
For self-pollination, a flower should be
(a) Asexual
(b) Monosexual
(c) Unisexual
(d) Bisexual
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Pollination is the transfer of pollen grain from the male anther of the flower to the stigma female part of the flower.
Complete step by step answer:
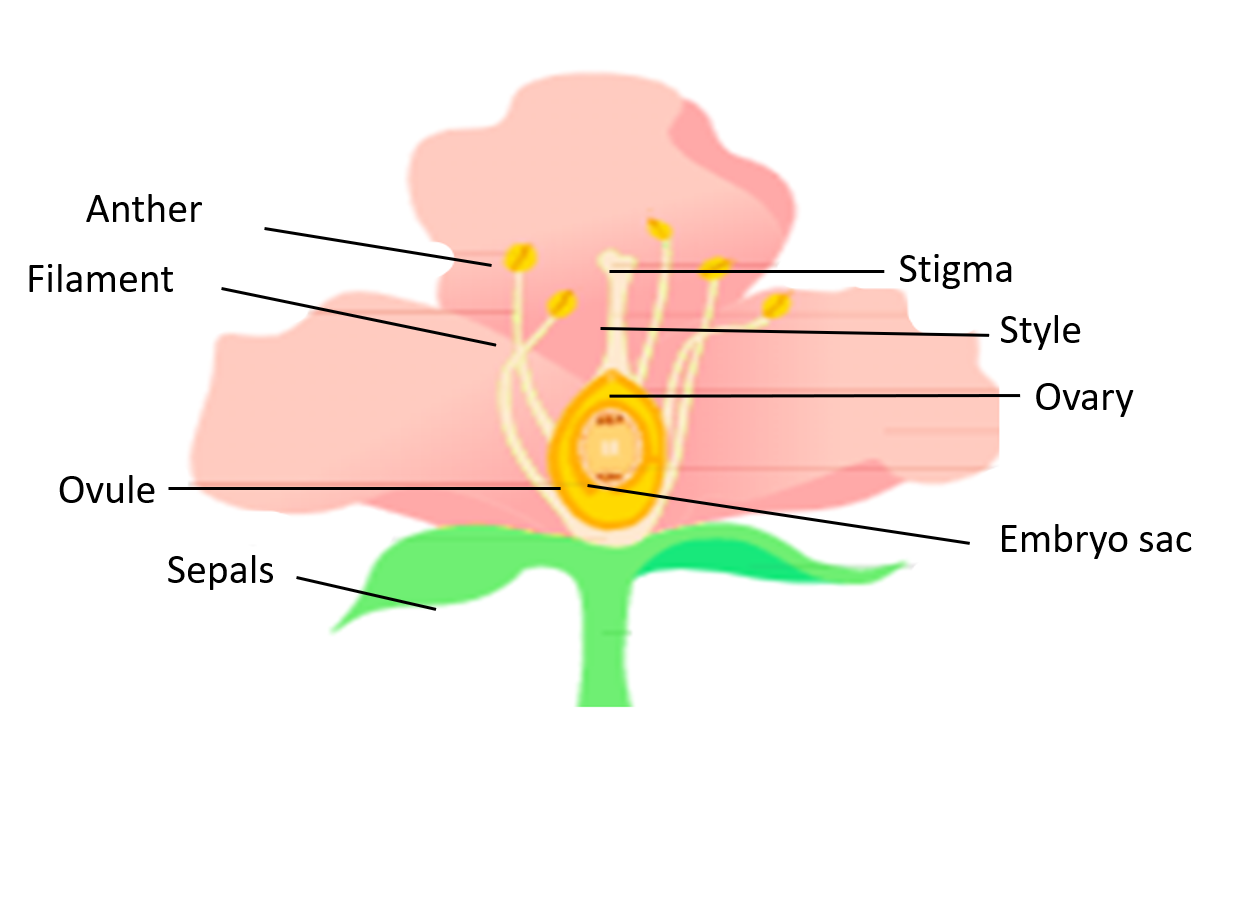
For self-pollination, a flower should be bisexual. Examples of several types of bisexual flowers are orchids, sunflowers, dandelions. When pollen grain from the same plant arrives at the stigma of a flower of the same flower or to another flower of the same plant is called self-pollination.
There are two types of pollination- Cross-pollination, and Self-pollination.
Cross-pollination: The pollination in which the pollen is transferred from anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. It always depends on pollinating agents. It is also known as allogamy.
Self-pollination: This type of pollination occurs in hermaphrodite plants which contain both female and male sexual parts on the same flower. Self-pollination can be divided into two types- Autogamy and geitonogamy.
When the pollination occurs before the flower bloom such types of pollination are pure self-pollination is called cleistogamy. Example - chasmogamous flower. Pollination can take place by air, water, wind, rain, bees, birds, bats.
Advantages of self-pollination
- Helps to keep desired well-suited genotypes stable in species.
- Not dependent on pollinating agents.
- Less wastage of pollen grain.
- Features of species maintained with purity
- The disadvantage of self-pollination
- Lack of variation.
- It can lead to inbreeding depression caused by a deleterious recessive mutation.
- Genetic defects in self-pollination plants cannot be eliminated by genetic recombination.
So, the correct answer is, 'bisexual flower.’
Note:
- Eighty percent of all flowering plants contain both sexes in the same flower i.e. plants are hermaphroditic.
- About forty-two percent of flowering plants show a mixed mating system.
- Dandelions are capable of self-pollination as well as cross-pollination.
- Examples of self-pollinating flowers are slipper orchid, tree-living orchids, red shepherd's purse, Madagascan orchid, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
For self-pollination, a flower should be bisexual. Examples of several types of bisexual flowers are orchids, sunflowers, dandelions. When pollen grain from the same plant arrives at the stigma of a flower of the same flower or to another flower of the same plant is called self-pollination.
There are two types of pollination- Cross-pollination, and Self-pollination.
Cross-pollination: The pollination in which the pollen is transferred from anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. It always depends on pollinating agents. It is also known as allogamy.
Self-pollination: This type of pollination occurs in hermaphrodite plants which contain both female and male sexual parts on the same flower. Self-pollination can be divided into two types- Autogamy and geitonogamy.
When the pollination occurs before the flower bloom such types of pollination are pure self-pollination is called cleistogamy. Example - chasmogamous flower. Pollination can take place by air, water, wind, rain, bees, birds, bats.

Advantages of self-pollination
- Helps to keep desired well-suited genotypes stable in species.
- Not dependent on pollinating agents.
- Less wastage of pollen grain.
- Features of species maintained with purity
- The disadvantage of self-pollination
- Lack of variation.
- It can lead to inbreeding depression caused by a deleterious recessive mutation.
- Genetic defects in self-pollination plants cannot be eliminated by genetic recombination.
So, the correct answer is, 'bisexual flower.’
Note:
- Eighty percent of all flowering plants contain both sexes in the same flower i.e. plants are hermaphroditic.
- About forty-two percent of flowering plants show a mixed mating system.
- Dandelions are capable of self-pollination as well as cross-pollination.
- Examples of self-pollinating flowers are slipper orchid, tree-living orchids, red shepherd's purse, Madagascan orchid, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




