
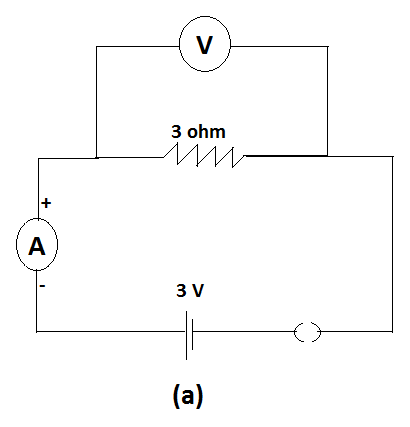
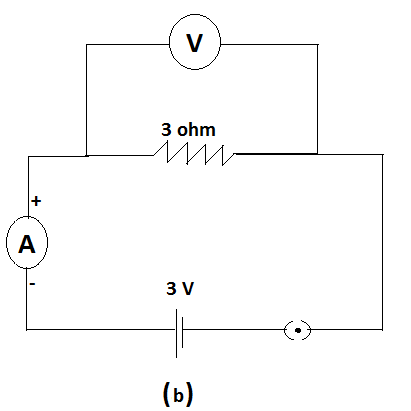
For circuits shown in fig (a) and fig (b). ,the ammeter reading would be-
(A). \[1A\,\] in both circuits
(B). \[0A\] in (a), \[1A\] in (b).
(C). \[1A\] in (a), \[0A\] in (b)
(D). \[0A\] in both the circuits


Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Using ohm’s law the value of current can be calculated by substituting the corresponding values. Also check whether the circuits are open or close as current only flows in closed circuits. The ammeter and voltmeter are used to determine the current and potential difference across two points respectively.
Formulas used:
\[R=\dfrac{V}{I}\]
Complete answer:
An ammeter is a device which is used to detect the magnitude of current flowing in the circuit. A voltmeter is a device which is used to measure the potential difference between two points in a circuit.
In the fig (a)
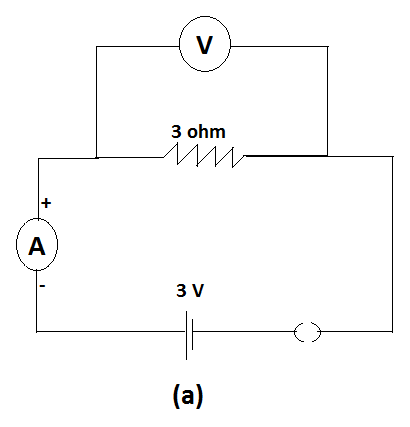
The switch is open which means that the circuit is not complete. If the circuit is open no current can flow in it. Therefore the current here is zero. So the ammeter reading is zero.
In fig (b)
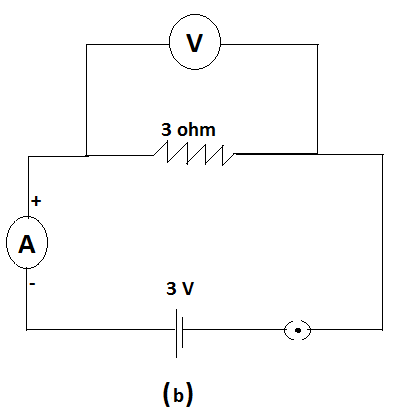
In this circuit, since the switch is closed, the circuit is complete, so current flows.
According to ohm’s law
\[R=\dfrac{V}{I}\]
\[\Rightarrow V=IR\] - (1)
Here,
\[R\] is the resistance
\[I\] is the current
\[V\] is the potential difference
There is almost no potential drop on the ammeter as its resistance is negligible. While the potential drop on voltmeter is equal to the potential drop on the resistor as they are connected in parallel.
Using eq (1) In fig (b), we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 3V=I\times 3\Omega \\
& \dfrac{3}{3}=I \\
& \therefore I=1A \\
\end{align}\]
The current in the circuit of fig (b) is\[1A\]
Since the current in the circuit of fig (a) is zero and in fig (b) it is \[1A\], the correct option is (B).
Note:
Devices in a circuit can be connected in either series or parallel. When they are connected in series, the current flowing through all the devices is the same but potential drop is different and depends on the value of resistance. When devices are connected in parallel, the potential drop is the same but current is different.
Formulas used:
\[R=\dfrac{V}{I}\]
Complete answer:
An ammeter is a device which is used to detect the magnitude of current flowing in the circuit. A voltmeter is a device which is used to measure the potential difference between two points in a circuit.
In the fig (a)

The switch is open which means that the circuit is not complete. If the circuit is open no current can flow in it. Therefore the current here is zero. So the ammeter reading is zero.
In fig (b)

In this circuit, since the switch is closed, the circuit is complete, so current flows.
According to ohm’s law
\[R=\dfrac{V}{I}\]
\[\Rightarrow V=IR\] - (1)
Here,
\[R\] is the resistance
\[I\] is the current
\[V\] is the potential difference
There is almost no potential drop on the ammeter as its resistance is negligible. While the potential drop on voltmeter is equal to the potential drop on the resistor as they are connected in parallel.
Using eq (1) In fig (b), we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 3V=I\times 3\Omega \\
& \dfrac{3}{3}=I \\
& \therefore I=1A \\
\end{align}\]
The current in the circuit of fig (b) is\[1A\]
Since the current in the circuit of fig (a) is zero and in fig (b) it is \[1A\], the correct option is (B).
Note:
Devices in a circuit can be connected in either series or parallel. When they are connected in series, the current flowing through all the devices is the same but potential drop is different and depends on the value of resistance. When devices are connected in parallel, the potential drop is the same but current is different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




