
For an $ SN^2 $ reaction, which of the following statements are true?
(A) The rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the nucleophile.
(B) The nucleophile attacks the C-atom on the side of the molecule opposite to the group being displaced.
(C) The reaction proceeds with simultaneous bond formation and rupture.
(D) All of the above.
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: $ S{N^2} $ reactions are bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions. The term bimolecular refers to reactions in which there are two reactants involved in the rate determining step. In these reactions the attack of the nucleophile and the leaving group are on the same C-atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
$ S{N^2} $ reactions are bimolecular reactions that take place in a single step. Therefore, this step is the rate determining step.
An example of $ S{N^2} $ reaction is,
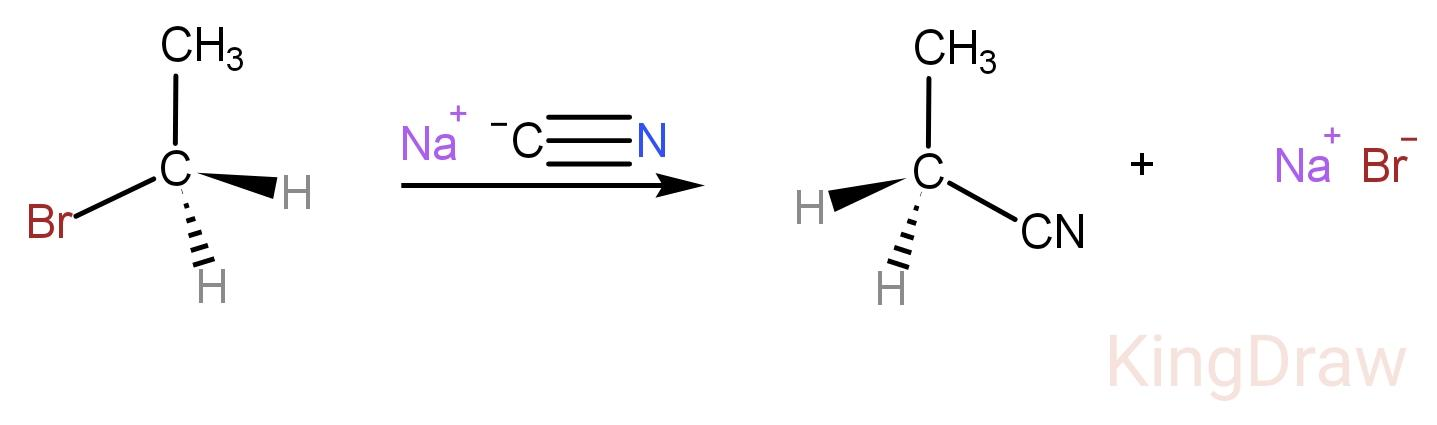
Here, $ C{N^ - } $ is the attacking nucleophile and $ B{r^ - } $ is the leaving group.
Mechanism of the reaction is,
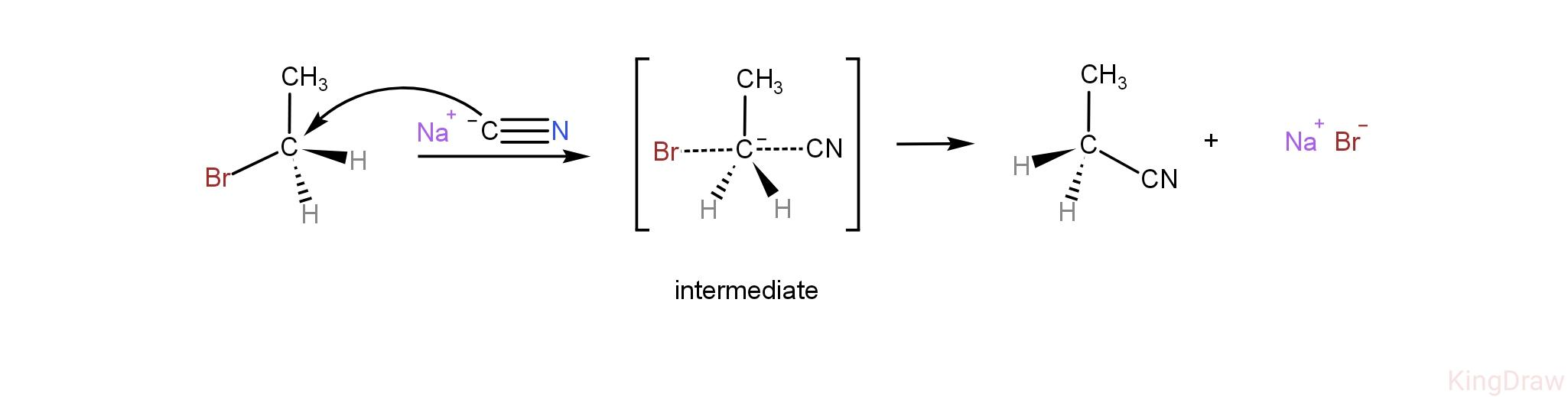
As we can see, this step involves the attack of incoming nucleophiles and the elimination of leaving groups simultaneously with the formation of an intermediate. Therefore, the rate of the reaction will depend on the concentration of both the reactants, that is, the nucleophile and the molecule undergoing substitution reaction.
The bond formation and bond breaking are occurring on the same C-atom simultaneously, so the attacking group must attack from the side opposite to that of the leaving group.
Therefore, options B and C are correct.
Note:
Due to the simultaneous attack of nucleophiles and elimination of the leaving group, this reaction is carried out with utmost ease in molecules having H-atoms as substituents. As the substituent groups become large and bulky, the difficulty becomes for the reaction to take place due to steric hindrance. Therefore, order of reactivity in alkyl halides is,
$ C{H_4} > 1^\circ > 2^\circ $
It does not take place in $ 3^\circ $ alkyl halides.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
$ S{N^2} $ reactions are bimolecular reactions that take place in a single step. Therefore, this step is the rate determining step.
An example of $ S{N^2} $ reaction is,

Here, $ C{N^ - } $ is the attacking nucleophile and $ B{r^ - } $ is the leaving group.
Mechanism of the reaction is,

As we can see, this step involves the attack of incoming nucleophiles and the elimination of leaving groups simultaneously with the formation of an intermediate. Therefore, the rate of the reaction will depend on the concentration of both the reactants, that is, the nucleophile and the molecule undergoing substitution reaction.
The bond formation and bond breaking are occurring on the same C-atom simultaneously, so the attacking group must attack from the side opposite to that of the leaving group.
Therefore, options B and C are correct.
Note:
Due to the simultaneous attack of nucleophiles and elimination of the leaving group, this reaction is carried out with utmost ease in molecules having H-atoms as substituents. As the substituent groups become large and bulky, the difficulty becomes for the reaction to take place due to steric hindrance. Therefore, order of reactivity in alkyl halides is,
$ C{H_4} > 1^\circ > 2^\circ $
It does not take place in $ 3^\circ $ alkyl halides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




