
For a satellite projected from the Earth’s surface with a velocity greater than orbital velocity, the nature of the path it takes when its energy is negative, zero and positive respectively is?
A) Elliptical, parabolic and hyperbolic
B) Hyperbolic, parabolic and elliptical
C) Elliptical, circular and parabolic
D) Parabolic, circular and elliptical
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The type of path and energy that will be taken up by a satellite projected from the Earth’s surface will depend upon its velocity. The relation between the satellite’s velocity and the escape velocity determines the path of the satellite.
Complete step by step solution:
By definition, Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for a free, non-propelled object to escape from the gravitation influence of a massive body, that is, to achieve an infinite distance from it. It’s mathematical formula is given as,
\[{{\text{v}}_{\text{e}}}{\text{ = }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2{\text{GM}}}}{{\text{R}}}} {\text{ = }}\sqrt {2{\text{gR}}} \]
where, G – universal gravitational constant($6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}$) ; M – mass of a planet; R – radius of a planet. For Earth the value of escape velocity is 11.2 km/s.
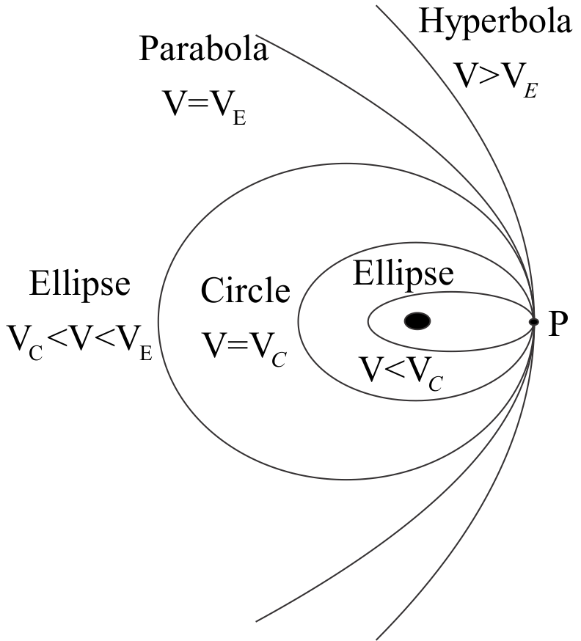
For a satellite projected from the Earth’s surface with a velocity greater than orbital velocity, the three general cases possible are,
1. When the velocity of a satellite is less than the escape velocity, the total energy of the satellite is negative and its path is elliptical. The centre of the Earth is one of its focus.
2. When the velocity of a satellite is equal to the escape velocity, the total energy of the satellite is zero and its path is parabolic.
3. When the velocity of a satellite is greater than the escape velocity, the total energy of the satellite is positive and the path followed is hyperbolic.
Hence, (A) option is correct.
Note: The basic types of paths in space are determined by the gravitational attraction properties of the concentrated masses of material and the laws of motion discovered by Newton. Though gravitational attraction properties are not the strongest but still we are manageable to get types of path in vacuum (space).
Complete step by step solution:
By definition, Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for a free, non-propelled object to escape from the gravitation influence of a massive body, that is, to achieve an infinite distance from it. It’s mathematical formula is given as,
\[{{\text{v}}_{\text{e}}}{\text{ = }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2{\text{GM}}}}{{\text{R}}}} {\text{ = }}\sqrt {2{\text{gR}}} \]
where, G – universal gravitational constant($6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}$) ; M – mass of a planet; R – radius of a planet. For Earth the value of escape velocity is 11.2 km/s.

For a satellite projected from the Earth’s surface with a velocity greater than orbital velocity, the three general cases possible are,
1. When the velocity of a satellite is less than the escape velocity, the total energy of the satellite is negative and its path is elliptical. The centre of the Earth is one of its focus.
2. When the velocity of a satellite is equal to the escape velocity, the total energy of the satellite is zero and its path is parabolic.
3. When the velocity of a satellite is greater than the escape velocity, the total energy of the satellite is positive and the path followed is hyperbolic.
Hence, (A) option is correct.
Note: The basic types of paths in space are determined by the gravitational attraction properties of the concentrated masses of material and the laws of motion discovered by Newton. Though gravitational attraction properties are not the strongest but still we are manageable to get types of path in vacuum (space).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




