
For undergoing glycolysis, glucose requires priming with the help of how many ATP?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: Glycolysis is part of the cellular respiration that takes place in the cytoplasm of all living organisms to release energy in the form of ATP. But before the release of ATP, few ATPs are utilized by glucose to add a phosphate group to it (priming) .
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Glycolysis is a respiratory pathway operating to partially oxidize glucose to pyruvic acid with a net gain of 2 ATPs. This pathway is also known as the EMP pathway named after its discoverers Embden, Meyerhof, and Parnas. It is a 10 steps process that is catalyzed by different enzymes at each step.
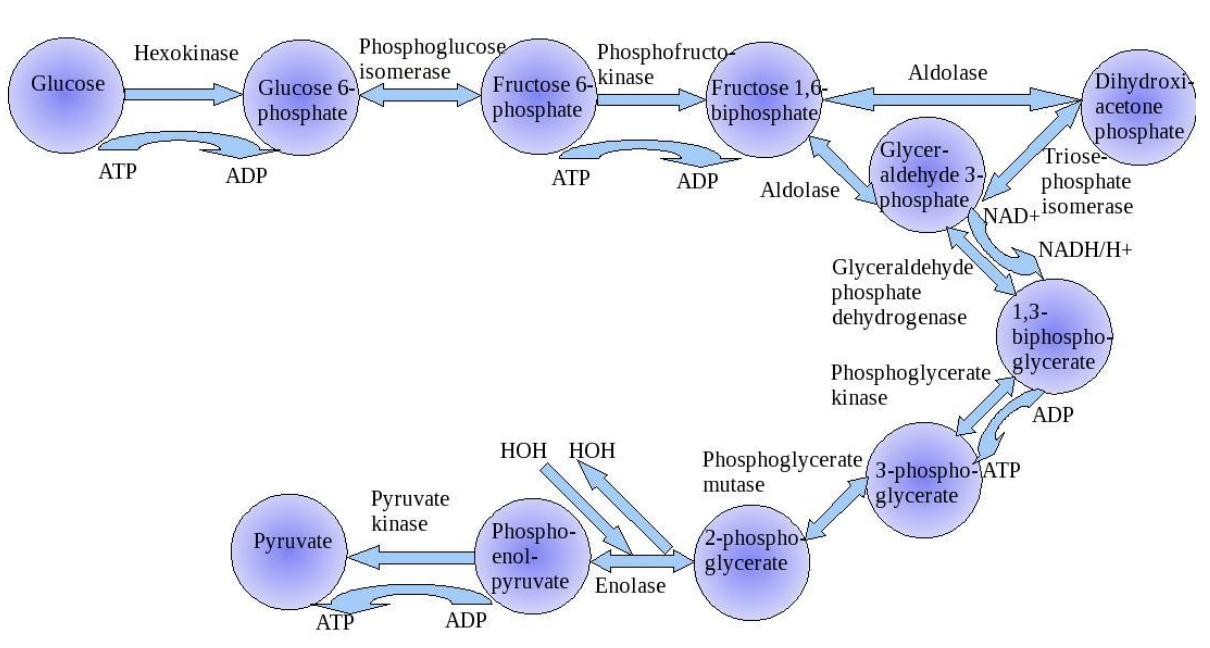
The priming of glucose with the utilization of ATP is done in 2 steps.
- For the conversion of glucose into glucose 6-phosphate.
- For the conversion of fructose 6- phosphate into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
So, the correct answer is ‘2’.
Additional information:
Now let us learn about the steps where the production of ATP takes place.
- The conversion of 1,3 bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPGA) into 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) is an energy- yielding process and gives 1 ATP. 2 molecules of BPGA are there so 2 ATP.
- Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvic acid gives 1 ATP. 2 molecules of PEP so 2 ATP.
In total 4 ATP are produced and 2 ATP are consumed. So, the net gain of ATP in glycolysis is 2 ATP.
Note:
- Glycolysis is followed by link reaction, Kreb’s cycle, and Electron transport chain ETS in aerobic organisms.
- In anaerobic organisms, the pyruvic acid is converted either into lactic acid (muscle cells) or ethanol (yeast) with the release of 2 ATPs. This happens in the absence of oxygen and is known as fermentation.
- In glycolysis, 2 NADH molecules are also produced which are then converted into ATP through the process of ETS.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Glycolysis is a respiratory pathway operating to partially oxidize glucose to pyruvic acid with a net gain of 2 ATPs. This pathway is also known as the EMP pathway named after its discoverers Embden, Meyerhof, and Parnas. It is a 10 steps process that is catalyzed by different enzymes at each step.

The priming of glucose with the utilization of ATP is done in 2 steps.
- For the conversion of glucose into glucose 6-phosphate.
- For the conversion of fructose 6- phosphate into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
So, the correct answer is ‘2’.
Additional information:
Now let us learn about the steps where the production of ATP takes place.
- The conversion of 1,3 bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPGA) into 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) is an energy- yielding process and gives 1 ATP. 2 molecules of BPGA are there so 2 ATP.
- Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvic acid gives 1 ATP. 2 molecules of PEP so 2 ATP.
In total 4 ATP are produced and 2 ATP are consumed. So, the net gain of ATP in glycolysis is 2 ATP.
Note:
- Glycolysis is followed by link reaction, Kreb’s cycle, and Electron transport chain ETS in aerobic organisms.
- In anaerobic organisms, the pyruvic acid is converted either into lactic acid (muscle cells) or ethanol (yeast) with the release of 2 ATPs. This happens in the absence of oxygen and is known as fermentation.
- In glycolysis, 2 NADH molecules are also produced which are then converted into ATP through the process of ETS.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




