
For a reaction $X\to ~Y$ , the graph of the product concentration (x) versus time (t) came out to be a straight line passing through the origin. Hence the graph of $-\dfrac{d\left[ X \right]}{dt}~$ and time would be:
(A) straight line with a negative slope and an intercept on y-axis
(B) straight line with positive slope and an intercept on y-axis
(C) a straight line parallel to x-axis
(D) a hyperbola
Answer
529.2k+ views
Hint: Try to attempt this question by using the graph condition in the reaction and with the help of it, find the order of the reaction. Then with respect to order of reaction we can draw the graph between $-\dfrac{d\left[ X \right]}{dt}~$(rate) and time. Rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place and order of reaction describes the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of the species taking part in it.
Complete answer:
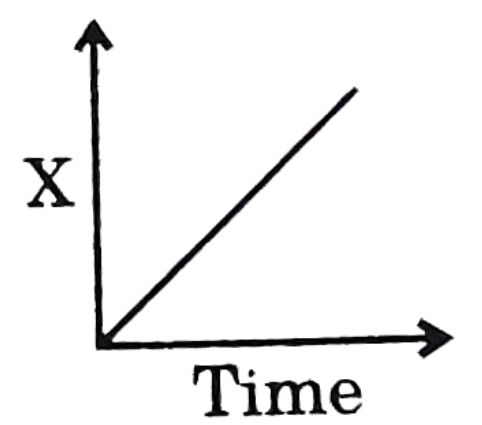
In the above graph, time is along the X-axis and concentration X is along the Y axis.
-Let us first understand the concept of rate of reaction and its order.
-The rate of reaction (or reaction rate) is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place and is defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time.
Rate of reaction = $\dfrac{[dX]}{[dt]}$
-The order of reaction can be referred to the power dependence of rate on the concentration of all reactants which means it tells us that, which species’ concentration affects the rate of the reaction.
-As it is given that the graph of the product concentration (x) versus time (t) came out to be a straight line passing through the origin which means there is no intercept and the equation formed is $x=Kt$ (where, K = rate constant). This is the equation of zero-order reaction, which means all the information provided in the question is about the zero order reaction.
-The graph between $-\dfrac{d\left[ X \right]}{dt}~$(rate) and time for zero order reaction is a straight parallel line to the x-axis because rate of reaction is constant for a zero order reaction which can also be proved by differentiating $x=Kt$ w.r.t to time (t)
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dt}(x=Kt) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{dKt}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=K \\
\end{align}$
(K is the constant)
Hence the correct answer is: (C) a straight line parallel to x-axis
Note:
- The misunderstandings we have while dealing with kinetics questions are as follows:
(A) The order of a reaction is equal to the molecularity of the reaction. This is true but only when it is an elementary reaction, not for complex reactions as molecularity is a positive integral value whereas order can be zero, negative, positive or fractional.
(B) Also we should not forget to consider stoichiometry while writing or using the rate expression or our obtained results will be wrong.
(C) We must know and learn the rate equations for zero, first and second order for faster calculations.
Complete answer:

In the above graph, time is along the X-axis and concentration X is along the Y axis.
-Let us first understand the concept of rate of reaction and its order.
-The rate of reaction (or reaction rate) is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place and is defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time.
Rate of reaction = $\dfrac{[dX]}{[dt]}$
-The order of reaction can be referred to the power dependence of rate on the concentration of all reactants which means it tells us that, which species’ concentration affects the rate of the reaction.
-As it is given that the graph of the product concentration (x) versus time (t) came out to be a straight line passing through the origin which means there is no intercept and the equation formed is $x=Kt$ (where, K = rate constant). This is the equation of zero-order reaction, which means all the information provided in the question is about the zero order reaction.
-The graph between $-\dfrac{d\left[ X \right]}{dt}~$(rate) and time for zero order reaction is a straight parallel line to the x-axis because rate of reaction is constant for a zero order reaction which can also be proved by differentiating $x=Kt$ w.r.t to time (t)
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dt}(x=Kt) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{dKt}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=K \\
\end{align}$
(K is the constant)
Hence the correct answer is: (C) a straight line parallel to x-axis
Note:
- The misunderstandings we have while dealing with kinetics questions are as follows:
(A) The order of a reaction is equal to the molecularity of the reaction. This is true but only when it is an elementary reaction, not for complex reactions as molecularity is a positive integral value whereas order can be zero, negative, positive or fractional.
(B) Also we should not forget to consider stoichiometry while writing or using the rate expression or our obtained results will be wrong.
(C) We must know and learn the rate equations for zero, first and second order for faster calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




