
For an ideal gas, show the nature of $ \dfrac{{{\text{PV}}}}{{{\text{nT}}}} $ versus $ {\text{P}} $ graph, where the symbols have their usual meaning.
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the ideal gas equation and the kinetic molecular gas theory. The ideal gas equation gives a relation between the properties that define any gas, namely, pressure exerted by the gas, volume occupied by the gas, number of moles of the gas and the temperature at which the system is maintained.
Formula used: Ideal Gas equation: $ {\text{PV}} = {\text{nRT}} $
Where, $ {\text{P}} $ denotes the pressure exerted by the gas on the walls of the container
$ {\text{V}} $ denotes the volume occupied by the gas or the volume of the given container containing the gas
$ {\text{n}} $ denotes the number of moles of the gas
And, $ {\text{T}} $ denotes the temperature of the gas.
Complete step by step solution:
We know the ideal gas equation can be written as $ {\text{PV}} = {\text{nRT}} $ .
So, we can also write $ \dfrac{{{\text{PV}}}}{{{\text{nT}}}} = {\text{R}} $
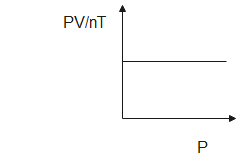
We know that $ {\text{R}} $ is a constant quantity known as the gas constant, thus, the graph between $ \dfrac{{{\text{PV}}}}{{{\text{nT}}}} $ and $ {\text{P}} $ will be a straight horizontal line. The gas constant does not change with change in pressure or volume.
Note:
The ideal gas equation does not apply to real gases. A real gas shows ideal behaviour at low pressure and high temperature conditions. The real gas equation is a modified version of the ideal gas equation that takes into consideration the factors that were ignored by the ideal gas law and the kinetic molecular gas law theory. The volume of the gas particles and the forces of attraction between the particles were ignored in these laws and included in the real gas law which gives a more accurate explanation for the behaviour of real gases.
Formula used: Ideal Gas equation: $ {\text{PV}} = {\text{nRT}} $
Where, $ {\text{P}} $ denotes the pressure exerted by the gas on the walls of the container
$ {\text{V}} $ denotes the volume occupied by the gas or the volume of the given container containing the gas
$ {\text{n}} $ denotes the number of moles of the gas
And, $ {\text{T}} $ denotes the temperature of the gas.
Complete step by step solution:
We know the ideal gas equation can be written as $ {\text{PV}} = {\text{nRT}} $ .
So, we can also write $ \dfrac{{{\text{PV}}}}{{{\text{nT}}}} = {\text{R}} $
We know that $ {\text{R}} $ is a constant quantity known as the gas constant, thus, the graph between $ \dfrac{{{\text{PV}}}}{{{\text{nT}}}} $ and $ {\text{P}} $ will be a straight horizontal line. The gas constant does not change with change in pressure or volume.

Note:
The ideal gas equation does not apply to real gases. A real gas shows ideal behaviour at low pressure and high temperature conditions. The real gas equation is a modified version of the ideal gas equation that takes into consideration the factors that were ignored by the ideal gas law and the kinetic molecular gas law theory. The volume of the gas particles and the forces of attraction between the particles were ignored in these laws and included in the real gas law which gives a more accurate explanation for the behaviour of real gases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




