
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify each as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion:
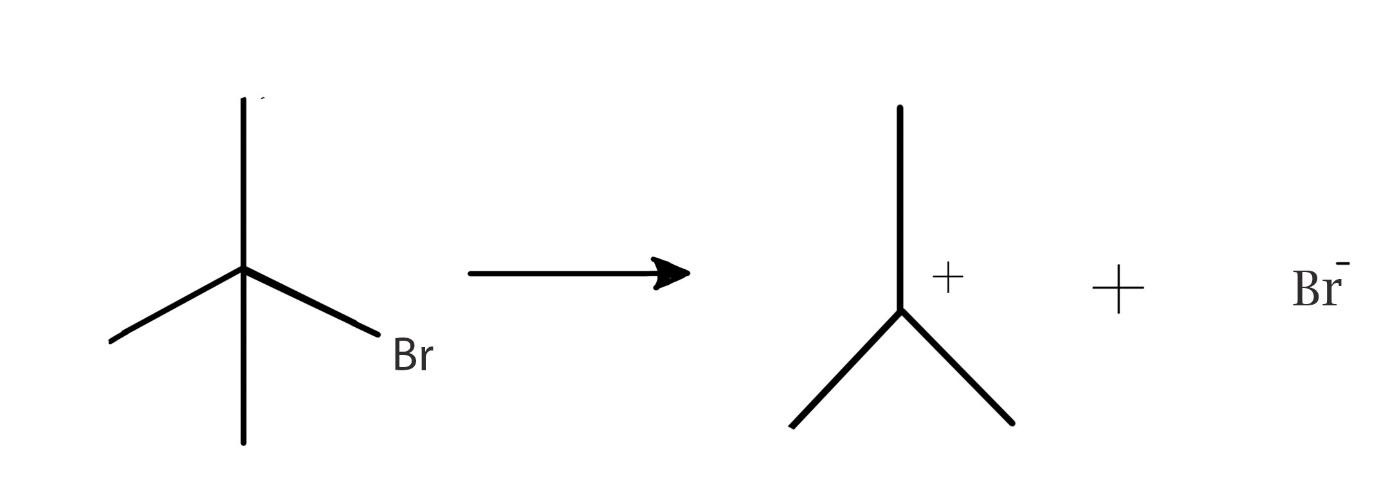

Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: the given reaction shows that the compound undergoes a cleavage to form a positively charged compound.
This means that the positively charged compound has lost electrons. Here the electrons are lost to bromine. Therefore, bromine becomes negatively charged.
Complete step by step answer:
The compound also known as $2,2\dim ethylethylbromide$ is a tertiary carbon atom. This compound is a tertiary alkyl halide which is attached to a bromine atom. This compound can spilt as shown in the reaction to form a tertiary carbocation and a electron rich bromine ion. The reaction is an example of a heterolytic cleavage because the alkyl part attains a positive charge and the halide part attains a negative charge. This is because the bromine ion attracts the electrons from the hydrocarbon part. The hydrocarbon then loses its own electron density. the electron transfer is shown below:
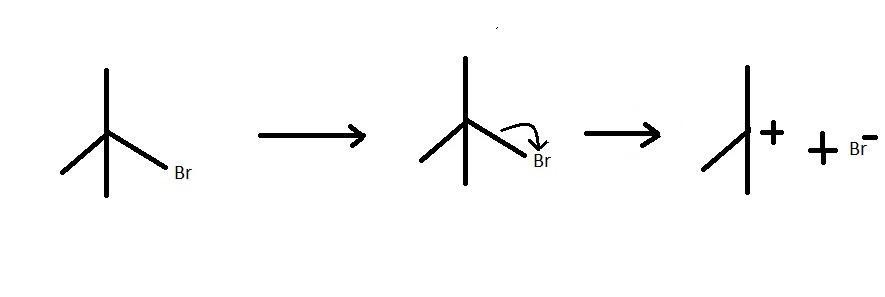
Here we can see that the higher electronegativity of bromine leads to the electron pair going to bromine to form a nucleophile. The alkyl part forms the electrophile in the reaction. The intermediate thus formed is a carbocation.
Therefore, the answer to the question is heterolysis leads to formation of carbocation.
Note:
The difference in the electronegativity leads to heterolytic cleavage which leads to the formation of an electron deficient intermediate called a carbocation. It also led to an electron rich product that is the bromine ion. This bromine ion will be known as the nucleophile.
Therefore, the reaction shows that the electron pair will be attracted to the more electronegative atom.
This means that the positively charged compound has lost electrons. Here the electrons are lost to bromine. Therefore, bromine becomes negatively charged.
Complete step by step answer:
The compound also known as $2,2\dim ethylethylbromide$ is a tertiary carbon atom. This compound is a tertiary alkyl halide which is attached to a bromine atom. This compound can spilt as shown in the reaction to form a tertiary carbocation and a electron rich bromine ion. The reaction is an example of a heterolytic cleavage because the alkyl part attains a positive charge and the halide part attains a negative charge. This is because the bromine ion attracts the electrons from the hydrocarbon part. The hydrocarbon then loses its own electron density. the electron transfer is shown below:

Here we can see that the higher electronegativity of bromine leads to the electron pair going to bromine to form a nucleophile. The alkyl part forms the electrophile in the reaction. The intermediate thus formed is a carbocation.
Therefore, the answer to the question is heterolysis leads to formation of carbocation.
Note:
The difference in the electronegativity leads to heterolytic cleavage which leads to the formation of an electron deficient intermediate called a carbocation. It also led to an electron rich product that is the bromine ion. This bromine ion will be known as the nucleophile.
Therefore, the reaction shows that the electron pair will be attracted to the more electronegative atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




