
For the reaction, of the first order, variation of $ \log \,{{T}_{50}} $ with $ \log a $ (where $ {{T}_{50}} $ is half-life period and $ a $ is the initial concentration) is given by
A)
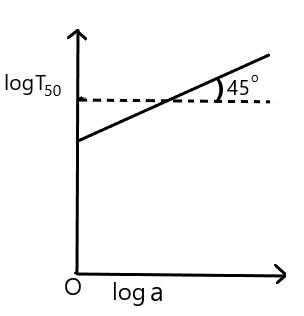
B)
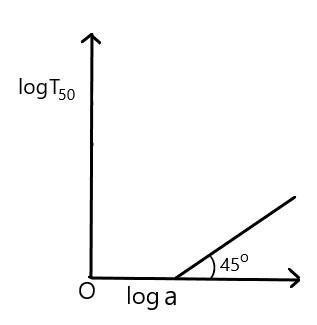
C)
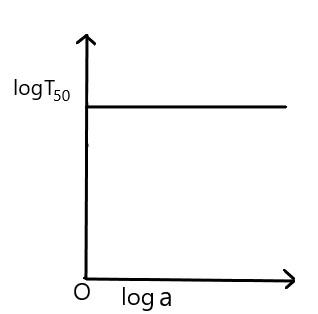
D)
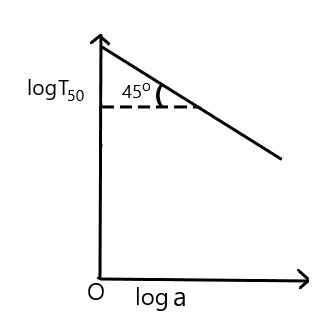




Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint :Half – life in chemical kinetics is defined as the time that is taken by the concentration of the reactant to reach half of its initial value. Half – life is denoted with a symbol, $ {{t}_{1/2}} $ . It is expressed in seconds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First order reaction is a unimolecular reaction that contains only one reactant. The rate of reaction varies with the change in the concentration of only one reactant. Therefore, the order of the reaction is equal to one.
To calculate the variation of $ \log {{T}_{50}} $ with $ \log a $ , first we have to see a formula,
$ {{T}_{50}}=\dfrac{{{2}^{n-1}}-1}{{{\left( a \right)}^{n-1}}\left( n-1 \right)k} $
As we can see that,
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\alpha \dfrac{1}{{{\left( a \right)}^{n-1}}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\alpha \dfrac{1}{{{\left( a \right)}^{1-1}}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\alpha 1 $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\ne a $
If $ n=1 $
The increase and decrease in the initial concentration $ \left( a \right) $ will show the value of $ {{T}_{50}} $ equal to constant.
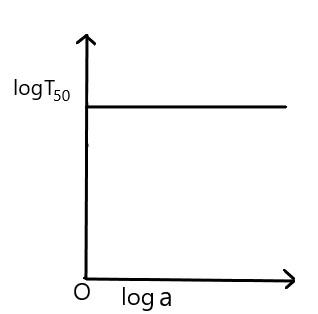
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Additional Information:
The rate of chemical reaction is defined as the speed at which a chemical reaction is moving forward.
The factors that affect the rate of a reaction are:
Surface area – is directly proportional to the rate of reaction. Increasing the surface area of a reactant increases the rate of reaction.
Temperature – is also directly proportional to the rate of reaction.
Reactant concentration: Increasing the concentration of a reactant increases the rate of reaction.
Note :
First order reaction is defined as a reaction that only depends on the concentration of one reactant.
In this question, we have discussed the variation of $ \log {{T}_{50}} $ and $ \log a $ in first order reaction. The increase and decrease in the initial concentration does not show any change in the value of half life, it remains constant.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First order reaction is a unimolecular reaction that contains only one reactant. The rate of reaction varies with the change in the concentration of only one reactant. Therefore, the order of the reaction is equal to one.
To calculate the variation of $ \log {{T}_{50}} $ with $ \log a $ , first we have to see a formula,
$ {{T}_{50}}=\dfrac{{{2}^{n-1}}-1}{{{\left( a \right)}^{n-1}}\left( n-1 \right)k} $
As we can see that,
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\alpha \dfrac{1}{{{\left( a \right)}^{n-1}}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\alpha \dfrac{1}{{{\left( a \right)}^{1-1}}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\alpha 1 $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {{T}_{50}}\ne a $
If $ n=1 $
The increase and decrease in the initial concentration $ \left( a \right) $ will show the value of $ {{T}_{50}} $ equal to constant.

Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Additional Information:
The rate of chemical reaction is defined as the speed at which a chemical reaction is moving forward.
The factors that affect the rate of a reaction are:
Surface area – is directly proportional to the rate of reaction. Increasing the surface area of a reactant increases the rate of reaction.
Temperature – is also directly proportional to the rate of reaction.
Reactant concentration: Increasing the concentration of a reactant increases the rate of reaction.
Note :
First order reaction is defined as a reaction that only depends on the concentration of one reactant.
In this question, we have discussed the variation of $ \log {{T}_{50}} $ and $ \log a $ in first order reaction. The increase and decrease in the initial concentration does not show any change in the value of half life, it remains constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




