figure, we can observe that the area between the curve and the straight line is equal to the summation of the area of the curve with the positive x-axis and area of the straight line with the positive x-axis …………………………………………..(5)
Since the straight line is below the x-axis so, the area of the straight line will be negative.
But, the area cannot be negative so, we have to include a negative sign before it.
The area of the straight line with the x-axis = \[-\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{mx}dx\] ………………………………..(6)
The area of the curve with the x-axis = \[\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)}dx\] ……………………………………..(7)
Now, from equation (5), equation (6), and equation (7), we get
The area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx}-\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{mx}dx\] ………………………(8)
On solving equation (8), we get
\[\begin{align}
& =\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}}-mx \right)dx} \\
& =\int_{0}^{\left( 1-m \right)}{\left( 1-m \right)x-{{x}^{2}}dx} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right){{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right]}_{0}}^{\left( 1-m \right)}-{{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right]}_{0}}^{\left( 1-m \right)} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right)\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \\
& =\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \\
& =\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}\] …………………………………(9)
But, in the question, we are given that the area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line is \[\dfrac{9}{2}\] ………………………………………….(10)
On comparing equation (9) and equation (10), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}=\dfrac{9}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}=27 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-m=3 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-3=m \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow -2=m\] ……………………………….(11)
Now, let us consider that m is positive, \[m>0\] ………………………………(12)
Taking the above into consideration, the straight line \[y=mx\] will have a positive slope.
Now, on plotting the graph of the curve \[y=x-{{x}^{2}}\] and \[y=mx\] , we get

In the above figure, we can observe that the area between the curve and the straight line is equal to the subtraction of the area of the curve with the negative x-axis and area of the straight line with the negative x-axis …………………………………………..(12)
Since the straight line is below the x-axis so, the area of the straight line will be negative.
Similarly, the area of the given with the x-axis is also negative.
But, area cannot be negative so, we have to include a negative sign before them.
The area of the straight line with the x-axis = \[-\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{mx}dx\] ………………………………..(13)
The area of the curve with the x-axis = \[-\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)}dx\] ……………………………………..(14)
Now, from equation (12), equation (13), and equation (14), we get
The area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[-\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{mx}dx-\left( -\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx} \right)\] ………………………(15)
On solving equation (15), we get
\[\begin{align}
& =\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( x-{{x}^{2}}-mx \right)dx} \\
& =\int_{\left( 1-m \right)}^{0}{\left( 1-m \right)x-{{x}^{2}}dx} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right){{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right]}_{\left( 1-m \right)}}^{0}-{{\left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right]}_{\left( 1-m \right)}}^{0} \\
& =\left( 1-m \right)\left[ 0-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{2}}}{2} \right]-\left[ 0-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \right] \\
& =-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{2}+\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{3} \\
& =-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the area of the region bounded between the curve and the straight line = \[-\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}\] …………………………………(16)
On comparing equation (10) and equation (16), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{{{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}}{6}=\dfrac{9}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 1-m \right)}^{3}}=-27 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-m=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow 1+3=m \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow 4=m\] ……………………………….(17)
From equation (11) and equation (17), we have the values of \[m\] , \[m=-2\] and \[m=4\] .
Hence, the correct option is (B) and (D).
Note:
In this question, we have to remember one point. That is, the area of the curve below the x-axis with the x-axis is negative. But, the area cannot be negative. So, we add an additional negative sign before it to make the area a positive value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




