
For the formation of terylene, the number of moles of ethylene glycol required per mole of terephthalic acid is:
(A)- 1
(B)- 2
(C)- 3
(D)- 4
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: The polymer formed consists of two bi-functional monomers, that is, diol and di-carboxylic acid, which join together with a loss of water molecule, followed by the linkage of the repetitive unit formed.
Complete step by step answer:
Terylene is a polyester linkage polymer, formed by the continuous combining of two monomers along with the loss of water molecule to form a long chain-like structure during the process. The two monomeric units for the formation of the polymer are Ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. So, we have a diol and a di-carboxylic acid as the monomers which combine together, losing a water molecule and forming an ester. This is followed by the repetitive linkage of the esters to produce a terylene polymer. Thus, the process is known as the condensation polymerisation. The reaction occurs in presence of a catalyst mixture of zinc acetate and antimony trioxide, at temperature 420-470 K as follows:
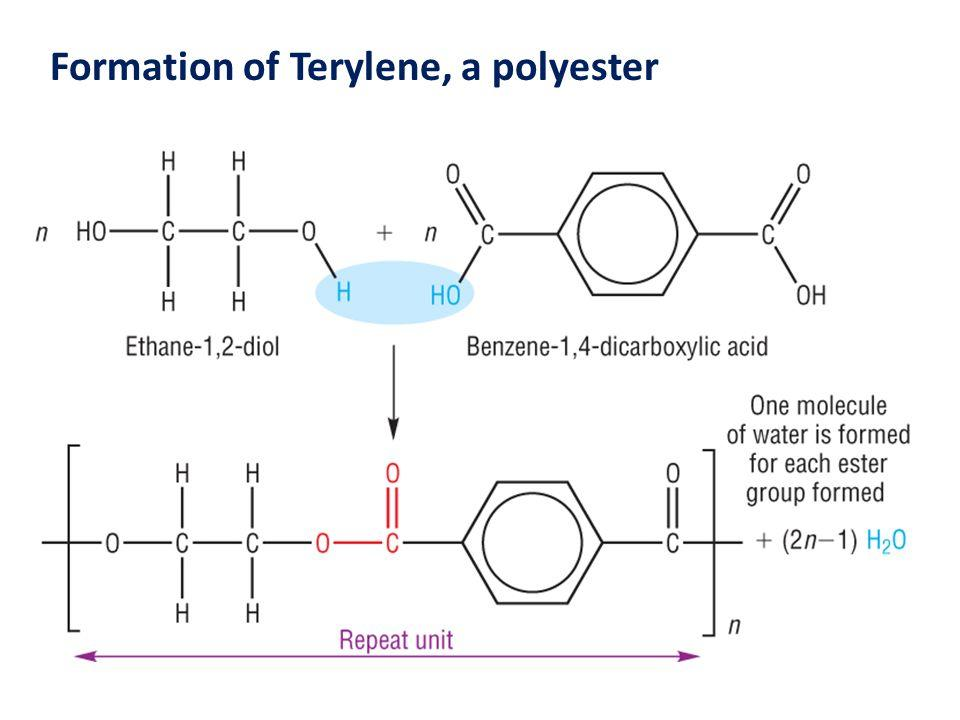
So, we see that n- moles of ethylene glycol and n-moles of terephthalic acid combine and condense together to form n-moles of terylene polymer. Then, for every one mole of terephthalic acid, one mole of ethylene glycol is used.
Therefore, for the formation of terylene, the number of moles of ethylene glycol required per mole of terephthalic acid is option (A)- 1.
Note: It is seen that, due to the presence of the bi-functional monomers, a straight chain linkage is possible to form a higher molecular mass terylene polymer. Also, known as Dacron. It is used in manufacturing of clothes as it is wrinkle free and also mixed with natural fibres like cotton.
Complete step by step answer:
Terylene is a polyester linkage polymer, formed by the continuous combining of two monomers along with the loss of water molecule to form a long chain-like structure during the process. The two monomeric units for the formation of the polymer are Ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. So, we have a diol and a di-carboxylic acid as the monomers which combine together, losing a water molecule and forming an ester. This is followed by the repetitive linkage of the esters to produce a terylene polymer. Thus, the process is known as the condensation polymerisation. The reaction occurs in presence of a catalyst mixture of zinc acetate and antimony trioxide, at temperature 420-470 K as follows:

So, we see that n- moles of ethylene glycol and n-moles of terephthalic acid combine and condense together to form n-moles of terylene polymer. Then, for every one mole of terephthalic acid, one mole of ethylene glycol is used.
Therefore, for the formation of terylene, the number of moles of ethylene glycol required per mole of terephthalic acid is option (A)- 1.
Note: It is seen that, due to the presence of the bi-functional monomers, a straight chain linkage is possible to form a higher molecular mass terylene polymer. Also, known as Dacron. It is used in manufacturing of clothes as it is wrinkle free and also mixed with natural fibres like cotton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




