
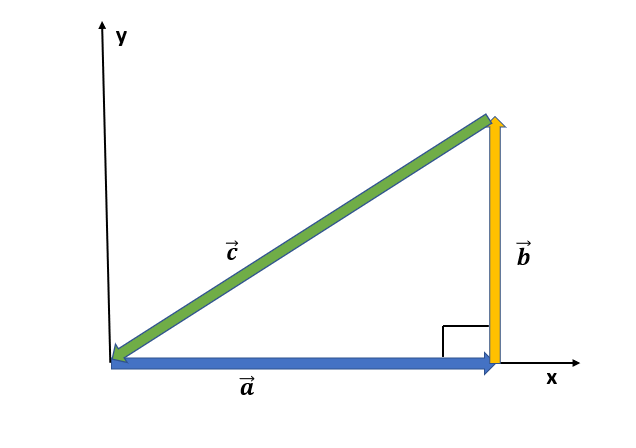
For the vector in fig., with $a = 4$, $b = 3$ and $c = 5$, what are (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction of $\vec{a} \times \vec{c}$ (c) the magnitude and (d) the direction of $\vec{a} \times \vec{b}$, and the magnitude and (f) the direction of $\vec{b} \times \vec{c}$(the z-axis is not shown)

Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: Cross product is a binary procedure on two vectors in $3-D$ space. Given two linearly independent vectors, a and b, the cross product of a and b is a perpendicular vector to both a and b. If two vectors have the identical direction or have the opposite direction from one another or have zero length, then their vector product is zero.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given: $|\vec{a}| = 4$, $|\vec{b}| = 3$, $|\vec{c}| = 5$
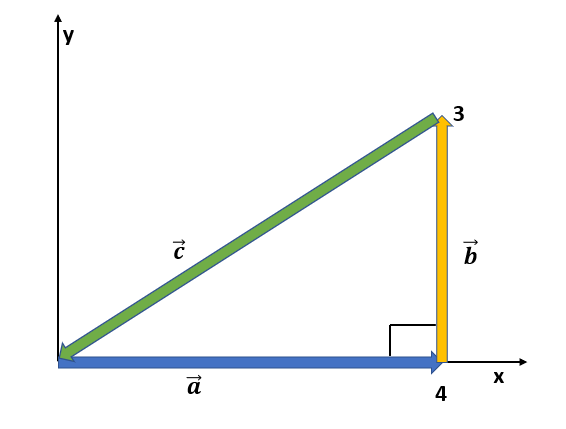
From figure, $\vec{a} = 4 \hat{i}$, $\vec{b} = 3 \hat{j}$ and $\vec{c} = 4 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}$
a) First, we find the magnitude of $\vec{a} \times \vec{c}$,
$\vec{a} \times \vec{c} = 4 \hat{i} \times (4 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}) $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{c} = 16 (\hat{i} \times \hat{i}) + 12 (\hat{i} \times \hat{j}) $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{c} = 12 \hat{k} $
b) The direction of $\vec{a} \times \vec{c}$ is $\hat{k}$.
c) Now, we find the magnitude $\vec{a} \times \vec{b}$,
$\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 4 \hat{i} \times 3 \hat{j} $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 12 (\hat{i} \times \hat{j}) $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 12 \hat{k} $
d) The direction of $\vec{a} \times \vec{b}$ is $\hat{k}$.
e) First, we find the magnitude of $\vec{b} \times \vec{c}$
$\vec{b} \times \vec{c} = 3 \hat{j} \times (4 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}) $
$\vec{b} \times \vec{c} = 12 (\hat{j} \times \hat{i}) + 9 (\hat{j} \times \hat{j}) $
$\vec{b} \times \vec{c} = -12 \hat{k} $
f) The direction of $\vec{b} \times \vec{c}$ is $\hat{-k}$.
Note:More commonly, the magnitude of the cross product is equal to the area of a parallelogram with vectors for sides; in particular, the magnitude of the product of two perpendicular vectors is the product of their lengths. The right-hand thumb rule is utilized in which we turn up the fingers of the right hand about a line perpendicular to the vectors planes a and b and fold the fingers in the way from a to b, then the extended thumb points in the way of c.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given: $|\vec{a}| = 4$, $|\vec{b}| = 3$, $|\vec{c}| = 5$

From figure, $\vec{a} = 4 \hat{i}$, $\vec{b} = 3 \hat{j}$ and $\vec{c} = 4 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}$
a) First, we find the magnitude of $\vec{a} \times \vec{c}$,
$\vec{a} \times \vec{c} = 4 \hat{i} \times (4 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}) $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{c} = 16 (\hat{i} \times \hat{i}) + 12 (\hat{i} \times \hat{j}) $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{c} = 12 \hat{k} $
b) The direction of $\vec{a} \times \vec{c}$ is $\hat{k}$.
c) Now, we find the magnitude $\vec{a} \times \vec{b}$,
$\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 4 \hat{i} \times 3 \hat{j} $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 12 (\hat{i} \times \hat{j}) $
$\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = 12 \hat{k} $
d) The direction of $\vec{a} \times \vec{b}$ is $\hat{k}$.
e) First, we find the magnitude of $\vec{b} \times \vec{c}$
$\vec{b} \times \vec{c} = 3 \hat{j} \times (4 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}) $
$\vec{b} \times \vec{c} = 12 (\hat{j} \times \hat{i}) + 9 (\hat{j} \times \hat{j}) $
$\vec{b} \times \vec{c} = -12 \hat{k} $
f) The direction of $\vec{b} \times \vec{c}$ is $\hat{-k}$.
Note:More commonly, the magnitude of the cross product is equal to the area of a parallelogram with vectors for sides; in particular, the magnitude of the product of two perpendicular vectors is the product of their lengths. The right-hand thumb rule is utilized in which we turn up the fingers of the right hand about a line perpendicular to the vectors planes a and b and fold the fingers in the way from a to b, then the extended thumb points in the way of c.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




