
For an octahedral complex, which of the following d-electron configurations will give maximum CFSE?
(A) High spin ${{d}^{6}},-0.4{{\Delta }_{o}}$ ${{d}^{6}},-0.4{{\Delta }_{o}}$
(B) Low spin ${{d}^{4}},-1.6{{\Delta }_{o}}$ ${{d}^{4}},-1.6{{\Delta }_{o}}$
(C) Low spin ${{d}^{5}},-2.0{{\Delta }_{o}}$
(D) High spin ${{d}^{7}},-0.8{{\Delta }_{o}}$

Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: The value of CFSE is more in the given options for the option (C). However it can be understood from the calculation.
Complete step by step answer:
Crystal field splitting energy, CFSE for octahedral complexes is calculated from the following formula,
$\left[ \left( -0.4\times 5 \right)+\left( +0.6\times 2 \right) \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
Let us calculate the CFSE for all the given electronic configurations. Let us consider,
- Option (A), in the high spin ${{d}^{6}}$ configuration, there will be 4 ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons and 2 ${{e}_{g}}$ electrons. The CFSE is $\left[ \left( -0.4\times 4 \right)+\left( +0.6\times 2 \right) \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$\left[ -1.6+1.2 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$-0.4{{\Delta }_{o}}$
- Option (B), in low spin ${{d}^{4}}$ configuration, there will be 4 ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons and 0 ${{e}_{g}}$ electrons and its CFSE is = $\left[ -0.4\times 4 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
= $-1.6{{\Delta }_{o}}$
- Option (C), for low spin ${{d}^{5}}$ configuration, the number of ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons are 5 and ${{e}_{g}}$ are 0, its CFSE is,$\left[ -0.4\times 5 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$=$-2.0{{\Delta }_{o}}$
- Option (D), in the high spin ${{d}^{7}}$ configuration, the number of ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons are 5 and ${{e}_{g}}$ are 2, its CFSE is,
=$\left[ \left( -0.4\times 5 \right)+\left( +0.6\times 2 \right) \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$\left[ -2.0+1.2 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$-0.8{{\Delta }_{o}}$
From the above obtained values of Crystal field stabilization energies, the value for low spin ${{d}^{5}}$ configuration is maximum which is, $-2.0{{\Delta }_{o}}$.
The correct answer is option “C” .
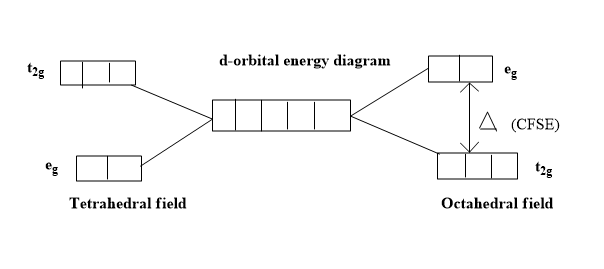
Additional Information : The stabilization energy gained by the complex by filling electrons in lower energy ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals of octahedral complexes is known as crystal field stabilization energy of octahedral complexes. ${{t}_{2g}}$ and ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals are sets of orbitals resulting from splitting of the degenerate d-orbitals. The d-orbitals in which their lobes are oriented along x and y axes are named as ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals; these are also called double degenerate orbitals. The d-orbitals whose lobes are oriented in between x, y, z axes are named as ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals. These are also called triple degenerate orbitals. These two sets of orbitals have differences in their energies.
Note: The electrons are filled in the orbitals for calculating CFSE by considering whether the given complex is a low spin complex or a high spin complex. In a low spin complex pairing of electrons takes place whereas in a high spin complex, all the degenerate orbitals are filled by one electron each and then pairing occurs.
Complete step by step answer:
Crystal field splitting energy, CFSE for octahedral complexes is calculated from the following formula,
$\left[ \left( -0.4\times 5 \right)+\left( +0.6\times 2 \right) \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
Let us calculate the CFSE for all the given electronic configurations. Let us consider,
- Option (A), in the high spin ${{d}^{6}}$ configuration, there will be 4 ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons and 2 ${{e}_{g}}$ electrons. The CFSE is $\left[ \left( -0.4\times 4 \right)+\left( +0.6\times 2 \right) \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$\left[ -1.6+1.2 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$-0.4{{\Delta }_{o}}$
- Option (B), in low spin ${{d}^{4}}$ configuration, there will be 4 ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons and 0 ${{e}_{g}}$ electrons and its CFSE is = $\left[ -0.4\times 4 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
= $-1.6{{\Delta }_{o}}$
- Option (C), for low spin ${{d}^{5}}$ configuration, the number of ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons are 5 and ${{e}_{g}}$ are 0, its CFSE is,$\left[ -0.4\times 5 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$=$-2.0{{\Delta }_{o}}$
- Option (D), in the high spin ${{d}^{7}}$ configuration, the number of ${{t}_{2g}}$ electrons are 5 and ${{e}_{g}}$ are 2, its CFSE is,
=$\left[ \left( -0.4\times 5 \right)+\left( +0.6\times 2 \right) \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$\left[ -2.0+1.2 \right]{{\Delta }_{o}}$
=$-0.8{{\Delta }_{o}}$
From the above obtained values of Crystal field stabilization energies, the value for low spin ${{d}^{5}}$ configuration is maximum which is, $-2.0{{\Delta }_{o}}$.
The correct answer is option “C” .
Additional Information : The stabilization energy gained by the complex by filling electrons in lower energy ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals of octahedral complexes is known as crystal field stabilization energy of octahedral complexes. ${{t}_{2g}}$ and ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals are sets of orbitals resulting from splitting of the degenerate d-orbitals. The d-orbitals in which their lobes are oriented along x and y axes are named as ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals; these are also called double degenerate orbitals. The d-orbitals whose lobes are oriented in between x, y, z axes are named as ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals. These are also called triple degenerate orbitals. These two sets of orbitals have differences in their energies.
Note: The electrons are filled in the orbitals for calculating CFSE by considering whether the given complex is a low spin complex or a high spin complex. In a low spin complex pairing of electrons takes place whereas in a high spin complex, all the degenerate orbitals are filled by one electron each and then pairing occurs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




