
For any two sets A and B, prove that:
1. \[A\cup B=B\cup A\] [Commutative law for the union of sets]
2. \[A\cap B=B\cap A\] [Commutative law for the intersection of sets]
Answer
610.2k+ views
Hint:First of all take an element \[x\in A\cup B\] and \[x\in A\cap B\] in each of the proofs respectively. Now, by the definition of intersection and union of sets, prove that \[x\in B\cup A\] and \[x\in B\cap A\]. From this, prove that \[A\cap B\subset B\cap A\] and vice versa. From this and its converse, prove the desired result. Similarly, do for the other one as well.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, for any two sets A and B, prove that
1. \[A\cup B=B\cup A\] [Commutative law for the union of sets]
2. \[A\cap B=B\cap A\] [Commutative law for the intersection of sets]
Let us prove that \[A\cup B=B\cup A\]. Let x be an element in the set \[A\cup B\]. So, we can write
\[x\in A\cup B\]
We know that \[A\cup B\] constitute elements in A or B or in both. So, if \[x\in A\cup B\], then \[x\in A\] or \[x\in B\]. We can also say that as \[x\in B\] or \[x\in A\], so, \[x\in B\cup A\].
So, from \[x\in A\cup B\], we get, \[x\in B\cup A\]. From this, we can say that \[A\cup B\] is a subset of \[B\cup A\]
So, we get,
\[A\cup B\subset B\cup A.....\left( i \right)\]
Let us consider the reverse of the commutative law of union of two sets that is \[B\cup A=A\cup B\]
Let \[x\in B\cup A\]. If \[x\in B\cup A\], then \[x\in B\] or \[x\in A\]. We can also say that \[x\in A\] or \[x\in B\]. So, \[x\in A\cup B\].
So, from \[x\in B\cup A\], we get, \[x\in A\cup B\]. From this, we can say that \[B\cup A\] is a subset of \[A\cup B\]. So, we get,
\[B\cup A\subset A\cup B.....\left( ii \right)\]
We know that when x is a subset of y and y is a subset of x, then x = y. So, from equation (i) and (ii), we get,
\[A\cup B=B\cup A\]
Hence, we have proved the commutative law from the union of sets.
Now let us prove that \[A\cap B=B\cap A\]. Let x be an element in \[A\cap B\]. So, we can write \[x\in A\cap B\]. We know that \[A\cap B\] constitute elements that are in set A as well as B.
So if, \[x\in A\cap B\], then \[x\in A\] and \[x\in B\]. Also, we can say that \[x\in B\] and \[x\in A\]. So, we get, \[x\in B\cap A\]. From \[x\in A\cap B\], we get \[x\in B\cap A\]. So, we can say that \[A\cap B\] is a subset of \[B\cap A\]. Therefore, we get,
\[A\cap B\subset B\cap A....\left( iii \right)\]
Now, let us consider the reverse of commutative law for the intersection of two sets that is
\[B\cap A=A\cap B\]
Let \[x\in B\cap A\], then \[x\in B\] , and \[x\in A\]. We can say that \[x\in A\] and \[x\in B\]. So, we get, \[x\in A\cap B\]. From \[x\in B\cap A\], we get, \[x\in A\cap B\]. So, we can say that \[B\cap A\] is a subset of \[A\cap B\]. Therefore, we get,
\[B\cap A\subset A\cap B....\left( iv \right)\]
We know that when x is a subset of y and y is a subset of x, then x = y.
So, from equation (iii) and (iv), we get,
\[A\cap B=B\cap A\]
Hence, we have proved that the commutative law for the intersection of two sets.
Note: Students can also verify their relationship by Venn Diagram as follows:
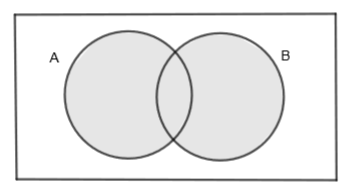
In the above diagram, we can write the shaded portion as \[A\cup B\] or \[B\cup A\]. So, we get, \[A\cup B=B\cup A\].

In the above diagram, we can write the shaded portion as \[A\cap B\] or \[B\cap A\]. So, we get, \[A\cap B=B\cap A\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, for any two sets A and B, prove that
1. \[A\cup B=B\cup A\] [Commutative law for the union of sets]
2. \[A\cap B=B\cap A\] [Commutative law for the intersection of sets]
Let us prove that \[A\cup B=B\cup A\]. Let x be an element in the set \[A\cup B\]. So, we can write
\[x\in A\cup B\]
We know that \[A\cup B\] constitute elements in A or B or in both. So, if \[x\in A\cup B\], then \[x\in A\] or \[x\in B\]. We can also say that as \[x\in B\] or \[x\in A\], so, \[x\in B\cup A\].
So, from \[x\in A\cup B\], we get, \[x\in B\cup A\]. From this, we can say that \[A\cup B\] is a subset of \[B\cup A\]
So, we get,
\[A\cup B\subset B\cup A.....\left( i \right)\]
Let us consider the reverse of the commutative law of union of two sets that is \[B\cup A=A\cup B\]
Let \[x\in B\cup A\]. If \[x\in B\cup A\], then \[x\in B\] or \[x\in A\]. We can also say that \[x\in A\] or \[x\in B\]. So, \[x\in A\cup B\].
So, from \[x\in B\cup A\], we get, \[x\in A\cup B\]. From this, we can say that \[B\cup A\] is a subset of \[A\cup B\]. So, we get,
\[B\cup A\subset A\cup B.....\left( ii \right)\]
We know that when x is a subset of y and y is a subset of x, then x = y. So, from equation (i) and (ii), we get,
\[A\cup B=B\cup A\]
Hence, we have proved the commutative law from the union of sets.
Now let us prove that \[A\cap B=B\cap A\]. Let x be an element in \[A\cap B\]. So, we can write \[x\in A\cap B\]. We know that \[A\cap B\] constitute elements that are in set A as well as B.
So if, \[x\in A\cap B\], then \[x\in A\] and \[x\in B\]. Also, we can say that \[x\in B\] and \[x\in A\]. So, we get, \[x\in B\cap A\]. From \[x\in A\cap B\], we get \[x\in B\cap A\]. So, we can say that \[A\cap B\] is a subset of \[B\cap A\]. Therefore, we get,
\[A\cap B\subset B\cap A....\left( iii \right)\]
Now, let us consider the reverse of commutative law for the intersection of two sets that is
\[B\cap A=A\cap B\]
Let \[x\in B\cap A\], then \[x\in B\] , and \[x\in A\]. We can say that \[x\in A\] and \[x\in B\]. So, we get, \[x\in A\cap B\]. From \[x\in B\cap A\], we get, \[x\in A\cap B\]. So, we can say that \[B\cap A\] is a subset of \[A\cap B\]. Therefore, we get,
\[B\cap A\subset A\cap B....\left( iv \right)\]
We know that when x is a subset of y and y is a subset of x, then x = y.
So, from equation (iii) and (iv), we get,
\[A\cap B=B\cap A\]
Hence, we have proved that the commutative law for the intersection of two sets.
Note: Students can also verify their relationship by Venn Diagram as follows:

In the above diagram, we can write the shaded portion as \[A\cup B\] or \[B\cup A\]. So, we get, \[A\cup B=B\cup A\].

In the above diagram, we can write the shaded portion as \[A\cap B\] or \[B\cap A\]. So, we get, \[A\cap B=B\cap A\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




