
For, a zero-order reaction, the plot of concentration of reactant versus time is:
(Intercepts refers to the concentration axis)
A. Linear with +ve slope and negative intercept
B. Linear with -ve slope and zero intercept
C. Linear with -ve slope and non-zero intercept
D. Linear with +ve slope and non-zero intercept
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Zero-order reaction is a chemical reaction where the rate of reaction does not vary with the increase or decrease in the concentration of the reactants. Therefore, the rate of these reactions is always equal to the rate constant of the specific reactions (since the rate of these reactions is proportional to the zeroth power of reactants concentration).
Complete step by step answer:
The differential form of zero-order reaction can be written as:
\[\Rightarrow Rate\text{ }=~\dfrac{~-dA}{dt}=k{{[A]}^{0}}=k\]
Where ‘Rate’ refers to the rate of the reaction and \[k\] is the rate constant of the reaction.
This differential form can be rearranged and integrated on both sides to get the required Integral form as shown below.
\[\Rightarrow Rate\text{ }=~\dfrac{~-dA}{dt}=k\], multiplying on both sides with \[dt\] we get;
\[\Rightarrow d[A]=-kdt\], integrating on both sides we get,
\[\int\limits_{{{[A]}_{0}}}^{[A]}{d[A]}=-\int\limits_{0}^{t}{kdt}\]
Where \[{{[A]}_{0}}\] is the initial concentration of the reactant [A] at time t=0. Solving for [A], we get:
\[\Rightarrow [A]={{[A]}_{0}}kt\]
\[\Rightarrow [A]=-kt+{{[A]}_{0}}\]
Which is the required integral form. On comparing this equation with the equation of a straight line \[(y=mx+b)\], an \[[A]\] against t graph can be plotted to get a straight line with slope equal to \[-k\] and intercept equal to \[{{[A]}_{0}}\] as shown below.
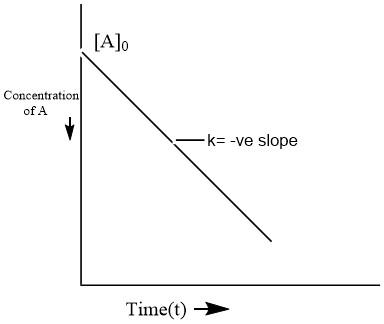
Here, we can see that the graph of a zero-order reaction is linear with -ve slope and non-zero intercept.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Other than zero-order reaction, there are first order reaction and second order reaction, whose graphs are different from zero-order reaction. The reaction of hydrogen with chlorine (Photochemical reaction) and decomposition of nitrous oxide over a hot platinum surface are examples of zero-order reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The differential form of zero-order reaction can be written as:
\[\Rightarrow Rate\text{ }=~\dfrac{~-dA}{dt}=k{{[A]}^{0}}=k\]
Where ‘Rate’ refers to the rate of the reaction and \[k\] is the rate constant of the reaction.
This differential form can be rearranged and integrated on both sides to get the required Integral form as shown below.
\[\Rightarrow Rate\text{ }=~\dfrac{~-dA}{dt}=k\], multiplying on both sides with \[dt\] we get;
\[\Rightarrow d[A]=-kdt\], integrating on both sides we get,
\[\int\limits_{{{[A]}_{0}}}^{[A]}{d[A]}=-\int\limits_{0}^{t}{kdt}\]
Where \[{{[A]}_{0}}\] is the initial concentration of the reactant [A] at time t=0. Solving for [A], we get:
\[\Rightarrow [A]={{[A]}_{0}}kt\]
\[\Rightarrow [A]=-kt+{{[A]}_{0}}\]
Which is the required integral form. On comparing this equation with the equation of a straight line \[(y=mx+b)\], an \[[A]\] against t graph can be plotted to get a straight line with slope equal to \[-k\] and intercept equal to \[{{[A]}_{0}}\] as shown below.

Here, we can see that the graph of a zero-order reaction is linear with -ve slope and non-zero intercept.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Other than zero-order reaction, there are first order reaction and second order reaction, whose graphs are different from zero-order reaction. The reaction of hydrogen with chlorine (Photochemical reaction) and decomposition of nitrous oxide over a hot platinum surface are examples of zero-order reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




