
For the given aqueous reactions, which of the following statements is/are true?
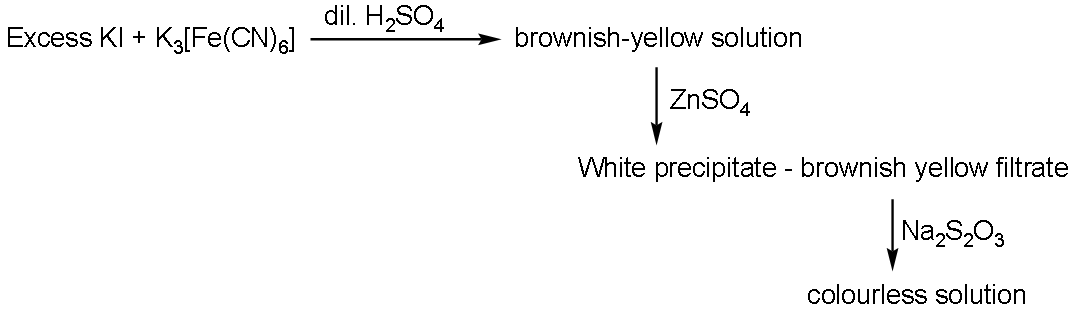
A. The first reaction is a redox reaction
B. White precipitate is \[\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}\]
C. Addition of the filtrate to the starch solution gives a blue colour
D. White precipitate is soluble in NaOH solution.

Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: For this problem, we have to write the reaction of each step by writing the molecular formula of each compound so that we can determine the molecular formula of each product and then choose the correct answer.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given question, we have to determine the correct statements about the given reactions.
- As we know that redox reactions are the reactions in which both oxidation and reduction reactions take place.
- Now, in the first reaction that is shown below:
$\text{KI + }{{\text{K}}_{3}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)\text{ }\to \text{ K}{{\text{I}}_{3}}\text{ + }{{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)$
- So, as we can see that here iron is reduced from $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{+3}}\text{ to F}{{\text{e}}^{2+}}$ and the iodine is oxidised from ${{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{ to I}_{3}^{-}$.
- So, we can say that the statement is A is correct.
- Now, we can see that the compound ${{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)$ which is formed in the first step has a brownish yellow colour.
- When ${{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)$ reacts with zinc sulphate then it yields a white precipitate complex as shown below:
${{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)\text{ + K}{{\text{I}}_{3}}\text{ + ZnS}{{\text{O}}_{4}}\text{ }\to \text{ }{{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}\text{ + I}_{3}^{-}\text{ + }{{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$
- Here, the brownish colour of the solution is due to the formation of $\text{I}_{3}^{-}$ whereas the white precipitate formed is due to ${{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}$ complex.
- So, statement B is incorrect.
- Now, when we add this filtrate of this white precipitate then it will give a blue colour solution whereas the iodine ion is added in $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}{{\text{S}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$ then it gives a colourless solution.
${{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}\text{ + Starch }\to \text{ Blue colour solution}$
$\text{I}_{3}^{-}\text{ + N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}{{\text{S}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{ }\to \text{ colourless solution}$
- So, statement C is also correct.
- Now, the white precipitate formed is also soluble in sodium hydroxide as it gives two complex ions as shown:
${{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}\text{ + NaOH }\to \text{ Zn}{{\left( \text{O}{{\text{H}}_{6}} \right)}^{-2}}\text{ + }{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}^{-4}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A, C and D”.
Note: The oxidation state of iron decreases from $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{+3}}\text{ to F}{{\text{e}}^{2+}}$as the oxidation of $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{3+}}$ is +3 and the oxidation of $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{2+}}$ is +2. Whereas the oxidation state of iodine increases from ${{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{ to I}_{3}^{-}$. As the oxidation state of ${{\text{I}}^{-}}$ is -1 and oxidation state of $\text{I}_{3}^{-}$ is -1/3.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given question, we have to determine the correct statements about the given reactions.
- As we know that redox reactions are the reactions in which both oxidation and reduction reactions take place.
- Now, in the first reaction that is shown below:
$\text{KI + }{{\text{K}}_{3}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)\text{ }\to \text{ K}{{\text{I}}_{3}}\text{ + }{{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)$
- So, as we can see that here iron is reduced from $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{+3}}\text{ to F}{{\text{e}}^{2+}}$ and the iodine is oxidised from ${{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{ to I}_{3}^{-}$.
- So, we can say that the statement is A is correct.
- Now, we can see that the compound ${{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)$ which is formed in the first step has a brownish yellow colour.
- When ${{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)$ reacts with zinc sulphate then it yields a white precipitate complex as shown below:
${{\text{K}}_{4}}\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)\text{ + K}{{\text{I}}_{3}}\text{ + ZnS}{{\text{O}}_{4}}\text{ }\to \text{ }{{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}\text{ + I}_{3}^{-}\text{ + }{{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$
- Here, the brownish colour of the solution is due to the formation of $\text{I}_{3}^{-}$ whereas the white precipitate formed is due to ${{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}$ complex.
- So, statement B is incorrect.
- Now, when we add this filtrate of this white precipitate then it will give a blue colour solution whereas the iodine ion is added in $\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}{{\text{S}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{3}}$ then it gives a colourless solution.
${{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}\text{ + Starch }\to \text{ Blue colour solution}$
$\text{I}_{3}^{-}\text{ + N}{{\text{a}}_{2}}{{\text{S}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{ }\to \text{ colourless solution}$
- So, statement C is also correct.
- Now, the white precipitate formed is also soluble in sodium hydroxide as it gives two complex ions as shown:
${{\text{K}}_{2}}\text{Z}{{\text{n}}_{3}}{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}_{2}}\text{ + NaOH }\to \text{ Zn}{{\left( \text{O}{{\text{H}}_{6}} \right)}^{-2}}\text{ + }{{\left( \text{Fe(CN}{{\text{)}}_{6}} \right)}^{-4}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A, C and D”.
Note: The oxidation state of iron decreases from $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{+3}}\text{ to F}{{\text{e}}^{2+}}$as the oxidation of $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{3+}}$ is +3 and the oxidation of $\text{F}{{\text{e}}^{2+}}$ is +2. Whereas the oxidation state of iodine increases from ${{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{ to I}_{3}^{-}$. As the oxidation state of ${{\text{I}}^{-}}$ is -1 and oxidation state of $\text{I}_{3}^{-}$ is -1/3.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




