
For an npn transistor $ {R_{out}} = 1.2 \times {10^5}\Omega $ , $ {R_{in}} = 6000\Omega $ , $ \beta = 50 $ . It is connected to amplify an input signal in active mode in common emitter configuration. The input signal is
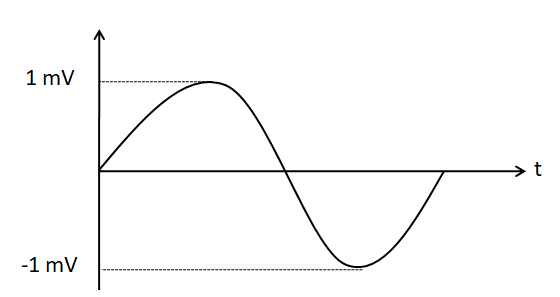
The output signal looks like
(A)
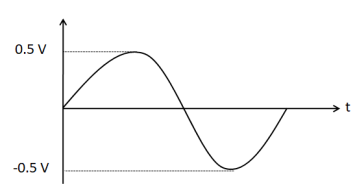
(B)
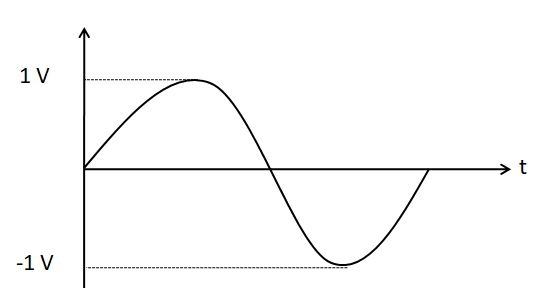
(C)
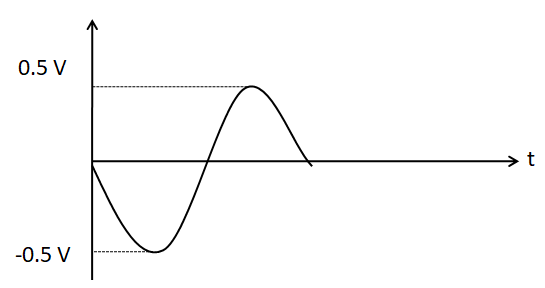
(D)





Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint
To answer this question, we have to use the formula of the voltage gain in the case of an npn transistor in active mode in common emitter configuration. The input voltage can be determined from the waveform of the input signal given. From the value of the voltage gain, we can determine the output voltage and hence predict the shape of the output signal.
Formula Used: The formula used to solve this question is
$ v = - \beta \dfrac{{{R_{out}}}}{{{R_{in}}}} $
Here $ v $ is the voltage gain, $ \beta $ is the current amplification factor or the current gain, $ {R_{out}} $ is the output resistance and $ {R_{in}} $ is the input resistance.
Complete step by step answer
According to the question, the current gain $ \beta = 50 $ , $ {R_{out}} = 1.2 \times {10^5}\Omega $ , and $ {R_{in}} = 6000\Omega $
We know that for an npn transistor in the common emitter configuration in the active mode, the voltage gain is given by
$ v = - \beta \dfrac{{{R_{out}}}}{{{R_{in}}}} $
Substituting the values, we get
$ v = - 50 \times \dfrac{{1.2 \times {{10}^5}}}{{6000}} $
$ v = - 50 \times 20 $
On solving, we get
$ v = - 1000 $ (1)
We know that the voltage gain is equal to the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage, that is,
$ v = \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_{out}}}}{{{{\text{V}}_{in}}}} $ (2)
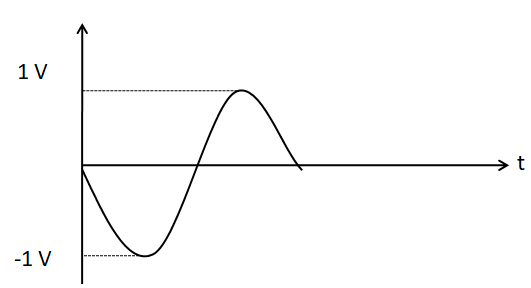
From the waveform of the input signal given in the question, we can see that the amplitude of the input voltage is equal to $ 1{\text{mV}} $ . That is, $ {{\text{V}}_{in}} = 1{\text{ mV}} $
$ \therefore v = \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_{out}}}}{{1{\text{ mV}}}} $
$ {{\text{V}}_{out}} = v \times (1{\text{ mV)}} $
Substituting from (1)
$ {{\text{V}}_{out}} = - 1000 \times (1{\text{ mV)}} $
$ {{\text{V}}_{out}} = - 1{\text{V}} $
Thus, the output voltage has the amplitude of $ 1{\text{V}} $ .
Hence, the options A and C are incorrect, as they do not have output voltage amplitude equal to $ 1{\text{V}} $ .
The negative sign in the expression of the voltage gain indicates a phase change of $ {180^ \circ } $ from the input to the output. Therefore after being amplified, the input voltage is inverted. So, the output voltage waveform should look like
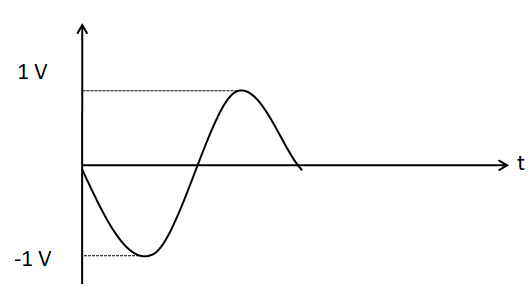
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note
Do not forget the negative sign present in the expression of the voltage gain. Always remember, the voltage is always inverted when a transistor is operated in the active mode in the common emitter configuration.
To answer this question, we have to use the formula of the voltage gain in the case of an npn transistor in active mode in common emitter configuration. The input voltage can be determined from the waveform of the input signal given. From the value of the voltage gain, we can determine the output voltage and hence predict the shape of the output signal.
Formula Used: The formula used to solve this question is
$ v = - \beta \dfrac{{{R_{out}}}}{{{R_{in}}}} $
Here $ v $ is the voltage gain, $ \beta $ is the current amplification factor or the current gain, $ {R_{out}} $ is the output resistance and $ {R_{in}} $ is the input resistance.
Complete step by step answer
According to the question, the current gain $ \beta = 50 $ , $ {R_{out}} = 1.2 \times {10^5}\Omega $ , and $ {R_{in}} = 6000\Omega $
We know that for an npn transistor in the common emitter configuration in the active mode, the voltage gain is given by
$ v = - \beta \dfrac{{{R_{out}}}}{{{R_{in}}}} $
Substituting the values, we get
$ v = - 50 \times \dfrac{{1.2 \times {{10}^5}}}{{6000}} $
$ v = - 50 \times 20 $
On solving, we get
$ v = - 1000 $ (1)
We know that the voltage gain is equal to the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage, that is,
$ v = \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_{out}}}}{{{{\text{V}}_{in}}}} $ (2)
From the waveform of the input signal given in the question, we can see that the amplitude of the input voltage is equal to $ 1{\text{mV}} $ . That is, $ {{\text{V}}_{in}} = 1{\text{ mV}} $
$ \therefore v = \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_{out}}}}{{1{\text{ mV}}}} $
$ {{\text{V}}_{out}} = v \times (1{\text{ mV)}} $
Substituting from (1)
$ {{\text{V}}_{out}} = - 1000 \times (1{\text{ mV)}} $
$ {{\text{V}}_{out}} = - 1{\text{V}} $
Thus, the output voltage has the amplitude of $ 1{\text{V}} $ .
Hence, the options A and C are incorrect, as they do not have output voltage amplitude equal to $ 1{\text{V}} $ .
The negative sign in the expression of the voltage gain indicates a phase change of $ {180^ \circ } $ from the input to the output. Therefore after being amplified, the input voltage is inverted. So, the output voltage waveform should look like

Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note
Do not forget the negative sign present in the expression of the voltage gain. Always remember, the voltage is always inverted when a transistor is operated in the active mode in the common emitter configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




