
For what value of E the potential of A is equal to the potential of B?
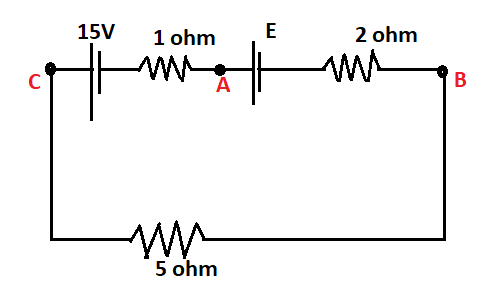

Answer
605.7k+ views
Hint: In this question we start with the KVL equation I the loop that is we get $ - I2 + E - I + 15 - 5I = 0$ but here two variables are present and only one equation is there so, we another condition that is given in the question which that the potential at A is equal to potential at point B and get ${V_B} - 2I + E = {V_A}$. Now by solving these two equations we get $I = \dfrac{{15}}{6}$and$E = 2 \times \dfrac{{15}}{6} = 5V$.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
First, we will find the current flowing in this circuit and for that let us assume a loop as shown in figure 2
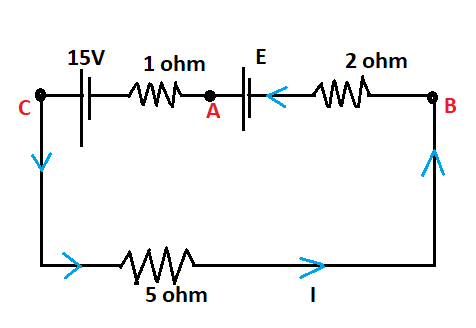
Now applying the Kirchhoff voltage law (KVL) in this loop that is the sum of all the potential differences is zero in a closed loop.
$ - I2 + E - I + 15 - 5I = 0$
$ \Rightarrow E + 15 = I8$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{E + 15}}{8}$-------------------------- (1)
We can see in equation (1) we have two variables and only one equation, so we need to find one more equation to get the values of the two variables.
Now it is given that the potential at A is equal to the potential at point B that is
${V_A} = {V_B}$
$ \Rightarrow \left| {{V_A} - {V_B}} \right| = 0$
So the potential difference across A and B is zero that is
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} - 2I + E = {V_A}$
$ \Rightarrow - 2I + E = {V_A} - {V_B}$
$ \Rightarrow - 2I + E = 0$
$ \Rightarrow E = 2I$--------------------------- (2)
Now substituting the equation (2) in equation (1) we get
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2I + 15}}{8}$
$ \Rightarrow 8I = 2I + 15$
\[ \Rightarrow 8I - 2I = 6I = 15\]
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{15}}{6}$------------------------------ (3)
Substituting equation (3) in equation (2) we will get
$ \Rightarrow E = 2 \times \dfrac{{15}}{6} = 5V$
Hence the required value of E is 5V which will make the potential at A and potential at B equal.
Note: For these types of question we need to know about the basics of KVL and KCL that is the Kirchhoff voltage law which state that the sum of all the potential drop in a loop will be zero and the Kirchhoff current law which state that the sum of all the current either incoming or outgoing at a node is zero. After these, we need to know the sign conventions so that we can write the equation properly.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
First, we will find the current flowing in this circuit and for that let us assume a loop as shown in figure 2

Figure 2
Now applying the Kirchhoff voltage law (KVL) in this loop that is the sum of all the potential differences is zero in a closed loop.
$ - I2 + E - I + 15 - 5I = 0$
$ \Rightarrow E + 15 = I8$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{E + 15}}{8}$-------------------------- (1)
We can see in equation (1) we have two variables and only one equation, so we need to find one more equation to get the values of the two variables.
Now it is given that the potential at A is equal to the potential at point B that is
${V_A} = {V_B}$
$ \Rightarrow \left| {{V_A} - {V_B}} \right| = 0$
So the potential difference across A and B is zero that is
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} - 2I + E = {V_A}$
$ \Rightarrow - 2I + E = {V_A} - {V_B}$
$ \Rightarrow - 2I + E = 0$
$ \Rightarrow E = 2I$--------------------------- (2)
Now substituting the equation (2) in equation (1) we get
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2I + 15}}{8}$
$ \Rightarrow 8I = 2I + 15$
\[ \Rightarrow 8I - 2I = 6I = 15\]
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{15}}{6}$------------------------------ (3)
Substituting equation (3) in equation (2) we will get
$ \Rightarrow E = 2 \times \dfrac{{15}}{6} = 5V$
Hence the required value of E is 5V which will make the potential at A and potential at B equal.
Note: For these types of question we need to know about the basics of KVL and KCL that is the Kirchhoff voltage law which state that the sum of all the potential drop in a loop will be zero and the Kirchhoff current law which state that the sum of all the current either incoming or outgoing at a node is zero. After these, we need to know the sign conventions so that we can write the equation properly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




