
For the formation of urea, which one of the following is required along with ammonia?
(A)Arginase, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and ${ O }_{ 2 }$
(B)Arginase, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and water
(C)Aspartate, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and water
(D)Aspartate, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and ${ O }_{ 2 }$
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The urea cycle is the characteristic of ureotelic organisms. It requires the transfer of its metabolites from the citric acid cycle. Urea is synthesized in our body by the Urea cycle or Ornithine cycle. It requires ammonia, a gas which we expel, and water, energy, and manganese-containing enzymes.
Complete answer:
The urea cycle is the process of formation of urea in the liver from the highly toxic ammonia for elimination. It is regarded as the first metabolic cycle to be discovered by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit in 1932. Urea is synthesized in our body by the Urea cycle or Ornithine cycle. It requires ammonia, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and water, ATP, and Arginase.
Additional Information: The steps involved in the urea cycle are-
-Firstly, the Carbamoyl phosphate gets converted into citrulline with the help of the enzyme ornithine transcarbamoylase. This is the rate-limiting step and takes place in the mitochondria while the rest of the steps occur in the cytoplasm.
-Then, aspartate reacts with the carbamoyl group of citrulline to form argininosuccinate with the help of the enzyme argininosuccinate synthetase.
-Argininosuccinate then breaks into arginine and fumarates by the enzyme argininosuccinase.
-Finally, arginine gets cleaved by the enzyme arginase to form urea and ornithine.
The urea is released into the blood for elimination and ornithine is sent back to mitochondria to participate in the next cycle.
So, the correct answer is ‘Arginase, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and water’.
Note: -The urea cycle is connected with the citric acid cycle. The aspartate of the urea cycle is formed by transamination from oxaloacetate and the fumarate formed in the urea cycle as an intermediate is transported to participate in the citric acid cycle.
-It results in the release of two NADH molecules which is used to produce energy.
-The rate-limiting step determines the overall speed and other parameters of a reaction.
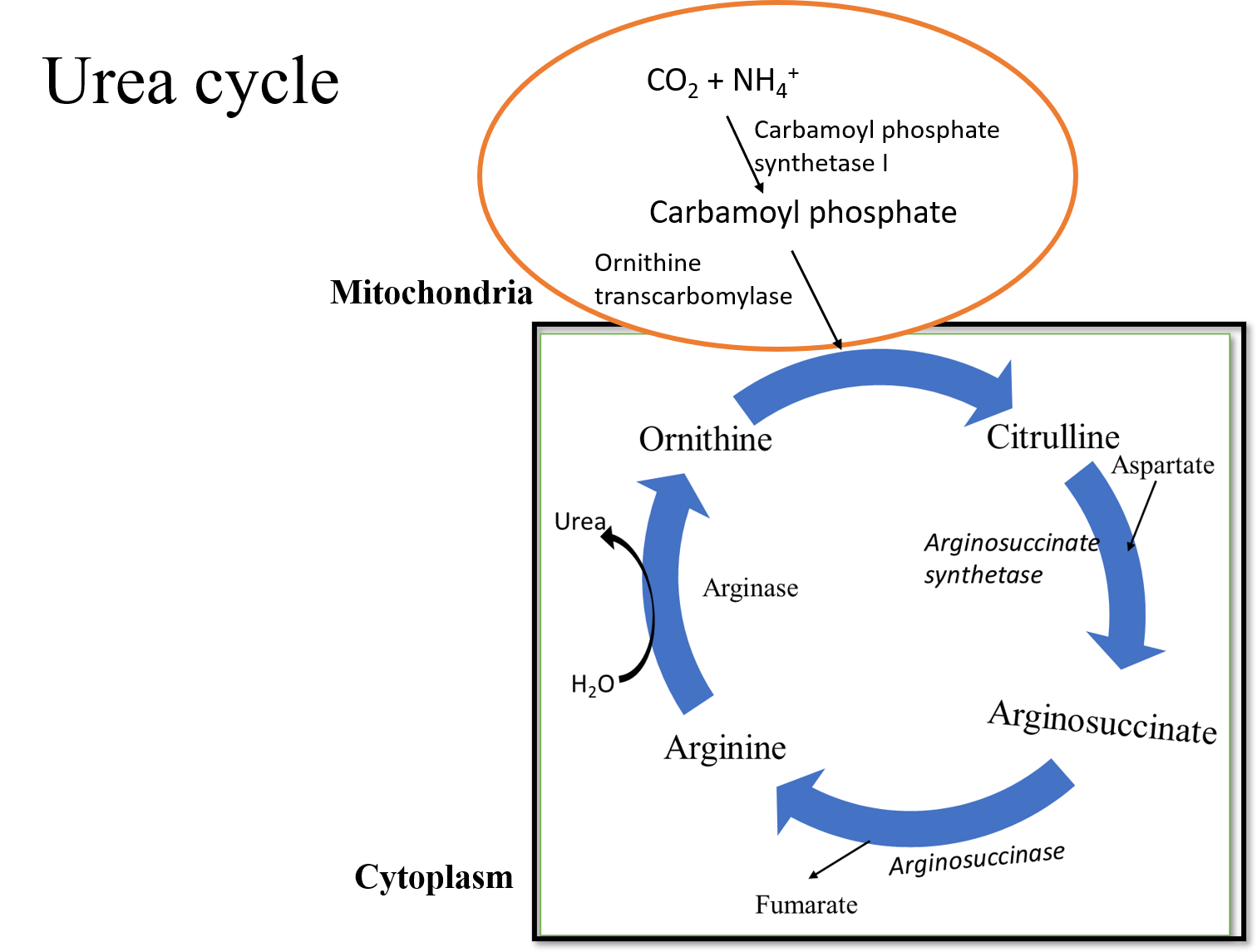
Complete answer:
The urea cycle is the process of formation of urea in the liver from the highly toxic ammonia for elimination. It is regarded as the first metabolic cycle to be discovered by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit in 1932. Urea is synthesized in our body by the Urea cycle or Ornithine cycle. It requires ammonia, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and water, ATP, and Arginase.
Additional Information: The steps involved in the urea cycle are-
-Firstly, the Carbamoyl phosphate gets converted into citrulline with the help of the enzyme ornithine transcarbamoylase. This is the rate-limiting step and takes place in the mitochondria while the rest of the steps occur in the cytoplasm.
-Then, aspartate reacts with the carbamoyl group of citrulline to form argininosuccinate with the help of the enzyme argininosuccinate synthetase.
-Argininosuccinate then breaks into arginine and fumarates by the enzyme argininosuccinase.
-Finally, arginine gets cleaved by the enzyme arginase to form urea and ornithine.
The urea is released into the blood for elimination and ornithine is sent back to mitochondria to participate in the next cycle.
So, the correct answer is ‘Arginase, ${ C }{ O }_{ 2 }$, and water’.
Note: -The urea cycle is connected with the citric acid cycle. The aspartate of the urea cycle is formed by transamination from oxaloacetate and the fumarate formed in the urea cycle as an intermediate is transported to participate in the citric acid cycle.
-It results in the release of two NADH molecules which is used to produce energy.
-The rate-limiting step determines the overall speed and other parameters of a reaction.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




