
for a reaction, \[A\rightleftharpoons P\], the plots of $\left[ A \right]$ and $\left[ P \right]$ with time at temperature ${{T}_{1}}$ and ${{T}_{2}}$ are given below.
If ${{T}_{2}}>{{T}_{1}}$ , the correct state is/are:
(Assume $\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}$ and $\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}$ are independent of temperature and ratio of $\ln K$ at ${{T}_{1}}$ to $\ln K$at ${{T}_{2}}$is greater than $\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}$ . Here $H,S,G$ and $K$ are enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs energy and equilibrium constant, respectively.)
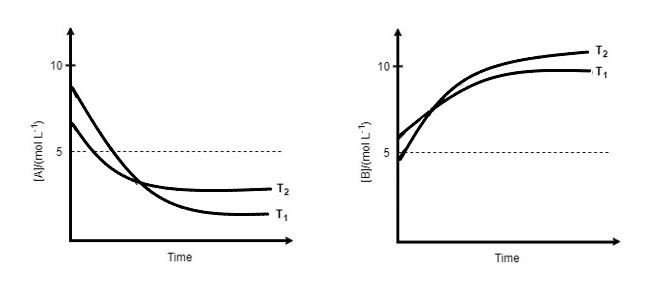
A. $\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}<0,\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
B. $\Delta {{G}^{{}^\circ }}<0,\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}>0$
C. $\Delta {{G}^{{}^\circ }}<0,\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
D. $\Delta {{G}^{{}^\circ }}<0,\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}>0$

Answer
542.7k+ views
Hint: equilibrium is defined as the state of a system where the concentration of the reactant and the concentration of the product do not change with time and there will be no change in the properties of the system. A chemical equilibrium is achieved when the rate of forward reaction is equal to rate of backward reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Enthalpy is defined as the sum of internal energy and the product of pressure and volume. The symbol of enthalpy is E. Enthalpy is the measurement of energy. When a process begins, the evolved heat becomes equal to the change in enthalpy at constant pressure. To calculate enthalpy change, we can write a mathematical expression as:
$\Delta H=\Delta U+P\Delta V$
Where $\Delta H$ is the change in enthalpy, $\Delta U$ is the change in internal energy, $P$ is the pressure and $\Delta V$ is the change in volume.
Entropy is defined as the measure of thermal energy per unit temperature. The symbol of entropy is S. The SI unit of entropy is joules per Kelvin.
We can calculate entropy by:
$\Delta S=\dfrac{{{q}_{rev}}}{T}$
Where, $\Delta S$ Is change in entropy, ${{q}_{rev}}$ is the reverse of heat, $T$ is the temperature.
According to the Arrhenius equation,
$\ln K=\dfrac{-{{E}_{a}}}{RT}+\ln A$
Where, $K$ is rate constants, ${{E}_{a}}$ is activation energy, $R$ is gas constant, $T$ is temperature, $A$ is pre exponential factor.
Here, as we can see that $K\alpha \dfrac{1}{T}$
Hence, $\dfrac{\ln {{K}_{1}}}{\ln {{K}_{2}}}>\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}$
As, ${{T}_{2}}>{{T}_{1}}$
On cross multiplying we get,
${{T}_{1}}\ln {{K}_{1}}>{{T}_{2}}\ln {{K}_{2}}$
$R{{T}_{1}}\ln {{K}_{1}}>RT\ln {{K}_{2}}$
As we know,
$\Delta {{G}^{{}^\circ }}=-RT\ln K$
Therefore, $\Delta {{G}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
Hence, we can write it as,
$\left( -\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}+{{T}_{1}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }} \right)>\left( -\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}+{{T}_{2}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }} \right)$
$\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
Therefore, ${{T}_{1}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}>{{T}_{2}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}$
${{T}_{2}}>{{T}_{1}}$
Hence,
$\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: Gibbs free energy is defined as the amount of work done when temperature and pressure remains constant in a thermodynamic system. The Arrhenius equation is used to tell the rate constant for an elementary step of reaction, it does not tell us about the rate of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Enthalpy is defined as the sum of internal energy and the product of pressure and volume. The symbol of enthalpy is E. Enthalpy is the measurement of energy. When a process begins, the evolved heat becomes equal to the change in enthalpy at constant pressure. To calculate enthalpy change, we can write a mathematical expression as:
$\Delta H=\Delta U+P\Delta V$
Where $\Delta H$ is the change in enthalpy, $\Delta U$ is the change in internal energy, $P$ is the pressure and $\Delta V$ is the change in volume.
Entropy is defined as the measure of thermal energy per unit temperature. The symbol of entropy is S. The SI unit of entropy is joules per Kelvin.
We can calculate entropy by:
$\Delta S=\dfrac{{{q}_{rev}}}{T}$
Where, $\Delta S$ Is change in entropy, ${{q}_{rev}}$ is the reverse of heat, $T$ is the temperature.
According to the Arrhenius equation,
$\ln K=\dfrac{-{{E}_{a}}}{RT}+\ln A$
Where, $K$ is rate constants, ${{E}_{a}}$ is activation energy, $R$ is gas constant, $T$ is temperature, $A$ is pre exponential factor.
Here, as we can see that $K\alpha \dfrac{1}{T}$
Hence, $\dfrac{\ln {{K}_{1}}}{\ln {{K}_{2}}}>\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}$
As, ${{T}_{2}}>{{T}_{1}}$
On cross multiplying we get,
${{T}_{1}}\ln {{K}_{1}}>{{T}_{2}}\ln {{K}_{2}}$
$R{{T}_{1}}\ln {{K}_{1}}>RT\ln {{K}_{2}}$
As we know,
$\Delta {{G}^{{}^\circ }}=-RT\ln K$
Therefore, $\Delta {{G}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
Hence, we can write it as,
$\left( -\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}+{{T}_{1}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }} \right)>\left( -\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}+{{T}_{2}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }} \right)$
$\Delta {{H}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
Therefore, ${{T}_{1}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}>{{T}_{2}}\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}$
${{T}_{2}}>{{T}_{1}}$
Hence,
$\Delta {{S}^{{}^\circ }}<0$
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: Gibbs free energy is defined as the amount of work done when temperature and pressure remains constant in a thermodynamic system. The Arrhenius equation is used to tell the rate constant for an elementary step of reaction, it does not tell us about the rate of the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




